Dec 20, 2013
Technology1. Download Putty, it’s a green software, click it and then you got its configuration window.
2. Configure the ssh Tunnel via following
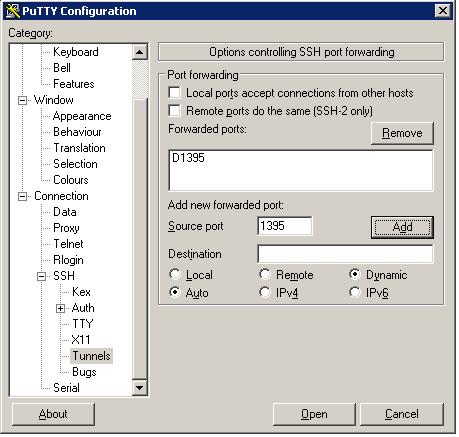
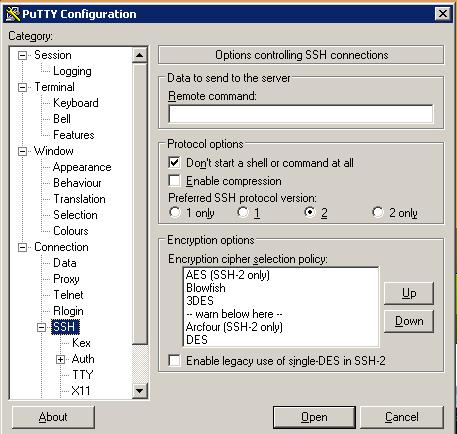
3. Disable the Command line interface.
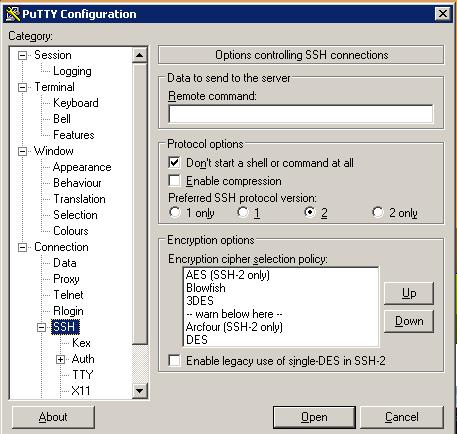
4. Now using the configuration you can logon to remote server.
5. Now you can use socket proxy via “127.0.0.1”, port is 1395.
Dec 19, 2013
TechnologyAfter 4 days struggling, I finally make bluetooth headset working on my ArchLinux. Following is the detailed how-to which shows how to enable bluetooth playing.
###Software Installation
Currently blueman is still the best bluetooth management software, we can install it via:
$ yaourt blueman
1 aur/blueman-bzr 726-2 [installed] (38)
GTK+ bluetooth management utility
Then we have to install bluez related items:
$ pacman -S bluez-utils bluez-libs python2-pybluez
$ yaourt -S bluez4
$ yaourt pulseaudio-bluez4
###Bluetooth Configuration
First make sure your bluetooth service is enabled.
$ sudo systemctl start bluetooth
$ sudo systemctl enable bluetooth
Now we need to make change to following files:
[Trusty@XXXyyy ~]$ cat /etc/bluetooth/audio.conf
[General]
Enable=Socket
[A2DP]
SBCSources=1
Now we can manually startup blueman manager via:
$ blueman-manager
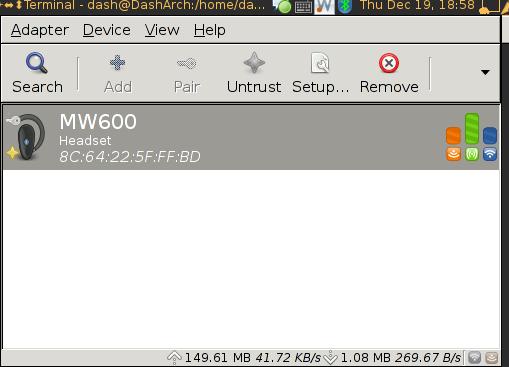
Click “Search” to find the avaiable headset, pair, trust, setup. Right click the found headset, choose “Audio Sink”, if successful, you will see the equipment has been successfully added into the system.
Add blueman automatically to the system startup script. We can add it into the awsome window manager:
autorunApps =
{
--.........
"blueman-manager",
--.........
