May 7, 2019
Technology参考材料
https://www.golinuxhub.com/2017/05/how-to-create-customized-bootable-boot.html
目的
定制化rhel7.4安装ISO.
添加以下功能:
1.
准备
rhel7.4虚拟机一台,DVD安装光盘rhel-server-7.4-x86_64-dvd.iso已加载到/mnt目录:
root@server128:/media/sdd/raw/Rong_win/upgrade/Rong1905-redhat$ vagrant ssh
Last login: Tue May 7 09:23:02 2019 from 192.168.121.1
[vagrant@k8s2100upgrade-1 ~]$ cat /etc/redhat-release
Red Hat Enterprise Linux Server release 7.4 (Maipo)
[vagrant@k8s2100upgrade-1 ~]$ sudo mount /dev/sr0 /mnt
mount: /dev/sr0 is write-protected, mounting read-only
步骤
1. 准备编译服务器
准备工作目录,用于复制DVD中对应的目录结构以便于定制化:
# mkdir /root/geniso
# mount /dev/sr0 /mnt
# cp -rvf /mnt/* /root/geniso
2. 定制化kickstart文件
先用一个样例文件用于安装, 后面再根据需要修改:
# Kickstart configuration for RHEL7.4
#platform=x86, AMD64, or Intel EM64T
# System authorization information
auth --enableshadow --passalgo=sha512
# Clear the Master Boot Record
zerombr
# Partition clearing information
clearpart --drives=sda --all
# Use text mode install
#text
graphical
# Firewall configuration
firewall --disabled
# Run the Setup Agent on first boot
firstboot --reconfig --enable
# System keyboard
keyboard us
# System language
lang en_US.UTF-8
# Skipping input of key
#key --skip
# Installation logging level
logging --level=info
# Use NFS installation media
cdrom
# Network Information
network --bootproto=static --hostname=my-linux --device=eth0 --gateway=1.2.3.1 --ip=1.2.3.4 --netmask=255.255.255.0 --noipv6 --nodns --onboot=on --activate
# System bootloader configuration
bootloader --location=mbr --driveorder=sda
# The following is the partition information you requested
ignoredisk --only-use=sda
# Disk Partioning
clearpart --all --initlabel
autopart
#Root password
rootpw --iscrypted $6$KjCAXxUM2u5OcTtD$PcDbFkQCck97S6synqPIsxjHuOwQ1w5OENVE08l0gCG4fx3aW5DEl7Lw.1IjFflDT7iaESYUWKxO9877r7LAy0
# SELinux configuration
selinux --disabled
# Do not configure the X Window System
# Do not configure the X Window System
skipx
#Disabling kdump services, owing to few problems with current kexec package
services --disabled kdump
# System timezone
timezone --utc Asia/Shanghai
# Install OS instead of upgrade
install
# Reboot after installation
reboot
# list of packages to be installed
%packages
@ Core
@ Base --nodefaults
# packages deleted according to OS minimization
%end
其中密码可以通过以下命令来生成:
# python -c 'import crypt,getpass; print crypt.crypt(getpass.getpass())'
Password:
将上面的文件命名为ks.cfg并拷贝到/root/geniso目录。
3. 更改GRUB菜单
更换目录至isolinux目录并添加写权限给GRUB定义文件:
# pwd
/root/geniso/isolinux
# chmod a+w isolinux.cfg
在isolinux.cfg文件中查找到以下位置(约61行):
label linux
menu label ^Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4
kernel vmlinuz
append initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=RHEL-7.4\x20Server.x86_64 quiet
更改为:
label linux
menu label ^Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4
kernel vmlinuz
append initrd=initrd.img inst.stage2=hd:LABEL=RHEL-7.4\x20Server.x86_64 quiet
label autolinux
menu label ^Auto Install Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.4
kernel vmlinuz
append initrd=initrd.img inst.repo=cdrom ks=cdrom:/ks.cfg net.ifnames=0 biosdevname=0
4. 生成ISO
安装genisoimage包,用于编译ISO:
[root@k8s2100upgrade-1 geniso]# cd Packages/
[root@k8s2100upgrade-1 Packages]# rpm -Uvh libusal-1.1.11-23.el7.x86_64.rpm genisoimage-1.1.11-23.el7.x86_64.rpm
warning: libusal-1.1.11-23.el7.x86_64.rpm: Header V3 RSA/SHA256 Signature, key ID fd431d51: NOKEY
Preparing... ################################# [100%]
Updating / installing...
1:libusal-1.1.11-23.el7 ################################# [ 50%]
执行以下命令,将在/root下生成new.iso:
# cd /root/geniso
# mkisofs -o /root/new.iso -b isolinux/isolinux.bin -c isolinux/boot.cat --no-emul-boot --boot-load-size 4 --boot-info-table -J -R -V "RHEL-7.4\x20Server.x86_64" .
细调kickstart
1. 主机名
更改网络信息:
network --bootproto=static --hostname=node ...............
2. 添加用户/密码
在ks.cfg最后添加以下,以便创建test和vagrant用户, test使用sudo时将免密码登录:
%post
groupadd vagrant -g 1001
useradd test -g vagrant -G wheel -u 1001
useradd vagrant -g vagrant -G wheel -u 1001
echo "test" | passwd --stdin xxxxx
echo "vagrant" | passwd --stdin vagrant
echo "test ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers.d/test
echo "vagrant ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers.d/test
sed -i "s/^.*requiretty/#Defaults requiretty/" /etc/sudoers
mkdir /home/vagrant/.ssh
echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA6NF8iallvQVp22WDkTkyrtvp9eWW6A8YVr+kz4TjGYe7gHzIw+niNltGEFHzD8+v1I2YJ6oXevct1YeS0o9HZyN1Q9qgCgzUFtdOKLv6IedplqoPkcmF0aYet2PkEDo3MlTBckFXPITAMzF8dJSIFo9D8HfdOV0IAdx4O7PtixWKn5y2hMNG0zQPyUecp4pzC6kivAIhyfHilFR61RGL+GPXQ2MWZWFYbAGjyiYJnAmCP3NOTd0jMZEnDkbUvxhMmBYSdETk1rRgm+R4LOzFUGaHqHDLKLX+FIPKcF96hrucXzcWyLbIbEgE98OHlnVYCzRdK8jlqm8tehUc9c9WhQ== vagrant insecure public key" > /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys
%end
3. 预注入key
接着注入key:
# Add user
user --name=test --groups=wheel --plaintext --password=xxxxx
# ssh key
sshpw --username=root --sshkey 'ssh-rsa AAAAB3x......'
4. 自动侦探第一块磁盘
需要更改%pre中的选项
5. 添加test/vagrant用户等
%post中需要有对应的更改
ks.cfg完整版
最终版本的ks.cfg如下:
# Kickstart configuration for RHEL7.4
#platform=x86, AMD64, or Intel EM64T
# System authorization information
auth --enableshadow --passalgo=sha512
# Use text mode install
text
#graphical
# Firewall configuration
firewall --disabled
# Run the Setup Agent on first boot
#firstboot --reconfig --enable
firstboot --disable
# System keyboard
keyboard us
# System language
lang en_US.UTF-8
# Skipping input of key
#key --skip
# Installation logging level
logging --level=info
# Use NFS installation media
cdrom
# Network Information
network --bootproto=static --hostname=node --device=eth0 --gateway=1.2.3.1 --ip=1.2.3.4 --netmask=255.255.255.0 --noipv6 --nodns --onboot=on --activate
# Include generated partition layout
%include /tmp/part-include
#Root password
rootpw --iscrypted $6$KjCAXxUM2u5OcTtD$PcDbFkQCck97S6synqPIsxjHuOwQ1w5OENVE08l0gCG4fx3aW5DEl7Lw.1IjFflDT7iaESYUWKxO9877r7LAy0
# SELinux configuration
selinux --disabled
# Do not configure the X Window System
# Do not configure the X Window System
skipx
#Disabling kdump services, owing to few problems with current kexec package
services --disabled kdump
# System timezone
timezone --utc Asia/Shanghai
# Install OS instead of upgrade
install
# Reboot after installation
reboot
# list of packages to be installed
%packages
@ Core
@ Base --nodefaults
# packages deleted according to OS minimization
%end
################################################################################
# Pre section
################################################################################
%pre
#!/bin/bash
# Set networking defaults.
# Parse the Kernel boot options for overrides. (Key=Value)
cmdline=($(cat /proc/cmdline))
for cmd in ${cmdline[@]}; do
if [[ "$cmd" =~ '=' ]]; then
eval "$cmd"
fi
done
# Enumerate all disks.
disks=($(list-harddrives | awk '{ print $1 }'))
sizes=($(list-harddrives | awk '{ print $2 }'))
