Oct 19, 2013
Technology###BackGround
My requirement is quite simple: I read many english content based website everyday, this means I always encounter many unkown words. My solution is use a translatio software or directly refer them in translate.google.com. But all of these ways were time-consuming process: you have to switch to other software, or you have to open new tabs in your web brower. So do we have a more sufficient way for doing these steps? I used a whole morning of my saturday and finished this procedure.
###Preparation
You have to install google translator for CLI in ArchLinux’s yaourt, you can choose git version or standard version , I choose git version:
$ yaourt -S google-translate-cli-git
After the installation, you can refer to http://www.soimort.org/google-translate-cli/ for more detailed usage for this tool. For example:
[Trusty@DashArch ~]$ trs {=zh} "Hello, world"
你好,世界
###Using Notification under awesome
Yes we can use “notify-send” to directly display something on the screen, but notify-send is not convinient for us to control its behavior,
notify-send $title $result --icon=dialog-information
So we will use awesome’s own notification module, name naughty. But first we have to add a new globle variable in rc.lua which under your own configuration directory, mine is under:
[Trusty@DashArch ~]$ cat /home/Trusty/.config/awesome/rc.lua | more
-- Standard awesome library
-- Notification library
local naughty = require("naughty")
naughty1 = require("naughty")
If we directly using rc.lua’s local variable “naughty”, awesome will complaint it cannot find the variable thus cannot display notification.
The method for displaying notification via naughty is as:
echo ‘naughty1.notify({title = “testing”, text = “naughty”})’ | awesome-client -
Notice naughty1 is the newly added variable in our configuration file.
###Our own bash script
#!/bin/bash
# check parameters
EXPECTED_ARGS=1
if [ $# -lt $EXPECTED_ARGS ]
then
echo "Usage: `basename $0` Your_Tranlate_Word"
notify-send "null" "null" --icon=dialog-information
exit -1
fi
title=$@
declare -a result1
result1=`trs {=zh} "$@"`
result=""
for var in ${result1[@]};do
result=$result' '$var
done
echo "naughty1.notify({title = \"$title\", text = \"$result\", timeout = 5, height = 100, font = \"Verdana 20\", bg = \"BB68D9\", timeout=5})" | awesome-client -
###Result
The script is called via:
when you are browsing the webpage, if you encounter the words, simply press mod4+r, it will call the ‘run’ window, input mytrans.sh “Your words” then you will get the notification window at the top right of your monitor. This window will last for 5 seconds, then vanished. the image is like following:
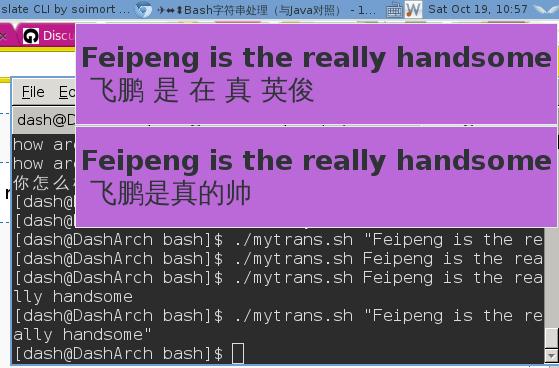
Finally we can enjoy the non-blocking thinking reading now.
Oct 17, 2013
TechnologyFirst we have to get the description of the DVB-T USB stick, use lsusb will get the result of the inserted DVB Disk:
$ lsusb
Bus 002 Device 004: ID 0bda:2838 Realtek Semiconductor Corp. RTL2838 DVB-T
Also we can check the demsg information to get the DVB-T stick information:
[44867.951615] usb 2-2: new high-speed USB device number 4 using xhci_hcd
[44868.345834] usbcore: registered new interface driver dvb_usb_rtl28xxu
[44868.345912] usb 2-2: dvb_usb_v2: found a 'Realtek RTL2832U reference design' in warm state
[44868.416639] usb 2-2: dvb_usb_v2: will pass the complete MPEG2 transport stream to the software demuxer
[44868.416662] DVB: registering new adapter (Realtek RTL2832U reference design)
[44868.537249] usb 2-2: DVB: registering adapter 0 frontend 0 (Realtek RTL2832 (DVB-T))...
[44868.543138] r820t 9-001a: creating new instance
[44868.555987] r820t 9-001a: Rafael Micro r820t successfully identified
[44868.563544] Registered IR keymap rc-empty
[44868.563698] input: Realtek RTL2832U reference design as /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.7/0000:25:00.0/usb2/2-2/rc/rc0/input33
[44868.563806] rc0: Realtek RTL2832U reference design as /devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.7/0000:25:00.0/usb2/2-2/rc/rc0
[44868.566081] usb 2-2: dvb_usb_v2: schedule remote query interval to 400 msecs
[44868.581802] usb 2-2: dvb_usb_v2: 'Realtek RTL2832U reference design' successfully initialized and connected
Now we can check whtether DVB-T stick works:
[root@XXXyyy ~]# ls /dev/v4l
by-id by-path
[root@XXXyyy ~]# ls /dev/dvb
adapter0
To get the first digital signal, we have to install linuxtv-dvb-apps
# pacman -S linuxtv-dvb-apps
Oct 17, 2013
Technologyiw dev will show the wireless device:
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# iw dev
phy#0
Interface wlo1
ifindex 2
wdev 0x1
addr xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx
type managed
Then use the deivce name got from last step, ip link set it up
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# ip link set wlo1 up
# Check the status:
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# iw dev wlo1 link
Not connected.
Scan the available wireless network:
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# iw dev wlo1 scan | more
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# iw dev wlo1 scan | grep SSID
SSID: WLAN14
SSID: VISITOR
.........
Connect to the existing Wireless LAN:
Install the wpa_supplicant:
$ pacman -S wpa_supplicant
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# touch /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# wpa_supplicant -i wlo1 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant.conf
Successfully initialized wpa_supplicant
Generate the wpa_supplicant:
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# wpa_passphrase OpenWrt_11 XXXXXX > /etc/wpa_supplicant/openwrt.conf
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# cat /etc/wpa_supplicant/openwrt.conf
network={
ssid="OpenWrt_11"
#psk="XXXXXX"
psk=xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
}
[root@XXXyyy Trusty]# wpa_supplicant -i wlo1 -c /etc/wpa_supplicant/openwrt.conf
Successfully initialized wpa_supplicant
wlo1: Trying to associate with xx:xx:xx:xx: (SSID='OpenWrt_11' freq=2462 MHz)
ioctl[SIOCSIWFREQ]: Device or resource busy
wlo1: Association request to the driver failed
wlo1: Associated with xx:xx:xx:xx
wlo1: WPA: Key negotiation completed with xx:xg:xx:xx:xx [PTK=CCMP GTK=TKIP]
wlo1: CTRL-EVENT-CONNECTED - Connection to xx:xx:xx:xx:xx completed [id=0 id_str=]
Get the Wireless address:
$ [root@XXXyyy Trusty]# dhcpcd wlo1
dhcpcd[3344]: version 6.0.5 starting
dhcpcd[3344]: wlo1: soliciting an IPv6 router
dhcpcd[3344]: wlo1: soliciting a DHCP lease
dhcpcd[3344]: wlo1: offered 10.0.0.232 from 10.0.0.1
dhcpcd[3344]: wlo1: leased 10.0.0.232 for 7200 seconds
dhcpcd[3344]: wlo1: adding host route to 10.0.0.232 via 127.0.0.1
dhcpcd[3344]: wlo1: adding route to 10.0.0.0/24
dhcpcd[3344]: wlo1: adding default route via 10.0.0.1
dhcpcd[3344]: forked to background, child pid 3434
Now we can access the internet via Wireless!
Oct 15, 2013
Technology1. Change Mercury MW151RM3G into TP-Link 703N. You have to download the firmware named “MW151rm3G_to_wr703nv1” from google searched result. After flashing this onto your Mercury MW151RM3G, In fact you have got a TP-LINK 703N.
2. Download the latest firmware of TP-LINK 703N from openwrt.org. The Download URL is located at http://wiki.openwrt.org/toh/tp-link/tl-wr703n. You can get two files, named “squashfs-factory.bin” and “squashfs-sysupgrade.bin”, the factory.bin is for flashing firstly, after flashed this image, flash another named sysupgrade.bin. This will lead your MW151RM3G into a OpenWRT based system.
3. Now you have to change the status of your MW151RM3G’s ethernet port from static ip address into dhcp based address. Then plug it into the Wireless Router, you will found the OpenWRT’s IP address from you router’s connected equipments. Log on it, open the openssh server, log into the router.
4. Now we can boot the system using flash disk, because the inner image is too small for run applications.
5. Prepare the flash disk, format it into ext3 based partition.
6. Install the necessary package on OpenWRT:
$ opkg update
$ opkg install block-mount
$ opkg install kmod-usb-storage
$ opkg install fdisk
$ opkg install kmod-fs-ext4
After the installation, you can mount the flash disk using mount, and your system shall support ext3 based partitions.
7. Edit the fstab file, /etc/config/fstab
config mount
option target /overlay
option device /dev/sda1
option fstype ext3
option options rw,sync
option enabled 1
option enabled_fsck 0
Now reboot your MW151RM3G, you will got an 8G based flash disk OpenWRT.
Oct 14, 2013
Technology###Preparation
For using SNMP for administrating PogoPlug, we have to install following packages first:
# apt-get install snmpd smartmontools super
snmpd is the daemon process for snmp, smartmontools is the monitor tools for harddisk, super let you run daemon process in super priviledge.
###Configuration
Configure snmp firstly.
###Client Configuration
Install the webserver using the following command:
$ pacman -S apache php php-apache mariadb
After install the packages, if you want to change the configuration file, directly edit the /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf or extra/httpd-default.conf, then using systemd to restart the httpd daemon.
Change priviledge of the public_html directory:
$ chmod o+x ~
$ chmod o_x ~/public_html
# A more safe way for controlling the safety
# usermod -aG groupname http
###SSL Configuration
Generate a new self-signed certificate(key size and the number of days of validity will be customized):
# openssl genrsa -out server.key 2048
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus
..........................+++
...........................................................................................................................................................+++
e is 65537 (0x10001)
[root@XXXyyy conf]# ls
extra httpd.conf magic mime.types server.key
[root@XXXyyy conf]# chmod 600 server.key
[root@XXXyyy conf]# openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
You are about to be asked to enter information that will be incorporated
into your certificate request.
What you are about to enter is what is called a Distinguished Name or a DN.
There are quite a few fields but you can leave some blank
For some fields there will be a default value,
If you enter '.', the field will be left blank.
-----
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:
Locality Name (eg, city) []:
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:
Common Name (e.g. server FQDN or YOUR name) []:
Email Address []:
Please enter the following 'extra' attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
[root@XXXyyy conf]# openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt
Signature ok
subject=/C=AU/ST=Some-State/O=Internet Widgits Pty Ltd
Getting Private key
[root@XXXyyy conf]# ls
extra httpd.conf magic mime.types server.crt server.csr server.key
Then, uncomment the line containing following lines in /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
Include conf/extra/httpd-ssl.conf
Restart httpd to see the result.
###Enable php
Place Following line after LoadModule dir_module modules/mod_dir.so in /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf:
LoadModule php5_module modules/libphp5.so
Place following line at the end of the Include list:
Include conf/extra/php5_module.conf
Make sure you uncommented following line:
TypesConfig conf/mime.types
# Optional uncomment:
MIMEMagicFile conf/magic
Add this line in /etc/httpd/conf/mime.types:
application/x-httpd-php php php5
Make sure libphp5.so is under /etc/httpd/modules, if not, you may forgot to install php-apache.
Test the php via following line under test.php:
<?php phpinfo(); ?>
###Configure MariaDB
Uncomment at least one line under /etc/php/php.ini:
extension=pdo_mysql.so
extension=mysqli.so
extension=mysql.so
###Mysql Configuration
[root@XXXyyy http]# mysqld_safe --skip-grant-tables &
[1] 26315
[root@XXXyyy http]# 131014 16:55:07 mysqld_safe Logging to '/var/lib/mysql/XXXyyy.err'.
131014 16:55:07 mysqld_safe Starting mysqld daemon with databases from /var/lib/mysql
[root@XXXyyy http]# mysql -u root mysql
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 6
Server version: 5.5.33a-MariaDB-log Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle, Monty Program Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [mysql]> UPDATE mysql.user SET Password=PASSWORD('******') WHERE User='root';
Query OK, 4 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Rows matched: 4 Changed: 4 Warnings: 0
MariaDB [mysql]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [mysql]> exit
Bye
[root@XXXyyy http]# systemctl start mysqld
###CACTI configuration
Install cacti via:
$ pacman -S cacti
$ pacman -S php-snmp
uncomment the following lines in /ec/php/php.ini:
;extension=mysql.so
;extension=sockets.so
;extension=snmp.so
open_basedir=...
;date.timezone =
Start mysqld:
$ systemctl enable mysqld.service
$ systemctl start mysqld.service
Start snmpd:
$ systemctl enable snmpd
$ systemctl start snmpd
Change the configuration file /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf, inside <Directory “/srv/http"> block, ensure you have:
AllowOverride All
Create the mysql based db:
$ mysqladmin -u root -p create cacti
Enter password:
Generate the sql table using existing template:
[root@XXXyyy http]# mysql -u root -p cacti < /usr/share/webapps/cacti/cacti.sql
Enter password:
Update the configuration of the database, you can replace the password from “some_password” to your own password.
[root@XXXyyy http]# mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 10
Server version: 5.5.33a-MariaDB-log Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2013, Oracle, Monty Program Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MariaDB [(none)]> GRANT ALL ON cacti.* TO cacti@localhost IDENTIFIED BY 'some_password';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> exit
Bye
Change the username and password of the config.php of cacti:
$ vim /usr/share/webapps/cacti/include/config.php
$ database_username = "cacti";
$ database_password = "some_password";
Clean up the cacti directory:
chown -R http:http /usr/share/webapps/cacti/{rra,log}
rm /usr/share/webapps/cacti/.htaccess
chmod +x /usr/share/webapps/cacti/{cmd,poller}.php /usr/share/webapps/cacti/lib/ping.php
Install caccti-spine, a fast poller for cacti, from AUR. Change the db name and db password to:
$ vim /etc/spine.conf
DB_User cacti
DB_Pass some_password
Restart crontab:
$ systemctl restart cronie.service
$ systemctl restart httpd

