WorkingTipsOnGravitee
Nov 13, 2019Technology
AIM
Deploy gravitee on Kubernetes cluster, and use it as cluster’s API gateway.
Ingress-Controller
Deploy nginx-ingress-controller in kubespray’s configuration is listed as following:
ingress_nginx_enabled: true
ingress_nginx_host_network: true
ingress_nginx_nodeselector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: "tsts-2"
Specify the ingress’s entry machine is tsts-2, cause in some node we have the 80 and 443 port occupied.
Run the task:
# ansible-playbook -i inventory/kkkk/hosts.ini cluster.yml --extra-vars @kkkk-vars.yml --tags ingress-controller
Verify the ingress deployed:
# kubectl get pods -n ingress-nginx
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ingress-nginx-controller-b959g 1/1 Running 0 4d16h
Helm/Charts installation
Use helm/charts for deploying the gravitee apim.
# git clone https://github.com/gravitee-io/helm-charts.git
# cd apim
# helm repo update .
# helm dependency update .
After dependency updated we will see the folder structure is listed as:
➜ apim tree
.
├── charts
│ ├── elasticsearch-1.32.0.tgz
│ └── mongodb-replicaset-3.10.1.tgz
├── Chart.yaml
├── NOTES.txt
├── README.md
├── requirements.lock
├── requirements.yaml
├── templates
│ ├── api-autoscaler.yaml
│ ├── api-configmap.yaml
│ ├── api-deployment.yaml
│ ├── api-ingress.yaml
│ ├── api-service.yaml
│ ├── gateway-autoscaler.yaml
│ ├── gateway-configmap.yaml
│ ├── gateway-deployment.yaml
│ ├── gateway-ingress.yaml
│ ├── gateway-service.yaml
│ ├── _helpers.tpl
│ ├── ui-autoscaler.yaml
│ ├── ui-configmap.yaml
│ ├── ui-deployment.yaml
│ ├── ui-ingress.yaml
│ └── ui-service.yaml
└── values.yaml
Configure the helm/charts values:
# vim values.yml
//.................
mongo:
rs: rs0
rsEnabled: true
dbhost: gravitee45-mongodb-replicaset
//.................
mongodb-replicaset:
enabled: true
replicas: 1
//.................
persistentVolume:
enabled: false
//.................
es:
//.................
endpoints:
- http://gravitee45-elasticsearch-client.default.svc.cluster.local:9200
//.................
elasticsearch:
enabled: true
cluster:
name: "elasticsearch"
//.................
master:
//.................
persistence:
enabled: false
//.................
data:
//.................
persistence:
enabled: false
//.................
api:
enabled: true
name: api
logging:
debug: false
restartPolicy: OnFailure
updateStrategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxUnavailable: 1
type: RollingUpdate
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: graviteeio/management-api
tag: 1.29.5
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
service:
type: ClusterIP
externalPort: 83
internalPort: 8083
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 1
//.....................
gateway:
enabled: true
type: Deployment
name: gateway
logging:
debug: false
replicaCount: 2
# sharding_tags:
# tenant:
websocket: false
image:
repository: graviteeio/gateway
tag: 1.29.5
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
service:
type: ClusterIP
externalPort: 82
internalPort: 8082
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 1
//.......................
ui:
enabled: true
name: ui
title: API Portal
managementTitle: API Management
documentationLink: http://docs.gravitee.io/
scheduler:
tasks: 10
theme:
name: "default"
logo: "themes/assets/GRAVITEE_LOGO1-01.png"
loader: "assets/gravitee_logo_anim.gif"
portal:
apikeyHeader: "X-Gravitee-Api-Key"
devMode:
enabled: false
userCreation:
enabled: false
support:
enabled: true
rating:
enabled: false
analytics:
enabled: false
trackingId: ""
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: graviteeio/management-ui
tag: 1.29.5
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
autoscaling:
enabled: true
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 1
//............
Also replace all of the apim.example.com into apim.company.com.