count=${#disks[@]}
if grep -q -w "noformat" /proc/cmdline; then
# TODO: Do not format any attached disks.
true
else
# Format all attached disks.
if grep -q -w "nolvm" /proc/cmdline; then
# TODO: Do not use LVM.
true
else
# Use LVM
i=0
pvs=
parts=
for disk in ${disks[@]}; do
# Only part the first disk
if (( $i == 1 )); then
break
fi
# End of Only part the first disk
parts="${parts}part pv.$i --grow --size=1 --ondisk=/dev/${disk}"
pvs="$pvs pv.$i"
let i=$i+1
done
pvs=(${pvs})
cat > /tmp/part-include << EOF
# password
bootloader --location=mbr --driveorder=${disks[0]}
zerombr
clearpart --all
part /boot --label=boot --fsoptions=nodev,nosuid,noexec --size=512 --asprimary --ondisk=/dev/${disks[0]}
part pv.3 --size=100 --grow --ondisk=/dev/${disks[0]}
volgroup vg0 pv.3
#$parts
#volgroup vg0 ${pvs[@]}
# See CIS Benchmark / NSA SNAC guides for partitioning and fsoption explanations;
# https://www.nsa.gov/ia/_files/os/redhat/rhel5-guide-i731.pdf
# https://benchmarks.cisecurity.org/downloads/form/index.cfm?download=centos6.100
# Requires ~16GB HDD
logvol / --name=root --vgname=vg0 --size=15000 --grow
EOF
fi
fi
%end
################################################################################
# Post section
################################################################################
%post
groupadd vagrant -g 1001
groupadd test -g 1002
useradd test -g test -G wheel -u 1002
useradd vagrant -g vagrant -G wheel -u 1001
echo "xxxxxxx" | passwd --stdin test
echo "vagrant" | passwd --stdin vagrant
echo "test ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers.d/test
echo "vagrant ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers.d/vagrant
sed -i "s/^.*requiretty/#Defaults requiretty/" /etc/sudoers
mkdir /home/vagrant/.ssh
echo "ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA6NF8iallvQVp22WDkTkyrtvp9eWW6A8YVr+kz4TjGYe7gHzIw+niNltGEFHzD8+v1I2YJ6oXevct1YeS0o9HZyN1Q9qgCgzUFtdOKLv6IedplqoPkcmF0aYet2PkEDo3MlTBckFXPITAMzF8dJSIFo9D8HfdOV0IAdx4O7PtixWKn5y2hMNG0zQPyUecp4pzC6kivAIhyfHilFR61RGL+GPXQ2MWZWFYbAGjyiYJnAmCP3NOTd0jMZEnDkbUvxhMmBYSdETk1rRgm+R4LOzFUGaHqHDLKLX+FIPKcF96hrucXzcWyLbIbEgE98OHlnVYCzRdK8jlqm8tehUc9c9WhQ== vagrant insecure public key" > /home/vagrant/.ssh/authorized_keys
mkdir /root/.ssh
echo "ssh-rsa xagwoguwogu gwewg">/root/.ssh/authorized_keys
chmod 700 /root/.ssh
chmod 400 /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
%end
测试安装
因为我们指定了sda,因而我们这里先用virt-manager中的SATA驱动:
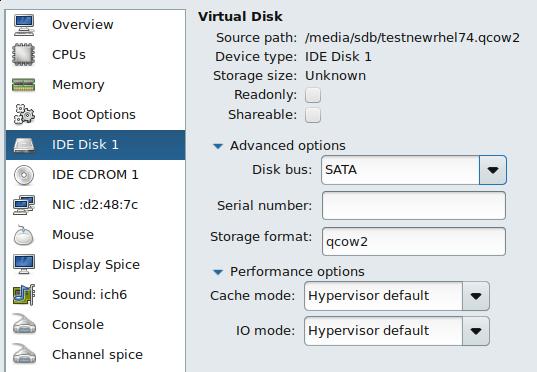
启动光盘,来到安装界面:
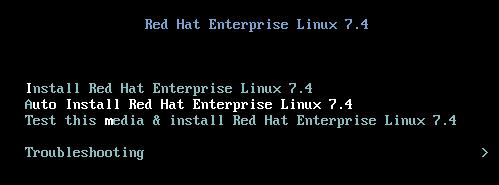
无需确认,一路安装直到安装完毕
May 5, 2019
TechnologyOS prepare
Download the tar.gz file from github, untar, then modify the Vagrantfile
with:
# vim cluster1.yml
---
- hosts: all
gather_facts: false
become: True
tasks:
- name: "Run shell"
shell: uptime
# vim Vagrantfile
SUPPORTED_OS = {
"wukong" => {box: "xxxx160406", user: "vagrant"},
}
$os = "wukong"
$playbook = "cluster1.yml"
# rm -rf .vagrant
# rm -f inventory/sample/vagrant_ansible_inventory
# vagrant up
Get Packages/Images
ssh into the deployed vagrant machine, set the networking with firewall-less
networking.
Configure the repository:
# vim /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-security main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-updates main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-proposed main restricted universe multiverse
deb http://mirrors.aliyun.com/ubuntu/ xenial-backports main restricted universe multiverse
Install ansible:
# apt-add-repository ppa:ansible/ansible
# apt-get update -y
# apt-get install -y ansible python-pip python ntp dbus python-apt bind9 bind9utils ntp nfs-common nfs-kernel-server python-netaddr nethogs iotop
Permit root nopasswrd login:
# vim /etc/ssh/sshd_config
PermitRootLogin yes
# systemctl restart sshd
# ssh-keygen
# ssh-copy-id root@172.17.48.101
Copy the Vagrant host’s kubespray folder into your vm folder, change the
inventory/sample/vagrant_ansible_inventory to :
k8s2110-1 ansible_host=172.17.48.101 ansible_port=22 ansible_user='root' ip=172.17.48.101 flannel_interface=eth1 kube_network_plugin=calico kube_network_plugin_multus=false ansible_ssh_user=root
[etcd]
k8s2110-[1:1]
[kube-master]
k8s2110-[1:1]
[kube-node]
k8s2110-[1:1]
[k8s-cluster:children]
kube-master
kube-node
Now deploy it via:
# ansible-playbook -i inventory/sample/vagrant_ansible_inventory cluster.yml
kubespray ansible will pull additional packages, also the docker images, for
setting up the kubernetes cluster.
