Aug 23, 2021
TechnologyHardware & OS
Refers to:
https://www.h3c.com/en/Support/Resource_Center/EN/Severs/Catalog/Optional_Parts/GPU/Technical_Documents/Install/User_Guide/H3C_XG310_GPU_UG-5W100/
# cat /etc/issue
Ubuntu 20.04.1 LTS \n \l
# uname -a
Linux xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx 5.4.48+ #1 SMP Wed Feb 3 10:57:04 CST 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
CPU and memory:
# cat /proc/cpuinfo
...
processor : 95
vendor_id : GenuineIntel
cpu family : 6
model : 85
model name : Intel(R) Xeon(R) Gold 6248R CPU @ 3.00GHz
...
# free -g
total used free shared buff/cache available
Mem: 503 3 496 0 3 497
Swap: 1 0 1
Steps
Steps:
# mkdir IntelAndroid
# tar xzvf xxxxxxxxxxxx.tar.gz
Aug 17, 2021
Technology硬件配置
2核2G, 虚拟机,
其磁盘文件为openwrt-21.02.0-rc3-x86-64-generic-ext4-combined.img.
网络配置
隔离网络:
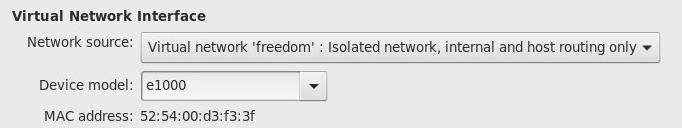
NAT网络:

启动完毕后,安装以下opkg包:
# opkg install redsocks
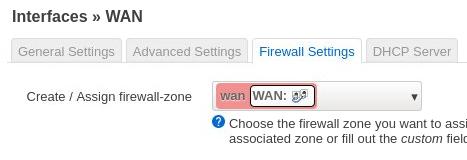
OpenWRT中配置:
Wan:

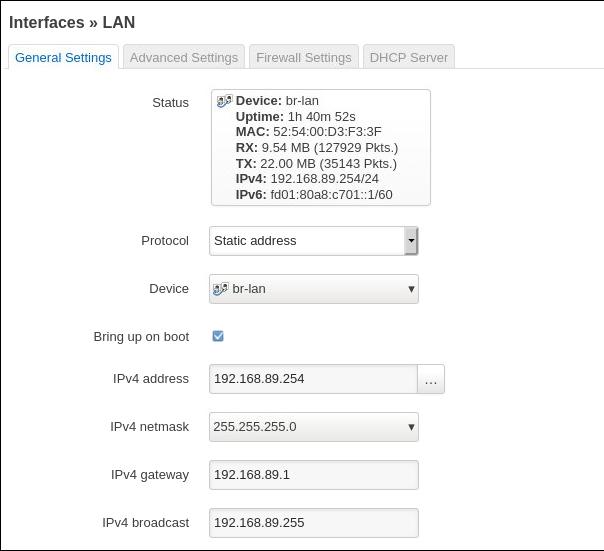
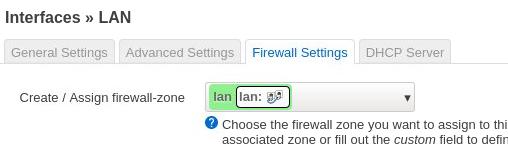
LAN:
Enable dhcp server:
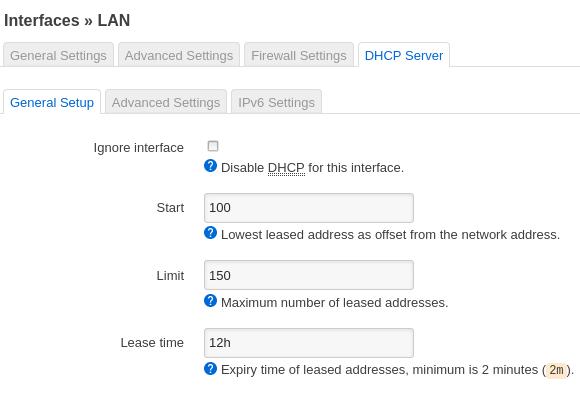
Devices:
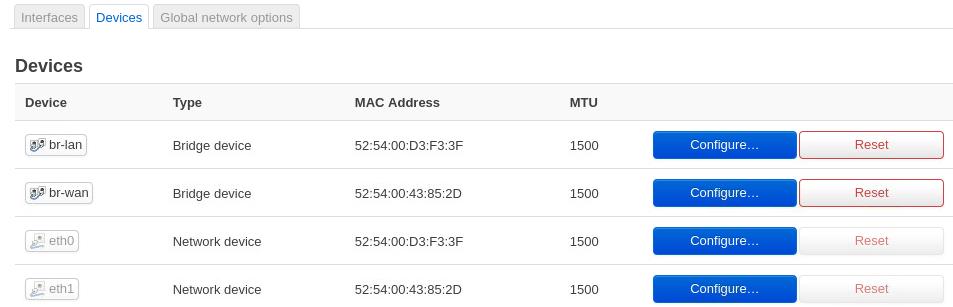
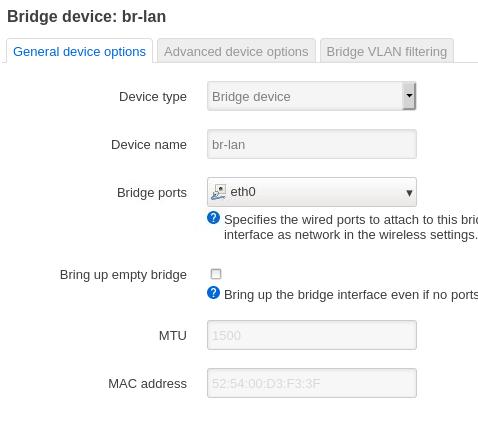
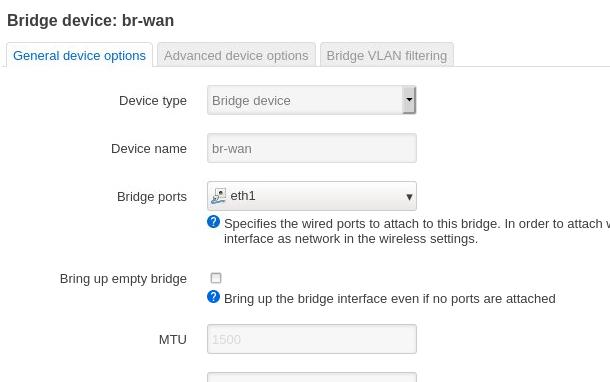
DNS:
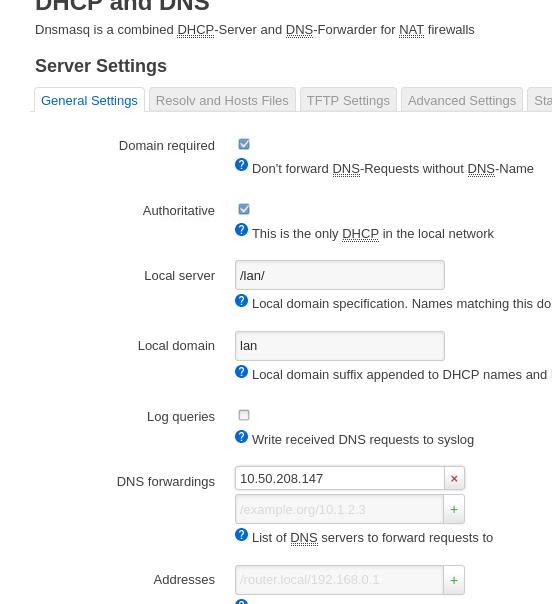
redsocks items
/etc/redsocks.conf:
base {
// debug: connection progress & client list on SIGUSR1
log_debug = off;
// info: start and end of client session
log_info = on;
/* possible `log' values are:
* stderr
* "file:/path/to/file"
* syslog:FACILITY facility is any of "daemon", "local0"..."local7"
*/
// log = stderr;
// log = "file:/path/to/file";
log = "syslog:local7";
// detach from console
daemon = on;
/* Change uid, gid and root directory, these options require root
* privilegies on startup.