Then install the charts via:
# helm install --name gravitee45 .
Examine the ingress via:
# root@tsts-1:~/apim# kubectl get ingress
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
gravitee45-apim-api apim.company.com 10.147.191.192 80, 443 19h
gravitee45-apim-firstapi apim.company.com 10.147.191.192 80, 443 17h
gravitee45-apim-gateway apim.company.com 10.147.191.192 80, 443 19h
gravitee45-apim-ui apim.company.com 10.147.191.192 80, 443 19h
Check the pods via:
root@tsts-1:~/apim# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
gravitee45-apim-api-7bfd555fbb-95cqz 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-apim-gateway-5757b5d6bf-gzstz 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-apim-ui-66ddddfd7f-ssl9z 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-elasticsearch-client-77cb95bc9f-8bdt8 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-elasticsearch-client-77cb95bc9f-xjxvs 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-elasticsearch-data-0 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-elasticsearch-data-1 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-elasticsearch-master-0 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-elasticsearch-master-1 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-elasticsearch-master-2 1/1 Running 0 19h
gravitee45-mongodb-replicaset-0 1/1 Running 0 19h
Test api
Run a local test api like echo api in gravitee website:
# docker run -d --name echo -p 18080:8080 graviteeio/gravitee-echo-api:latest
Test via:
# curl http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:18080/
{
"headers" : {
"Host" : "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:18080",
"User-Agent" : "curl/7.52.1",
"Accept" : "*/*"
}
API management
Open your browser and visit https://apim.company.com:

Click login and login with admin/admin:
Click Administration:
Click +:
Click ‘->` and create a new API:
Name is firstapi, version is 1.0, write some description, context-path is /firstapi, then click NEXT:
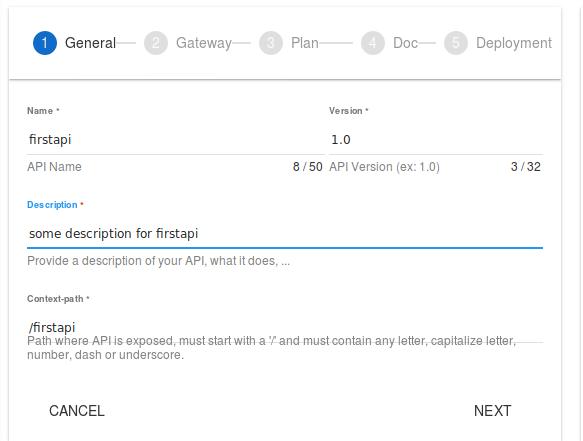
Specify the gateway to our test api, then click NEXT:
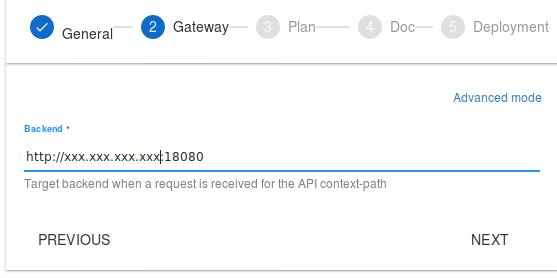
Write some description for plan, notice the security type should be API Key, you could also specify the Rate limit and Quota here, after configuration click NEXT for next step:
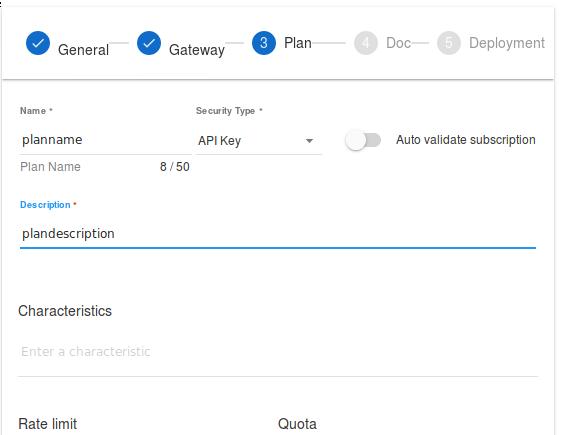
You could add the API documentation here, here we skip the documentation for next step, click SKIP:
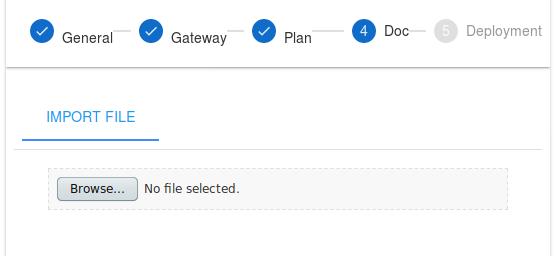
Here you could adjust the parameters, if everything is ok, we could click CREATE AND START THE API:
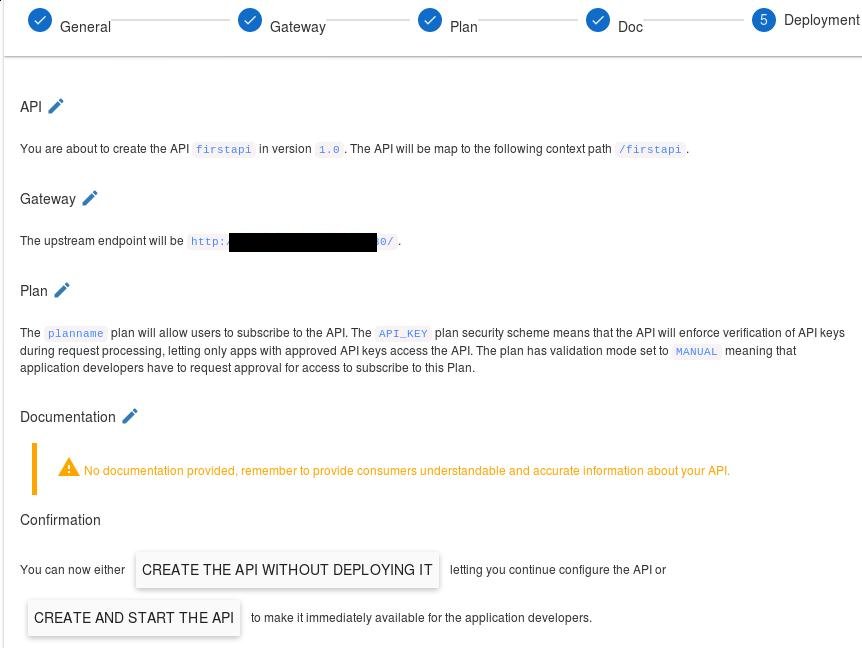
Confirm for CREATE:
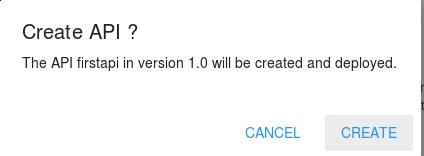
The api will be created and show like:
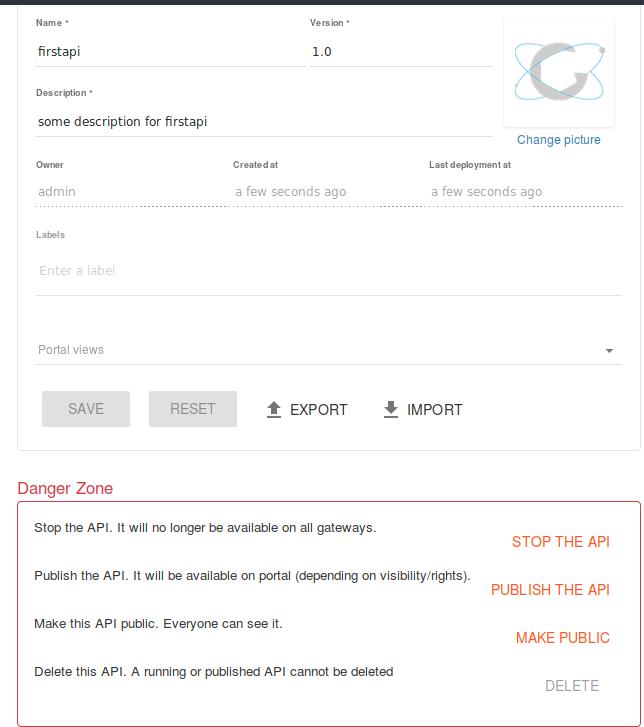
Click PUBLISH THE API and MAKE PUBLIC for plublishing this API:
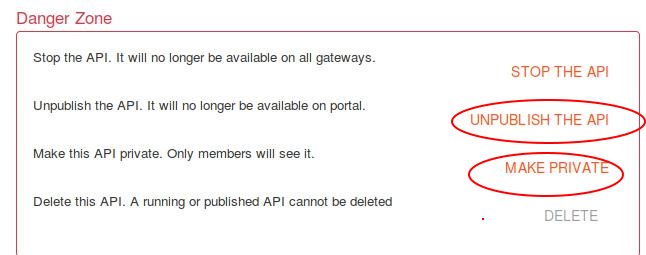
Next step we will create an API for using this API, click Applications:
Click + for adding a new application:
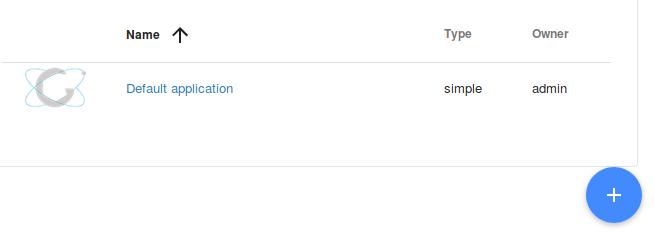
Write some description for this new app, and click NEXT for next step:
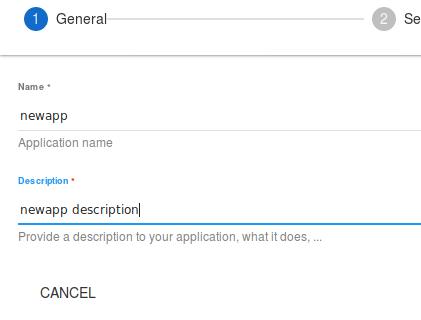
Specify webfor api type, then click NEXT:
Now we subscribe to our created API in this screen:
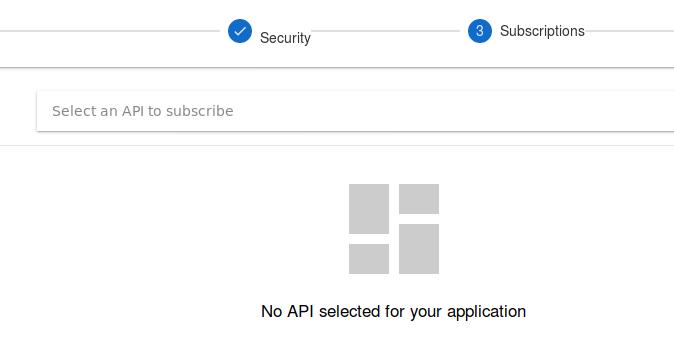
Click first api 1.0:
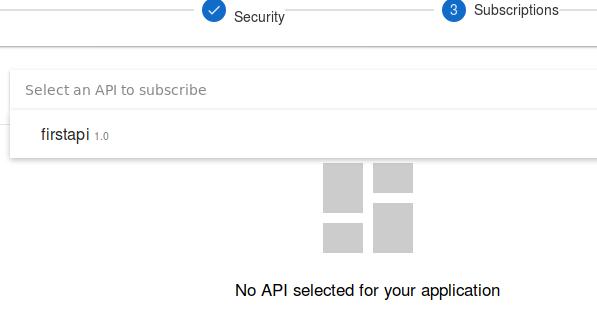
Click REQUEST FOR SUBSCRIPTION for subscribing to this API:
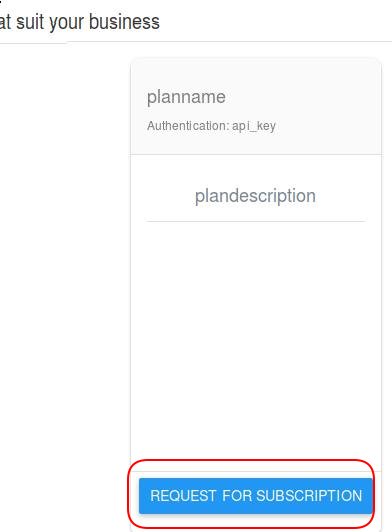
Check the SUBSCRIBED button and click NEXT:
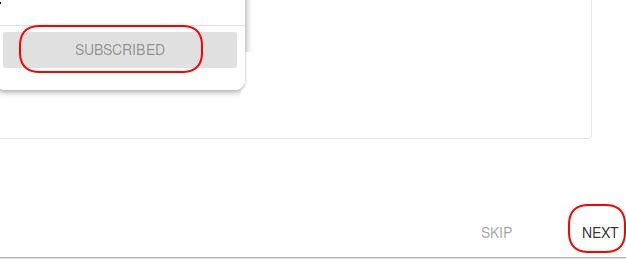
Click CREATE THE APPLICATION for the end of create app:

Click CREATE:
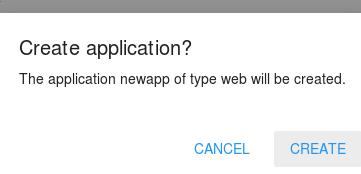
You should approve the subscription:
View the task:
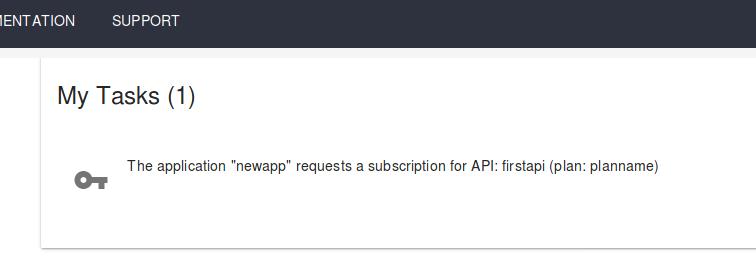
Click ACCEPT for approve the subscription:
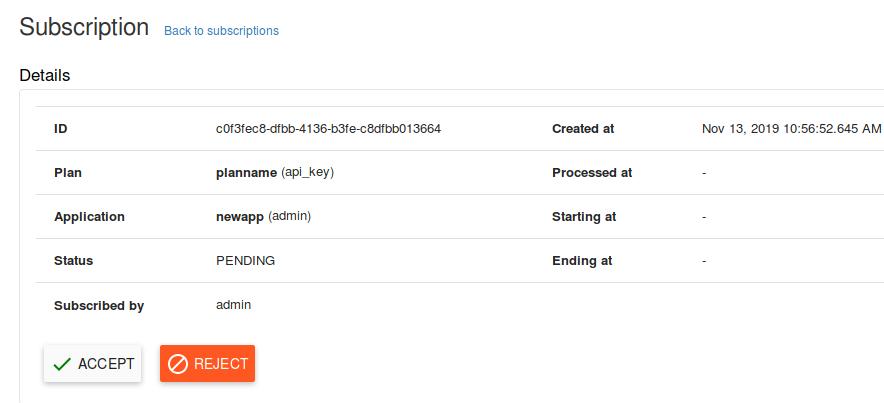
If you don’t specify the time, click CREATE:
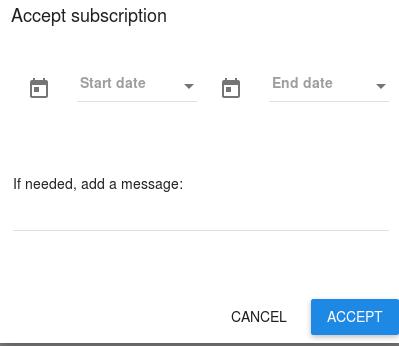
A new API key will be generated:
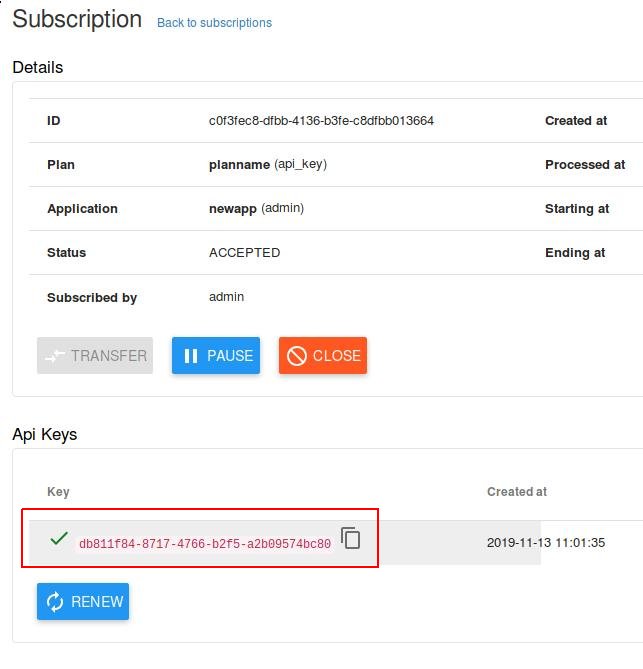
Now the API has been created and you could use the app for consuming it, record this
API key: db811f84-8717-4766-b2f5-a2b09574bc80, later we will use it.
Add ingress item
Since we use a ingress controller for controlling the service exposing, we have to add
a ingress item for accesing the /firstapi:
# kubectl get ingress gravitee45-apim-gateway -oyaml>firstapi.yaml
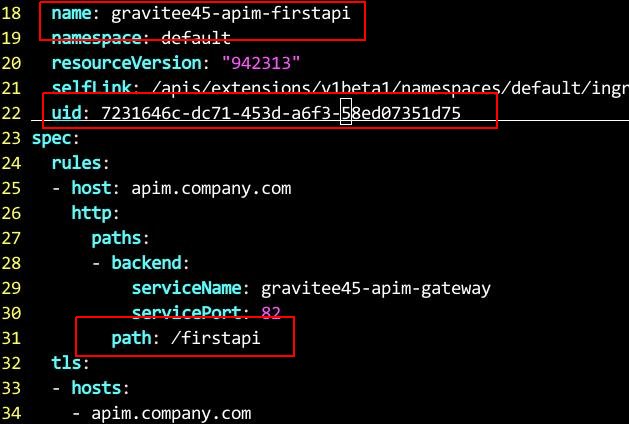
Modify the ingress path and name:
line 18, changes to gravitee45-apim-firstapi
line 22, delete uid
line 31, change to /firstapi
Create the ingress:
# kubectl apply -f firstapi.yaml
ingress.extensions/gravitee45-apim-firstapi created
Consuming API
In a node outside of the k8s cluster, do following steps:
# curl -ki -H "X-Gravitee-Api-Key: db811f84-8717-4766-b2f5-a2b09574bc80" https://apim.company.com/firstapi
HTTP/2 200
server: openresty/1.15.8.1
date: Wed, 13 Nov 2019 03:14:12 GMT
content-type: application/json
content-length: 536
vary: Accept-Encoding
x-gravitee-transaction-id: fc46603c-f4d8-4c60-8660-3cf4d8cc608d
strict-transport-security: max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains
{
"headers" : {
"Host" : "xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:18080",
"X-Request-ID" : "156ec51c42f84b52ae5d9e36b3efeeef",
"X-Real-IP" : "10.147.191.1",
"X-Forwarded-For" : "10.147.191.1",
"X-Forwarded-Host" : "apim.company.com",
"X-Forwarded-Port" : "443",
"X-Forwarded-Proto" : "https",
"X-Original-URI" : "/firstapi",
"X-Scheme" : "https",
"user-agent" : "curl/7.52.1",
"accept" : "*/*",
"X-Gravitee-Transaction-Id" : "fc46603c-f4d8-4c60-8660-3cf4d8cc608d",
"accept-encoding" : "deflate, gzip"
}
Write a script:
while true
do
curl -ki -H "X-Gravitee-Api-Key: db811f84-8717-4766-b2f5-a2b09574bc80" https://apim.company.com/firstapi
sleep 0.1
done
dashboard
View the dashboard:
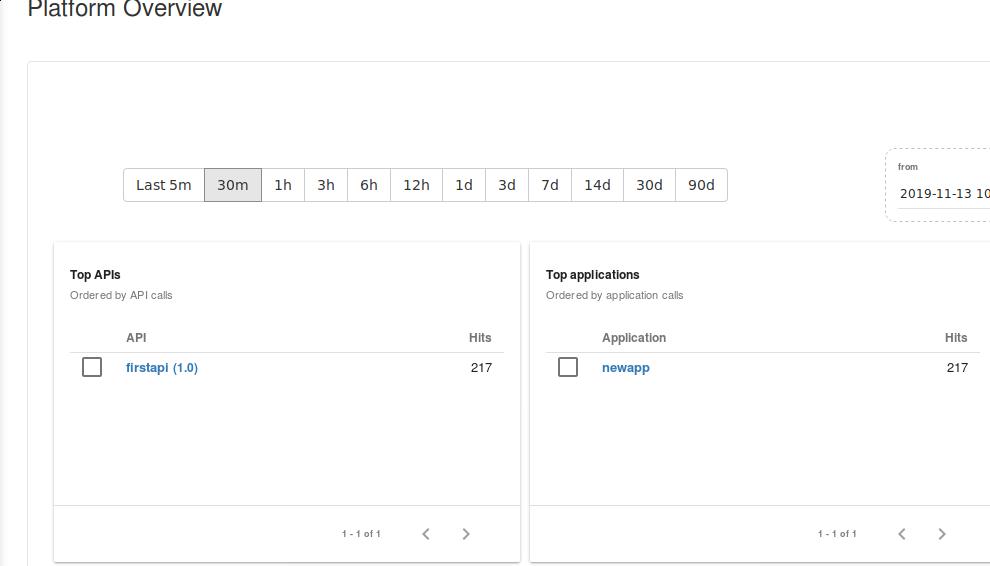
View the detailed statistics in dashboard:
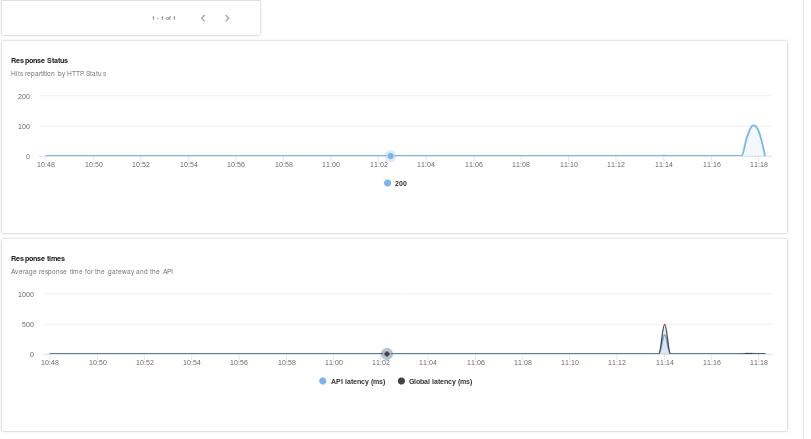
We could easily judge which application comsumes how many apis in statistics page, also we will see the status of the service in this page.