Generate the packages:
# mkdir -p /root/debs
# cd /var/cache
# find . | grep deb$ | xargs -I % cp % /root/debs/
# cd /root/
# mv debs static
# cd static
# dpkg-scanpackages . /dev/null | gzip -9c > Packages.gz
# cd ..
# tar cJvf 1604debs.tar.xz static
Transfer the 1604debs.tar.xz for uploading.
Save images via:
# docker save -o 2110.tar nginx:1.15 gcr.io/google_containers/metrics-server-amd64:v0.3.2 gcr.io/google-containers/kube-proxy:v1.14.1 gcr.io/google-containers/kube-apiserver:v1.14.1 gcr.io/google-containers/kube-controller-manager:v1.14.1 gcr.io/google-containers/kube-scheduler:v1.14.1 coredns/coredns:1.5.0 lachlanevenson/k8s-helm:v2.13.1 gcr.io/kubernetes-helm/tiller:v2.13.1 k8s.gcr.io/cluster-proportional-autoscaler-amd64:1.4.0 k8s.gcr.io/k8s-dns-node-cache:1.15.1 gcr.io/google-containers/coredns:1.3.1 quay.io/coreos/etcd:v3.2.26 gcr.io/google_containers/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.10.1 calico/node:v3.4.0 calico/cni:v3.4.0 calico/kube-controllers:v3.4.0 rancher/local-path-provisioner:v0.0.2 nfvpe/multus:v3.1.autoconf k8s.gcr.io/addon-resizer:1.8.3 quay.io/external_storage/local-volume-provisioner:v2.1.0 gcr.io/google-containers/pause:3.1 gcr.io/google_containers/pause-amd64:3.1
Use 2110.tar for replacing the secureregistryserver’s content.
Upload some files to the kube-deploy/files:
hyperkube
kubeadm
calicoctl
cni-plugins-amd64-v0.6.0.tgz
18.04.02
Use another 18.04.02 vagrant box for deploying, after installation, just zip
to another tar.xz file:
# tar cJvf 1804debs.tar.xz static/
kubadm ssl issue
Change the ssl issue needs do modification to source code and re-generate
kubeadm. Use the new-generated kubeadm for replacing the origin ones, and
replaces its sha256sum.
Apr 19, 2019
LinuxTips1. samba mount
mount samba via:
# mount -t cifs //192.168.0.219/samba /mnt -o username=uuuu,password=ffff
2. CentOS ansible
On vps we start a docker instance via:
# docker run -it centos:7 /bin/bash
# yum update -y
# yum install -y epel-release
# yum update -y
# yum install -y python-pip
# mkdir ~/ansible && cd ~/ansible
# pip download ansible
# tar czvf ansible.tar.gz ansible
Download the ansible.tar.gz to local, and transfer them into the centos
offline machines, install ansible via:
# tar xzvf ansible.tar.gz
# cd ansible
# pip install --no-index --find-links . ansible
# which ansible
/usr/bin/ansible
# ansible --version
ansible 2.7.10
Also you have to download the jinja2, upgrade to 2.10.1 version:
# pip download jinja2
...
# pip install --no-index --find-links . jinja2 --upgrade
3. Fast Kubespray
Download the tar.gz, untar it, then modify the Vagrantfile, then rm -f inventory/sample/hosts.ini, then vagrant up you could get all of the packages
and images downloaded to your vm.
Be sure to use firewall-less networking, and set the vm’s resolv.conf to your
firewall-less dns server.
# rm -f /etc/resolv.conf
# echo "nameserver 10.0.70.1">/etc/resolv.conf
4. kubeadm git tree state
Modify the file hack/lib/version.sh:
if [[ -n ${KUBE_GIT_COMMIT-} ]] || KUBE_GIT_COMMIT=$("${git[@]}" rev-parse "HEAD^{commit}" 2>/dev/null); then
if [[ -z ${KUBE_GIT_TREE_STATE-} ]]; then
# Check if the tree is dirty. default to dirty
if git_status=$("${git[@]}" status --porcelain 2>/dev/null) && [[ -z ${git_status} ]]; then
KUBE_GIT_TREE_STATE="clean"
else
KUBE_GIT_TREE_STATE="clean"
fi
fi
5. pandoc template
For generating pdf:
# wget https://github.com/Wandmalfarbe/pandoc-latex-template/releases/download/v1.2.2/Eisvogel-1.2.2.tar.gz
# mkdir -p ~/.pandoc/templates
# tar xzvf Eisvogel-1.2.2.tar.gz
# cp eisvogenl.tex ~/.pandoc/templates/eisvogel.latex
# cd ~/.pandoc/templates
# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/tzengyuxio/pages/gh-pages/pandoc/pm-template.latex
But this doesn’t work at all.
6. kubernetes leader election
Refers to:
https://tunein.engineering/implementing-leader-election-for-kubernetes-pods-2477deef8f13
https://github.com/kubernetes-retired/contrib/tree/master/election
7. reinstall rpm with dependencies
via following command:
# yum reinstall $(repoquery --requires --recursive --resolve packagename)
8. dmesg warning
After upgrading to newest kernel, I got some error message during dmesg:
[118383.485389] e1000e 0000:00:19.0 enp0s25: Detected Hardware Unit Hang:
TDH <0>
TDT <5>
next_to_use <5>
next_to_clean <0>
buffer_info[next_to_clean]:
time_stamp <102176c2b>
next_to_watch <0>
jiffies <1021c8e80>
next_to_watch.status <0>
MAC Status <80000>
PHY Status <7949>
PHY 1000BASE-T Status <0>
PHY Extended Status <3000>
PCI Status <10>
Solution is disable the TCP checksome offloading:
$ sudo ethtool -K enp0s25 tx off rx off
9. Proxmox iotop
For installing iotop on Proxmox, do following:
root@ks:~# cat /etc/issue
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Welcome to the Proxmox Virtual Environment. Please use your web browser to
configure this server - connect to:
https://
------------------------------------------------------------------------------
root@ks:~# cat /etc/debian_version
9.4
Find the debian version 9.4 is stretch, then we could find the package using
google, and download iotop package then uploading to server and install it.
10. bash debugging
Enable debugging for:
# bash -x ./bash_shell.sh
10. vncviewer disable send key
Via following commands:
$ vncviewer 192.168.0.101:5900 -FullscreenSystemKeys=0
11. kubectl run
Avoid pulling images always, specify following parameter:
--image-pull-policy
12. ssh tunnel
Using a tunnel for forwarding remote ssh port to local via:
alias sshtunnel='ssh -L 0.0.0.0:10022:192.xxx.xxx.xxx:10022 dash@192.168.0.33'
After you activated ssh tunnel, use ssh -p 10022 root@localhost for
accessing.
13. ifupdown
When encounting following error in vagrant:
/sbin/ifup 'eth1'
Stdout from the command:
Stderr from the command:
bash: line 4: /sbin/ifdown: No such file or directory
bash: line 20: /sbin/ifup: No such file or directory
Install apt-get install -y ifupdown, you could fix your problem.
14. usb networking issue
After upgrading to 5.1.6 kernel, my asix ethernet card won’t working, install
following packages for making it worked.
$ yaourt asix-dkms
15. delegate to issue
When using kubespray you got delegate to issue, do following:
# export ANSIBLE_INVALID_TASK_ATTRIBUTE_FAILED=False
# vagrant up --provider=libvirt
16. usb ethernet issue
via lsusb -t you could view the usb device tree and its speed.
17. view nvidia gpu temperature
via :
nvidia-smi -q -d temperature
18. pip network error
Install pip again via:
# curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py | python
19. consola issues
If you use gnome-terminal, then it’s hard to choose yahei consola, so we have to use xfce4-terminal.
20. Use cdrom as repository
Following steps will use ubuntu iso for installation:
sudo mkdir /aptoncd-mountpoint
sudo mount /media/USB/aptoncd.iso ~/aptoncd-mountpoint -oloop
sudo apt-cdrom -d=/aptoncd-mountpoint add
21. apt-get down
download the packages into /var/cache via:
# apt-get -d install xxxxxxxYourPackageName
22. ansible warning
How to resolve this warning.
[WARNING]: flush_handlers task does not support when conditional
23. build goharbor
with chartmuseum support, do following:
# make package_offline GOBUILDIMAGE=golang:1.9.2 COMPILETAG=compile_golangimage NOTARYFLAG=true
Make on arm64 architecture:
/media/sda/harbor/harbor-arm64-develop# make package_offline GOBUILDIMAGE=golang:1.9.2 COMPILETAG=compile_golangimage VERSIONTAG=1.7.0-arm64 PKGVERSIONTAG=1.7.0-arm64 CLAIRFLAG=true NOTARYFLAG=true CHARTFLAG=true
24. Get rpi temperature
via following command:
cpu=$(</sys/class/thermal/thermal_zone0/temp);echo "$((cpu/1000)) c"
25. Force dns query using tcp
Add following options into the /etc/resolv.conf:
options use-vc
nameserver 1.2.3.4
26. tips on Friday
working progress:
1. python-pip should be installed and docker-compose needed to be compile.
2. some packages are located in 128, also libssl/libssl-dev have to be added into the repository
3. secure registry server not stable, why?
4. package dependency problem should be solved.
5. docker push is ok, now we could push to the registry.
6. harbor need to be verified.
27. VncServer
not only listening on localhost, try following:
# vncserver -localhost no
28. delegate_to
Newest ansible version(v2.8.1) has changed the feature, so we have to use following commands:
# ANSIBLE_INVALID_TASK_ATTRIBUTE_FAILED=False
# ansible-playbook -i xxxx xxxx.cluster.yml
29. aarch64 vagrant issue
Encounter following:
Error while creating domain: Error saving the server: Call to virDomainDefineXML failed: unsupported configuration: ACPI requires UEFI on this architecture
pflash vs rom.
30. Copy only Packages.gz included
via following commands:
for i in `cat /root/Packages | grep '^Package:' | awk {'print $2'}`
do
echo cp $i"_*.deb" /root/pure/ | bash -
#cp $i_* /root/pure
done
31. kubespray openssl issue
Change the openssl signature for v3_ext definition.
[ v3_ext ]
authorityKeyIdentifier=keyid,issuer:always
basicConstraints=CA:FALSE
keyUsage=keyEncipherment,dataEncipherment
extendedKeyUsage=serverAuth,clientAuth
subjectAltName=@alt_names
root@arm02:/media/md0/Rong1907/roles/etcd# grep -i "v3_ext" ./ -r
./templates/openssl.conf.j2:[ v3_ext ]
./templates/make-ssl-etcd.sh.j2: openssl x509 -req -in member-${host}.csr -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -out member-${host}.pem -days {{certificates_duration}} -extensions v3_ext -extfile ${CONFIG} > /dev/null 2>&1
./templates/make-ssl-etcd.sh.j2: openssl x509 -req -in admin-${host}.csr -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -out admin-${host}.pem -days {{certificates_duration}} -extensions v3_ext -extfile ${CONFIG} > /dev/null 2>&1
./templates/make-ssl-etcd.sh.j2: openssl x509 -req -in node-${host}.csr -CA ca.pem -CAkey ca-key.pem -CAcreateserial -out node-${host}.pem -days {{certificates_duration}} -extensions v3_ext -extfile ${CONFIG} > /dev/null 2>&1
32. run commands in term
In linux via:
# xterm -hold -e 'apropos editor' &
33. netdata for ubuntu xenial
Using ppa version:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:sdeziel/ppa
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y netdata
34. minikube ssh/password
Default ssh username and password are docker and tcuser.
35. disable ipv6 on ubuntu
Edit the /etc/default/grub, add following definition:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX="ipv6.disable=1"
disable ipv6 will cause vagrant working, so I remove this line again, and fall back to ipv4/ipv6 co-exists.
36. rsync specify ssh ports
sync the remote with local directory:
rsync -a -e 'ssh -p 1xxxx' --progress kubespray-2.11.0 root@192.xxx.xxx.xxx:/media/sdd/kubespray-2.11.0
37. ansible docker for kubespray
For lacking the netaddr in ansible docker(lexauw/ansible-alpine:v2.7.9), do following steps:
$ sudo docker run -it lexauw/ansible-alpine:v2.7.9 /bin/sh
/ # pip3 install netaddr
.....
$ sudo docker commit d15d9a5910b4 core/ansible:v2.7.9
Now using the core/ansible:v2.7.9 for deployment, you will get through all of the playbooks.
38. videocutter
Install on ubuntu:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:ozmartian/apps
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install vidcutter
39. Making video
vidcutter+gnome-subtitles+ffmpeg:
$ ffmpeg -y -i gongjian.mp4 -vf subtitles=gongjiank8s.srt myoutput.mp4
40. wget quite and overwrite
via following parameters:
# wget -q http://xxxxxx -O /opt/bin/xxxxx
41. Enable bbr on Ubuntu18.04
Via following commands:
# echo "net.core.default_qdisc=fq" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
# echo "net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control=bbr" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
# sysctl -p
net.core.default_qdisc = fq
net.ipv4.tcp_congestion_control = bbr
# sysctl net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control
net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control = reno cubic bbr
# lsmod | grep bbr
tcp_bbr 20480 4
# sudo sysctl net.core.default_qdisc
fq
当输出中 net.core.default_qdisc 为 fq 且 net.ipv4.tcp_available_congestion_control 包含 bbr 即表示内核已启用 BBR 算法。
42. arm64 Installation
Desktop:
# apt-get install -y virt-manager xubuntu-desktop qemu-efi-aarch64 vnc4server chromium-browser
# systemctl start libvirtd
# systemctl enable libvirtd
# vim ~/.vnc/xstartup
xrdb $HOME/.Xresources
startxfce4 &
# vncserver
Thus you could get a vnc based virt-manager runnable environment.
43. pip install via requirements
Download via:
apt-get update -y
apt-get install -y python-pip python3-pip
mkdir pip
cd pip/
vi requirements.txt
pip install --download=`pwd` -r requirements.txt
pip3 install --download=`pwd` ruamel.yaml
tar czvf pip.tar.gz pip
Install offlinely via:
pip install --no-index --find-links=`pwd` -r requirements.txt
pip3 install --no-index --find-links=`pwd` ruamel.yaml
Examine via:
ansible --version
44. download 163 music
via a pip3 installed packages:
pip3 install pymusic-dl
music-dl -u https://music.163.com/#/song?id=502043537
via:
ffmpeg -i IMG_3125.MOV -vcodec h264 -acodec mp2 video1.mp4
46. Get repository of ubuntu
switch back to official repository mode:
$ cd /etc/apt/
$ sudo wget https://gist.githubusercontent.com/h0bbel/4b28ede18d65c3527b11b12fa36aa8d1/raw/a4ab1c13a92171822215143b1e3b3eb6add7a78d/sources.list
47. rdesktop to different port
via:
$ rdesktop xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:Port
48. promtail debug
Testing:
# curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPOST -s "http://localhost:3100/api/prom/push" --data-raw '{"streams": [{ "labels": "{foo=\"bar\"}", "entries": [{ "ts": "2019-10-21T08:28:06.801064-04:00", "line": "fizzbuzz" }] }]}'
# curl "http://localhost:3100/ready"
49. run es in docker
Run following command:
sudo docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -v `pwd`:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data elasticsearch:6.8.4
50. alerta quickstart
Via docker-compose:
version: '2.1'
services:
web:
image: alerta/alerta-web
ports:
- "8080:8080"
depends_on:
- db
environment:
- DEBUG=1 # remove this line to turn DEBUG off
- DATABASE_URL=postgres://postgres:postgres@db:5432/monitoring
- AUTH_REQUIRED=True
- ADMIN_USERS=admin,admin@alerta.io,devops@alerta.io #default password: alerta
- PLUGINS=reject,blackout,normalise,enhance
restart: always
db:
image: postgres
volumes:
- ./pg-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
environment:
POSTGRES_DB: monitoring
POSTGRES_USER: postgres
POSTGRES_PASSWORD: postgres
restart: always
Then visiti localhost:8080, to get the api key, write the configuration file:
# vim ~/.alerta.conf
[DEFAULT]
endpoint = http://localhost:8080/api
key = gaoweugowuegouVkJjzSbNwnod3wiRuywdrYfmoyB40GyJmk
[profile production]
endpoint = http://localhost:8080/api
key = gaoweugowuegouVkJjzSbNwnod3wiRuywdrYfmoyB40GyJmk
Then pip install the cli tools:
# sudo pip3 install alerta
# alerta send -r web01 -e HttpError -g Web -s major --attributes region="EU" --environment Production -S fuck
Now in the website you will see following alert available:
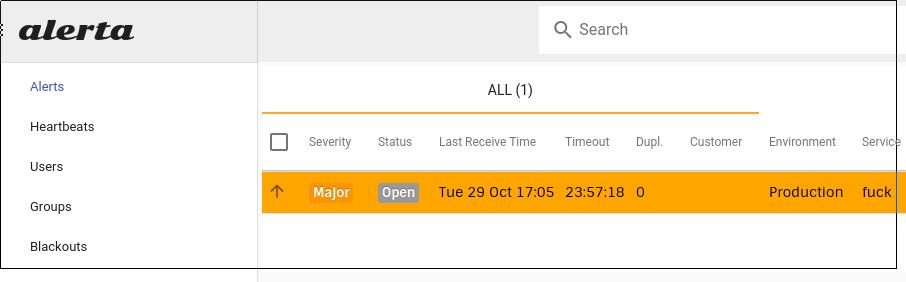
Next step I will setup the alerta together with netdata and prometheus.
51. setuid issue
Someone changed the priviledge of /usr/bin/sudo on server, thus every user in sudo group could not
switch to root user via sudo bash, the solution is via:
# su root
# chmod u+s /usr/bin/sudo
Or:
# chmod 4755 /usr/bin/sudo
52. awesome focus highlight
Via changing the awesome theme color:
# sudo vim /usr/share/awesome/themes/default/theme.lua
--theme.bg_focus = "#535d6c"
theme.bg_focus = "#14EEEE"
# echo 'awesome.restart()' | awesome-client
53. minikube items
Notice the metrics-scraper:
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system coredns-5644d7b6d9-lqpv2 1/1 Running 0 3m
kube-system coredns-5644d7b6d9-nrbcp 1/1 Running 0 3m
kube-system etcd-minikube 1/1 Running 0 2m
kube-system kube-addon-manager-minikube 1/1 Running 0 2m
kube-system kube-apiserver-minikube 1/1 Running 0 2m
kube-system kube-controller-manager-minikube 1/1 Running 0 2m
kube-system kube-proxy-2fx6d 1/1 Running 0 3m
kube-system kube-scheduler-minikube 1/1 Running 0 2m
kube-system nginx-ingress-controller-57bf9855c8-b5w68 1/1 Running 0 3m
kube-system storage-provisioner 1/1 Running 0 3m
kubernetes-dashboard dashboard-metrics-scraper-76585494d8-bn2cb 1/1 Running 0 3m
kubernetes-dashboard kubernetes-dashboard-57f4cb4545-jgpqz 1/1 Running 0 3m
54. boomaga
Boomaga could combine several print jobs into one pdf file.
55. xz with multiple context
Via xz -T4 big.tar, then you will get 400% speed of the single xz file.
56. react.js quickstart
With the npm version 6 we could start using react.js:
$ curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_10.x -o nodesource_setup.sh
$ npm -v
6.11.3
$ npm init react-app my-app
57. Quickly redsock libvirt
Via following command:
$ sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.conf.all.route_localnet=1
$ sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp -s 10.133.108.191/24 -j DNAT --to-destination 127.0.0.1:12345
Then the subnet of your libvirtd will get to internet via redsocks.
58. etchosts issue
kubespray when encountering etchosts issue, by setting from dhcp to static ip and setup the route could solve the issue.
59. 1604 to 1804 kubespray items
Manually resolve the package dependencies:
# apt-get install -y openssh-server update-motd parted build-essential telnet tcpdump python ebtables libgeoip1
60. destroy all running libvirt items
via :
virsh list | sed -n '1,2!p' | head -n -1 | awk {'print $1'}
61. find the modified timestamp
via find options:
find . -printf "%T@ %Tc %p\n" | sort -n
62. CentOS vagrant
vagrant for centos7 added following items:
# visudo
vagrant ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:ALL
Defaults:vagrant !requiretty
63. helm/chart nfs-client
via following command:
$ helm install nfs-client-provisioner-1.2.8.tgz --set nfs.server=10.147.191.1 --set nfs.path=/media/sdb/k8snfs --set storageClass.defaultClass=true
64. nfsd issue
When using nfsd, it defaultly reject the connections from NATed vm’s request, cause the port is over 1024, so you have to add following parameters into the nfsd configuration:
# vim /etc/exports
/var/nfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check,insecure)
/media/md0/nfs *(rw,sync,no_root_squash,no_subtree_check,insecure)
insecure let you accept connections >1024, thus your nfs client could connect to nfsd server.
65. git ignore big files
Get the whole size:
$ find . -size +2M | tr '\n' ' '
xxxx
$ du -ch xxxx
Add the file list into gitignore file:
$ find . -size +2M | cat >> .gitignore
66. trouble shooting on metrics-server
With k8s 1.13.5, metrics-server could not startup with tls error,
....
1 customresource_discovery_controller.go:203] Starting DiscoveryController
I0920 16:35:36.878076 1 log.go:172] http: TLS handshake error from 192.192.185.98:47446: EOF
I0920 16:35:36.878360 1 log.go:172] http: TLS handshake error from 192.192.185.98:47460: EOF
....
Copy the right one from kubespray 2.11.0, the newer configuration for metrics-server work properly.
Examine:
# kubectl get apiservice | grep metrics
v1beta1.metrics.k8s.io kube-system/metrics-server True 29m
67. Reinstall netdata
When reinstalling, encounter dpkg-statoverride issue. solved via following:
# bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh)
# dpkg-statoverride --remove /var/lib/netdata/registry
# bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh)
Now re-install and we could got the netdata installed again.
68. display ps’s hirieachy
via ps auxf you could see a process’s father/son, etc.
69. git ignore last commit
via following command:
$ git reset --soft HEAD~1
70. forward to vm
via following command:
$ iptables -I FORWARD -o virbr1 -d 192.168.111.36 -j ACCEPT
$ iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 9867 -j DNAT --to 192.168.111.36:22
71. coredns issue
issue:
[root@k8s-node-1 ~]# kubectl logs -f -n kube-system coredns-9d85fb698-tnrgn
.:53
2019-04-29T12:26:42.180Z [INFO] plugin/reload: Running configuration MD5 =
1335ba7188be742fe37cd05805faa0fa
2019-04-29T12:26:42.180Z [INFO] CoreDNS-1.5.0
2019-04-29T12:26:42.180Z [INFO] linux/amd64, go1.12.2, e3f9a80
CoreDNS-1.5.0
linux/amd64, go1.12.2, e3f9a80
2019-04-29T12:26:48.181Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:51809->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:26:51.181Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:52463->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:26:52.181Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:44654->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:26:53.181Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:35028->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:26:56.181Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:44331->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:26:59.182Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:38640->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:27:02.182Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:57424->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:27:05.182Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:56166->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:27:08.182Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:59509->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
2019-04-29T12:27:11.183Z [ERROR] plugin/errors: 2
8373768935828175380.8715076686105595443. HINFO: read udp
10.233.113.56:56157->10.233.0.3:53: i/o timeout
Solved via:
WARNING: IPtables FORWARD policy is DROP. Consider enabling traffic forwarding
with: sudo iptables -P FORWARD ACCEPT
fixing it worked for me
72. virt-manager issue
After upgrading to newest virt-manager(archlinux), vm could not boot for
no bootable devices, solved via:
# virsh edit xxxxx
Added:
<source file='/media/sda/ovirt/node1.qcow2' index='2'/>
+ <backingStore type='file' index='3'>
+ <format type='qcow2'/>
+ <source file='/media/sda/ovirt/Base/ovirtBase.qcow2'/>
+ <backingStore/>
+ </backingStore>
Then normally bootup the vm, the vm works properly.
73. vagrant plugin install speedup
via following command:
# vagrant plugin install vagrant-scp --plugin-clean-sources --plugin-source https://gems.ruby-china.com/
74. vagrant with debug
via following command:
VAGRANT_LOG=debug VAGRANT_DEFAULT_PROVIDER=libvirt vagrant up
75. Tips for building wopi
Bypass skip tests:
mvn clean package -DskipTests
76. pip mirror in china
edit:
mkdir ~/.pip
cat <<EOF > ~/.pip/pip.conf
[global]
trusted-host = mirrors.aliyun.com
index-url = http://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
EOF
77. using bridge in libvirtd
Create br and set br’s parameter:
$ sudo brctl addbr libvirt0
$ sudo brctl setfd libvirt0 0
Then specify the shared device to libvirt0.
78. xrandr for rotating screen
rotate left and reback to normal:
# xrandr --output HDMI-0 --rotate left --mode 2560x1440 --right-of eDP-1-1
# xrandr --output HDMI-0 --rotate normal --mode 2560x1440 --right-of eDP-1-1