* Note, your chroot may requre /etc/localtime if you write log to syslog.
* Log is opened before chroot & uid changing.
*/
// user = nobody;
// group = nobody;
// chroot = "/var/chroot";
/* possible `redirector' values are:
* iptables - for Linux
* ipf - for FreeBSD
* pf - for OpenBSD
* generic - some generic redirector that MAY work
*/
redirector = iptables;
}
redsocks {
/* `local_ip' defaults to 127.0.0.1 for security reasons,
* use 0.0.0.0 if you want to listen on every interface.
* `local_*' are used as port to redirect to.
*/
local_ip = 192.168.89.254;
local_port = 12345;
// listen() queue length. Default value is SOMAXCONN and it should be
// good enough for most of us.
// listenq = 128; // SOMAXCONN equals 128 on my Linux box.
// `max_accept_backoff` is a delay to retry `accept()` after accept
// failure (e.g. due to lack of file descriptors). It's measured in
// milliseconds and maximal value is 65535. `min_accept_backoff` is
// used as initial backoff value and as a damper for `accept() after
// close()` logic.
// min_accept_backoff = 100;
// max_accept_backoff = 60000;
// `ip' and `port' are IP and tcp-port of proxy-server
// You can also use hostname instead of IP, only one (random)
// address of multihomed host will be used.
ip = 10.50.208.147;
port = 8118;
// known types: socks4, socks5, http-connect, http-relay
type = socks5;
// login = "foobar";
// password = "baz";
}
redudp {
// `local_ip' should not be 0.0.0.0 as it's also used for outgoing
// packets that are sent as replies - and it should be fixed
// if we want NAT to work properly.
local_ip = 127.0.0.1;
local_port = 10053;
// `ip' and `port' of socks5 proxy server.
ip = 10.0.0.1;
port = 1080;
login = username;
password = pazzw0rd;
// redsocks knows about two options while redirecting UDP packets at
// linux: TPROXY and REDIRECT. TPROXY requires more complex routing
// configuration and fresh kernel (>= 2.6.37 according to squid
// developers[1]) but has hack-free way to get original destination
// address, REDIRECT is easier to configure, but requires `dest_ip` and
// `dest_port` to be set, limiting packet redirection to single
// destination.
// [1] http://wiki.squid-cache.org/Features/Tproxy4
dest_ip = 8.8.8.8;
dest_port = 53;
udp_timeout = 30;
udp_timeout_stream = 180;
}
dnstc {
// fake and really dumb DNS server that returns "truncated answer" to
// every query via UDP, RFC-compliant resolver should repeat same query
// via TCP in this case.
local_ip = 127.0.0.1;
local_port = 5300;
}
// you can add more `redsocks' and `redudp' sections if you need.
/etc/init.d/redsocks content:
##### /etc/init.d/redsocks######
#!/bin/sh /etc/rc.common
# Copyright (C) 2007 OpenWrt.org
START=90
# check if configuration exists
[ -e "/etc/redsocks.conf" ] || exit 0
start() {
if [ -e "/var/run/redsocks.pid" ]; then
echo "redsocks is already running"
exit 0
fi
/bin/echo -n "running redsocks ..."
# startup the safety-wrapper for the daemon
/usr/sbin/redsocks -p /var/run/redsocks.pid
/bin/echo " done"
}
stop() {
if [ ! -e "/var/run/redsocks.pid" ]; then
echo "redsocks is not running"
exit 0
fi
/bin/echo -n "stopping redsocks ..."
# kill the process
/bin/kill $(cat /var/run/redsocks.pid)
rm /var/run/redsocks.pid
echo " done"
}
Iptables rules:
iptables -t nat -N REDSOCKS
# Ignore LANs IP address
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 0.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 10.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 127.0.0.0/8 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 169.254.0.0/16 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 172.16.0.0/12 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 192.168.0.0/16 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 224.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -d 240.0.0.0/4 -j RETURN
# Anything else should be redirected to redsocks's local port
iptables -t nat -A REDSOCKS -p tcp -j REDIRECT --to-ports 12345
iptables -t nat -I zone_lan_prerouting -j REDSOCKS
Then with a reverse proxy you could cross gfw.
Reverse connect:
Internet machine(with 53 as its dns server):
ssh -o GatewayPorts=true -f -N -T -R *:18888:localhost:18888 docker@10.xxxxx
ssh -o GatewayPorts=true -f -N -T -R *:8118:10.10.3.19:1080 docker@10.xxxxxx
sudo socat tcp-listen:18888,reuseaddr,fork udp:127.0.0.1:53
Intranet machine:
socat -T15 udp4-recvfrom:53,bind=10.xxx.xxx.xx,fork tcp:localhost:18888
Aug 13, 2021
TechnologyVM Prepration
Download qcow2 from gitlab(arch built), then start a vm.
Update the mirrorlist from https://archlinux.org/mirrorlist/
Steps
Install yay:
$ sudo pacman -Sy git fakeroot vim pacman-mirrorlist
$ sudo pacman -Sy base-devel
$ cd /opt
$ sudo git clone https://aur.archlinux.org/yay-git.git
$ sudo chown -R arch:arch ./yay-git/
$ cd yay-git
$ makepkg -si
Install linux-mainline:
$ yay linux-mainline
Aug 11, 2021
Technologyflash
Create a new partition:
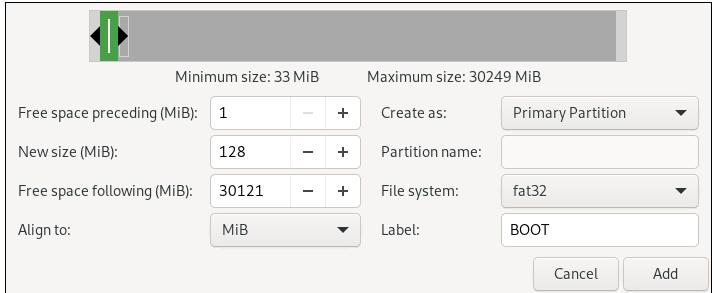
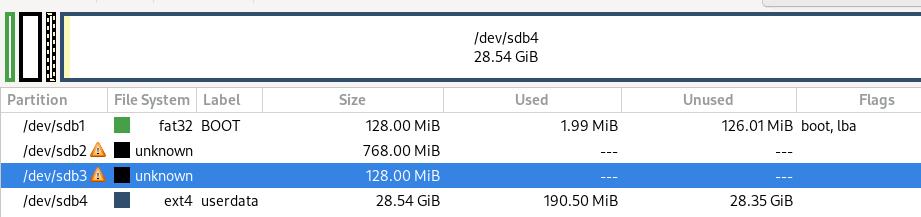
Create new unkown partitions, then a userdata partition:
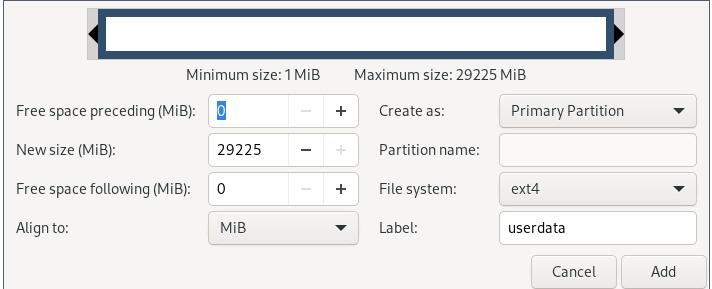
Layout:
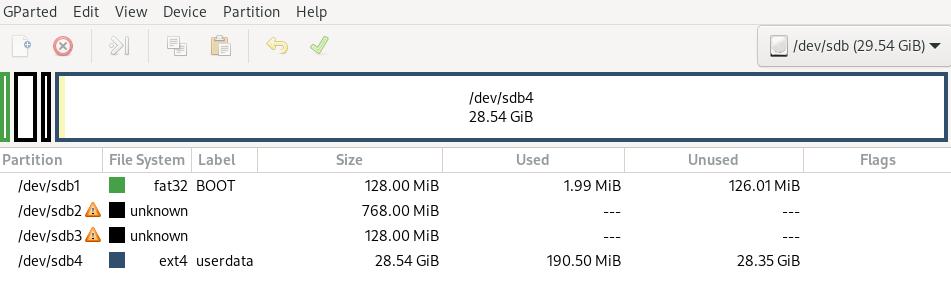
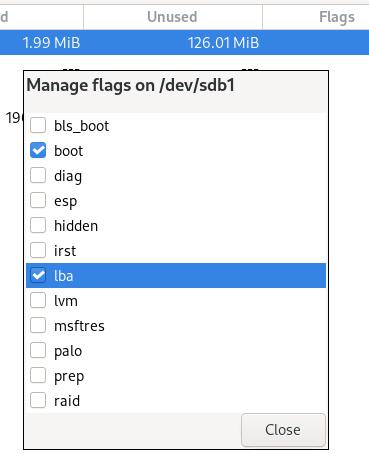
p1: 128MB for boot (fat32, boot & lba)
p2: 768MB for /system
p3: 128MB for /vendor
p4: remainings for /data (ext4)
Manage flags:
Final layout:
Write steps
Write via following steps:
➜ ~ cd rpi4
➜ rpi4 ls
bcm2711-rpi-4-b.dtb boot ramdisk.img system.img vc4-kms-v3d-pi4.dtbo vendor.img zImage
➜ rpi4 sudo dd if=system.img of=/dev/sdb2 bs=1M
768+0 records in
768+0 records out
805306368 bytes (805 MB, 768 MiB) copied, 12.812 s, 62.9 MB/s
➜ rpi4 sudo dd if=vendor.img of=/dev/sdb3 bs=1M
128+0 records in
128+0 records out
134217728 bytes (134 MB, 128 MiB) copied, 2.25087 s, 59.6 MB/s
➜ rpi4 sudo mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt
➜ rpi4 sudo cp boot/* /mnt
➜ rpi4 sudo cp zImage bcm2711-rpi-4-b.dtb ramdisk.img /mnt
➜ rpi4 sudo mkdir /mnt/overlays
➜ rpi4 sudo cp vc4-kms-v3d-pi4.dtbo /mnt/overlays
➜ rpi4 sudo sync
Aug 10, 2021
TechnologyWorkingSteps
Operation steps:
# adb connect 192.168.1.113
already connected to 192.168.1.113:5555
# adb shell
rpi4:/
Or:
# adb root
restarting adbd as root
# adb shell
rpi4:/ # ls
acct boot charger data dev init.environ.rc init.usb.rc mnt proc res sepolicy system vendor_service_contexts
apex bugreports config debug_ramdisk etc init.rc init.zygote32.rc odm product sbin storage ueventd.rc
bin cache d default.prop init init.usb.configfs.rc lost+found oem product_services sdcard sys vendor
rpi4:/ # exit
OR:
adb remount
remount succeeded
➜ Downloads adb shell
rpi4:/ # cd /system/bin/
rpi4:/system/bin # touch fff
rpi4:/system/bin # rm fff
rpi4:/system/bin #
Shutdown the phone:
sudo adb shell reboot -p