}
###PulseAudio Configuration
First we have to define the alsa device in /etc/asound.conf:
pcm.btheadset {
type plug
slave {
pcm {
type bluetooth
device 8C:64:goewugowugoeu
profile "auto"
}
}
hint {
show on
description "BT Headset"
}
}
ctl.btheadset {
type bluetooth
}
Now via “aplay -l” we can see the following item:
$ aplay -L
null
Discard all samples (playback) or generate zero samples (capture)
pulse
PulseAudio Sound Server
btheadset
BT Headset
In fact currently we can play sounds via mplayer, by specifying its default audio path is OK. But we want to make this audio sink path globally.
The steps for manually enabling the audio sink path via following steps:
Load device of btheadset
$ pactl load-module module-alsa-sink device=btheadset
Load bluetooth discover module
$ pacmd load_module module-bluetooth-discover
List the available cards
$ pactl list cards short
The upper output is still one audio card, but all we care is the audio sink, so we list all of the available audio sinks via:
$ pactl list sinks short
0 alsa_output.pci-0000_00_1b.0.analog-stereo module-alsa-card.c s16le 2ch 44100Hz SUSPENDED
1 alsa_output.btheadset module-alsa-sink.c s16le 2ch 44100Hz SUSPENDED
Set the default audio sink to bluetooth headset:
$ pacmd set-default-sink 1
Congratulations! Now you can listen to music via bluetooth headset!
###Automatically Configuration
Following is the configuration for my machine, you have to adjust the parameters according to yourself:
Comment the following items in /etc/pulse/default.pa, the module-bluetooth-policy should be commented, or the pulse audio will not start:
### Automatically load driver modules for Bluetooth hardware
#.ifexists module-bluetooth-policy.so
#load-module module-bluetooth-policy
#.endif
#
.ifexists module-bluetooth-discover.so
load-module module-bluetooth-discover
.endif
Surely you will start bluetooth daemon by default:
$ sudo systemctl enable bluetooth
Add “blueman-applet” into the awesome startup file(.config/awesome/rc.lua).
The right steps for using bluetooth:
- Startup Your machine with bluetooth background and blueman-applet enabled.
- Power on your bluetooth headset. If your key is accepted permanately, the bluetooth headset will connect automatically.
- Manually add the audio sink via “pactl load-module module-alsa-sink device=btheadset”.
- Set the default route path of the audio sink via “pacmd set-default-sink 1” ( all of the audio sink could be listed via “pactl list sinks short”)
Now you can enjoy the bluetooth, for convenient, I made an alias:
alias enableblue='pactl load-module module-alsa-sink device=btheadset && pacmd set-default-sink 1"
Dec 19, 2013
TechnologySince trying to enable BT headset failed on Ubuntu12.04 Server, I decide to try xubuntu version. So I download the image from http://joggler.exotica.org.uk/ubuntu/, then extract it to get the image.
###Get the filesystem
Use fdisk to get the img layout
root@joggler:/media/nfs/xubuntu# fdisk -l xubuntu_12.04-v1.4-ext4.img
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
xubuntu_12.04-v1.4-ext4.img1 * 2048 126975 62464 e W95 FAT16 (LBA)
xubuntu_12.04-v1.4-ext4.img2 126976 626687 249856 82 Linux swap / Solaris
xubuntu_12.04-v1.4-ext4.img3 626688 7800831 3587072 83 Linux
So we can caculate the offset is 626688X512=320864256.
Use following commands to copy the filesystem out to the actual disk:
$ mount ./xubuntu_12.04-v1.4-ext4.img -o offset=320864256 /mnt3/
$ mount /dev/uba5 /mnt
$ cp -ar /mnt3/* /mnt/
My disk layout is:
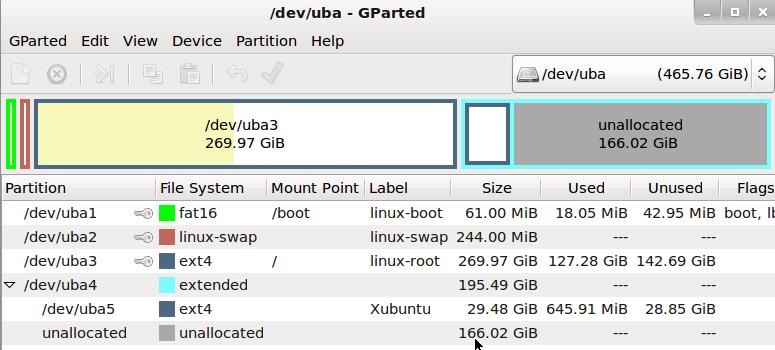 ###Modification for bootup Xubuntu
####Add new item for grub:
Get the disk labels:
###Modification for bootup Xubuntu
####Add new item for grub:
Get the disk labels:
$ ls /dev/disk/by-label/
Xubuntu linux-boot linux-root linux-swap mmc-boot mmc-root
The newly added label “Xubuntu” is the one we store the filesystem of Xubuntu. We need to add a new item to point at this partition.
root@joggler:/boot# cat grub.cfg
loadfont /unicode.pf2
terminal_output gfxterm
set timeout=5
menuentry "XUbuntu 12.04 LTS (Precise) - 3.2.32joggler1" {
linux /vmlinuz-3.2.32joggler1 root=LABEL=Xubuntu ro quiet splash text
initrd /initrd.img-3.2.32joggler1
}
#####Change the fstab
We have to change the root partition to “Xubuntu”
root@joggler:/mnt3# cat /mnt3/etc/fstab
# /etc/fstab: static file system information.
#
# Use 'blkid -o value -s UUID' to print the universally unique identifier
# for a device; this may be used with UUID= as a more robust way to name
# devices that works even if disks are added and removed. See fstab(5).
#
# <file system> <mount point> <type> <options> <dump> <pass>
proc /proc proc nodev,noexec,nosuid 0 0
LABEL=Xubuntu / ext4 errors=remount-ro,noatime 0 1
LABEL=linux-boot /boot vfat defaults 0 0
LABEL=linux-swap none swap sw 0 0
Now reboot to see if we could enter xubuntu? Since we cannot use keyboard in grub, we could only enable one distribution, this is different from the tranditional grub.
####Configure Bluetooth
Install module for pulseaudio
apt-get install pulseaudio-module-bluetooth
Then reboot. Currently connect the bluetooth, then in pulseaudio you will select the corresponding sound card. Enjoy it!
Tips for avoiding auto hiberate of usb disk, as root:
$ crontab -e
*/4 * * * * fdisk -l /dev/uba >/dev/null
Now your disk will never be hiberate, avoiding system from broken.
Dec 18, 2013
Technology###TroubleShooting on alsa
Current user canot use alsamixer
Trusty@joggler:~$ alsamixer
cannot open mixer: No such file or directory
This is because the current user is not in the “audio” group, use root to add current user into “audio” group:
root@joggler:~# usermod -a -G audio Trusty
Unmute the channel:
$ amixer sset Master unmute
Simple mixer control 'Master',0
Capabilities: pvolume pswitch penum
Playback channels: Front Left - Front Right
Limits: Playback 0 - 31
Mono:
Front Left: Playback 24 [77%] [-10.50dB] [on]
Front Right: Playback 24 [77%] [-10.50dB] [on]
Now we can use wired headset for listening music.
###Setup Bluetooth
Scan the available equipments:
Trusty@joggler:~$ hcitool scan
Scanning ...
geougwoguw geige
geougwoguw geige521
geougwoguw geige
geougwoguw geige723
Repair:
bluez-simple-agent hci0 dd:64:22:KK:FF:BD repair
Then edit your /etc/asound.conf file:
#/etc/asound.conf
pcm.btheadset {
type plug
slave {
pcm {
type bluetooth
device XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
profile "auto"
}
}
hint {
show on
description "BT Headset"
}
}
ctl.btheadset {
type bluetooth
}
mplayer using bluetooth:
mplayer -ao alsa:device=btheadset bad.mp3
###Set the default sound card to bluetooth
Edit the .asoundrc file.
Trusty@joggler:~$ cat .asoundrc
pcm.!default {
type plug
slave {
pcm {
type bluetooth
device dd:64:22:KK:FF:BD
profile "auto"
}
}
hint {
show on
description "BT Headset"
}
}
##ctl.btheadset {
## type bluetooth
##}
bluez-simple-agent hci0 dd:64:22:KK:FF:BD repair
Then edit your /etc/asound.conf file:
#/etc/asound.conf
pcm.btheadset {
type plug
slave {
pcm {
type bluetooth
device XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
profile "auto"
}
}
hint {
show on
description "BT Headset"
}
}
ctl.btheadset {
type bluetooth
}
mplayer using bluetooth:
mplayer -ao alsa:device=btheadset bad.mp3
###Set the default sound card to bluetooth
TBD, here I meet lots of problems.
Edit the .asoundrc file.
apt-get autoremove pulseaudio
pulseaudio --start
Why aplay -L and aplay -l will get different result? I have no idea.
Dec 17, 2013
TechnologyYou can use pkgfile to view the metadata of the pacman files:
pacman -Ss pkgfile
extra/pkgfile 11-1 [installed]
a pacman .files metadata explorer
Usage:
pkgfile ls
Then you will see “ls” belogns to which package.





 ###Modification for bootup Xubuntu
####Add new item for grub:
Get the disk labels:
###Modification for bootup Xubuntu
####Add new item for grub:
Get the disk labels: