Dec 30, 2013
Technology###Preparation
Mount the partition automatically, add following lines into the /etc/fstab:
/dev/sda3 /media/ntfs ntfs-3g permissions,locale=en_US.utf8 0 2
I decide to use samba to share the files, so I have to install samba
apt-get install samba
The samba server will start automatically, but we have to configure it to adapte to our situation.
Add the configuration to the samba config file:
/etc/samba/smb.conf
[raspshare]
comment = raspberry PI Share
path = /media/ntfs
valid users = Trusty
public = no
writable = yes
printable = no
create mask = 0765
Restart the samba server
/etc/init.d/samba restart
For using smbpasswd, you have to install samba-common-bin:
apt-get install samba-common-bin
Add some users to the samba sharing:
smbpasswd -a xxx
###Mount the shared partition in client
List all of the available samba shared items:
$ smbclient -L 10.0.0.230 -U%
Then we can mount it, I add following command into the .bashrc, so everytime I enter ‘mountraspsamba’ is ok
alias mountraspsamba='sudo mount -t cifs //10.0.0.230/raspshare/ -o user=xxxx,password=XXXX,workgroup=WORKGROUP /media/raspsamba'
Dec 29, 2013
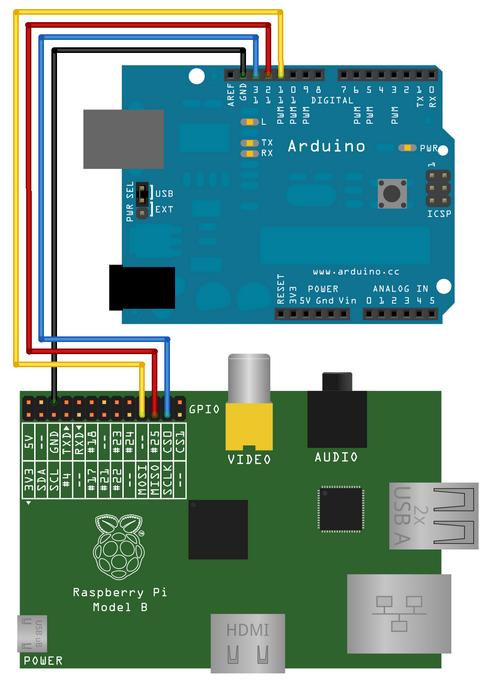
Technology###连线
Arduino I2C 连线:
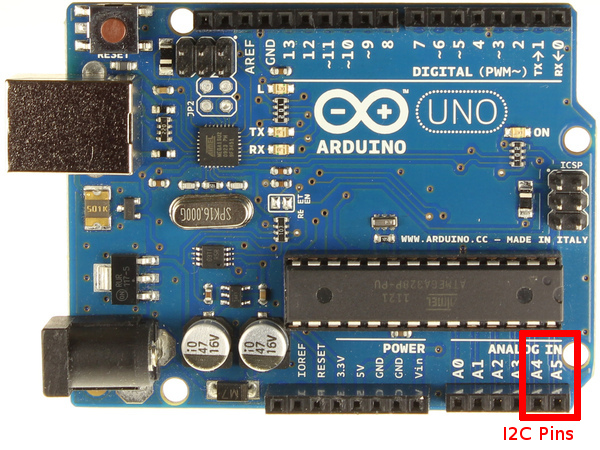
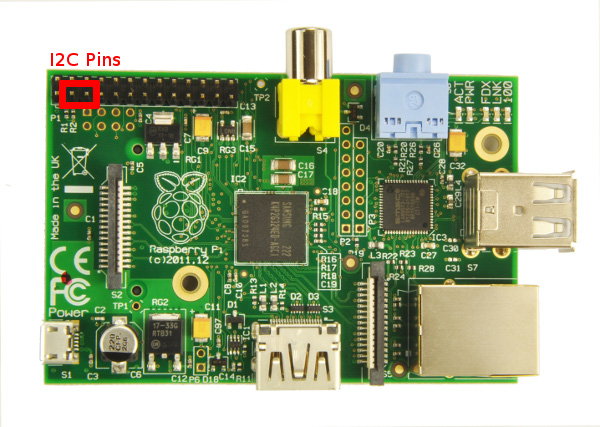
RaspberryPI I2C 连线:
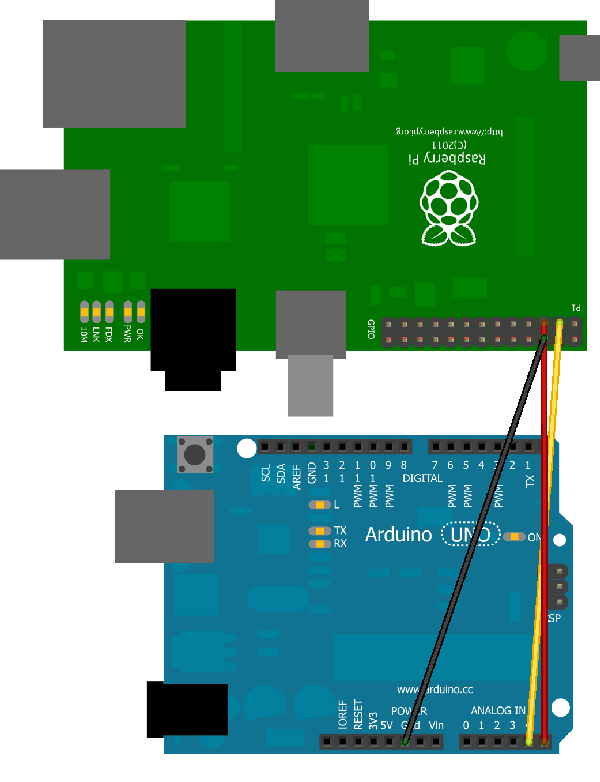
连线图:
RPI Arduino (Uno/Duemillanove)
--------------------------------------------
GPIO 0 (SDA) <--> Pin 4 (SDA)
GPIO 1 (SCL) <--> Pin 5 (SCL)
Ground <--> Ground
###Arduino端代码
#include <Wire.h>
#define SLAVE_ADDRESS 0x04
int number = 0;
int state = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(13, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); // start serial for output
// initialize i2c as slave
Wire.begin(SLAVE_ADDRESS);
// define callbacks for i2c communication
Wire.onReceive(receiveData);
Wire.onRequest(sendData);
Serial.println("Ready!");
}
void loop() {
delay(100);
}
// callback for received data
void receiveData(int byteCount){
while(Wire.available()) {
number = Wire.read();
Serial.print("data received: ");
Serial.println(number);
if (number == 1){
if (state == 0){
digitalWrite(13, HIGH); // set the LED on
state = 1;
}
else{
digitalWrite(13, LOW); // set the LED off
state = 0;
}
}
}
}
// callback for sending data
void sendData(){
Wire.write(number);
}
###RaspberryPI端准备
在/etc/modules中增加一行:
i2c-dev
注释掉黑名单:
$ cat /etc/modprobe.d/raspi-blacklist.conf
# blacklist spi and i2c by default (many users don't need them)
# blacklist spi-bcm2708
#blacklist i2c-bcm2708
安装i2c工具:
apt-get install i2c-tools
安装python库:
apt-get install python-smbus
探测i2c设备
i2cdetect -y 0
如果不是root用户,例如,如果是pi用户,则需要将当前用户增加到i2c组中:
$ sudo adduser pi i2c
###RaspberryPI端代码
import smbus
import time
# for RPI version 1, use "bus = smbus.SMBus(0)"
bus = smbus.SMBus(0)
# This is the address we setup in the Arduino Program
address = 0x04
def writeNumber(value):
bus.write_byte(address, value)
# bus.write_byte_data(address, 0, value)
return -1
def readNumber():
number = bus.read_byte(address)
# number = bus.read_byte_data(address, 1)
return number
while True:
var = input("Enter 1 - 9: ")
if not var:
continue
writeNumber(var)
print "RPI: Hi Arduino, I sent you ", var
# sleep one second
time.sleep(1)
number = readNumber()
print "Arduino: Hey RPI, I received a digit ", number
print
运行代码时要注意,0~255的数字输入进去,会在arduino i2c slave端收到对应的数据,并原封不动的被返回。超过255的数值将溢出。
Dec 29, 2013
Technology接着上一个日志来,玩一个小tricky,通过SPI总线自己想输入的字符。
主机端,添加下列头文件
#include <string.h>
这使得可以使用strcpy等函数。
重写transfer()函数
static void transfer_mine(int fd, char *buf)
{
int ret;
uint8_t tx[140];
int len = strlen(buf)+1;
memcpy(tx, buf, strlen(buf)+1);
tx[strlen(tx)] = '\n';
uint8_t rx[ARRAY_SIZE(tx)] = {0, };
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx,
//.len = ARRAY_SIZE(tx),
.len = len,
.delay_usecs = delay,
.speed_hz = speed,
.bits_per_word = bits,
};
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
if (ret < 1)
pabort("can't send spi message");
}
在main()函数里,改写调用的方式:
char myinput[140]="Trustywill, Hi, this is Trusty";
transfer_mine(fd, myinput);
这样就可以将自定义的字符传输过去了,140是随便设置的值,可以设置为别的更大或者更小的值。
当然你也可以从命令行输入想传输的字符, 这里就不深入了。。
Dec 29, 2013
Technology下面是使用SPI在RaspberryPI和Arduino Nano w之间进行双机通信的一个例子。借助它可以很好的理解SPI的工作原理。
###背景知识
RaspberryPI GPIO布局图:
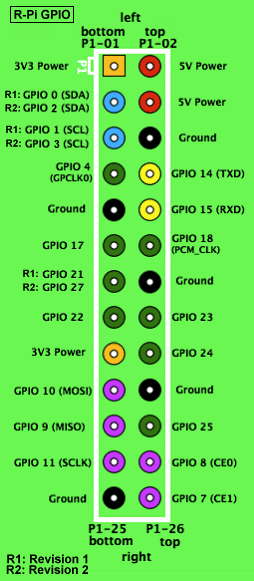
从图中我们可以看到,RaspberryPI上与SPI通信相关的主要是GPIO 10(MOSI), GPIO 9(MISO)和GPIO 11(SCLK).
Arduino布局图:
SPI: 10 (SS), 11 (MOSI), 12 (MISO), 13 (SCK). These pins support SPI communication using the SPI library. SS代表Slava Select.
事实上我们要使用的仅仅是11/12/13三个口而已。
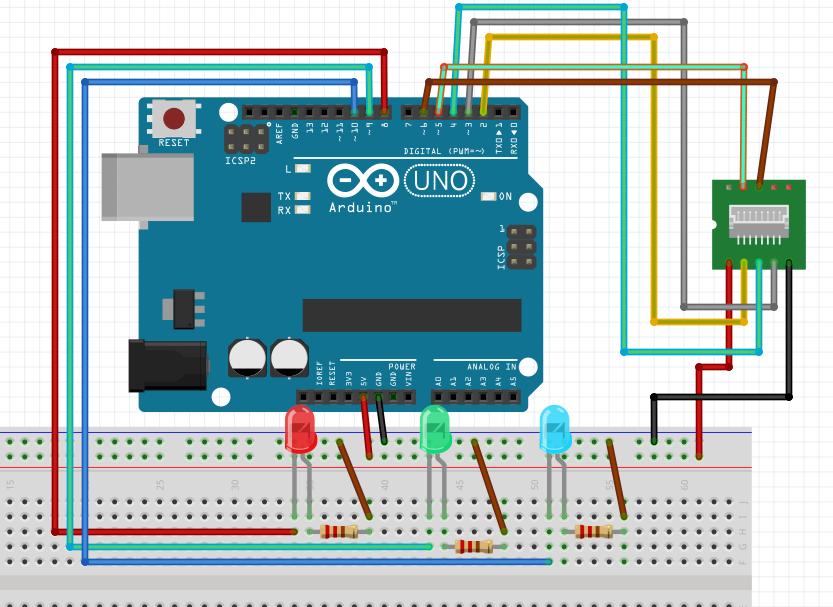
###连线图
如下图进行连线,简单来说,R(10 MOSI)->A(12 MISO), R(9, MISO)->A(11, MOSI), R(11, SCLK) ->A(13, SCK):
 ###Arduino端程序
###Arduino端程序
// Written by Nick Gammon
// February 2011
/**
* Send arbitrary number of bits at whatever clock rate (tested at 500 KHZ and 500 HZ).
* This script will capture the SPI bytes, when a '\n' is recieved it will then output
* the captured byte stream via the serial.
*/
#include <SPI.h>
char buf [100];
volatile byte pos;
volatile boolean process_it;
void setup (void)
{
Serial.begin (115200); // debugging
// have to send on master in, *slave out*
pinMode(MISO, OUTPUT);
// turn on SPI in slave mode
SPCR |= _BV(SPE);
//SPCR is Arduino SPI Control Register
// __BV's definition is like : #define _BV(bit) (1 << (bit))
// SPE is the register of the SPI Enable
// get ready for an interrupt
pos = 0; // buffer empty
process_it = false;
// now turn on interrupts
SPI.attachInterrupt();
} // end of setup
// SPI interrupt routine
ISR (SPI_STC_vect)
{
byte c = SPDR; // grab byte from SPI Data Register
// add to buffer if room
if (pos < sizeof buf)
{
buf [pos++] = c;
// example: newline means time to process buffer
if (c == '\n')
process_it = true;
} // end of room available
} // end of interrupt routine SPI_STC_vect
// main loop - wait for flag set in interrupt routine
void loop (void)
{
if (process_it)
{
buf [pos] = 0;
Serial.println (buf);
pos = 0;
process_it = false;
} // end of flag set
} // end of loop
Code Walking through:
Arduino SPI Control Register (SPCR), set it to
SPCR |= _BV(SPE);
SPI Data Register (SPDR), SPI数据寄存器。 中断程序中,每次从SPDR中取回一个byte 并存储在c中。
if (c == '\n')
process_it = true;
这里通过设置全局变量process_it来影响loop中对接收数据的处理,在loop()中有如下代码段:
if (process_it)
{
//.....
}
从上面看到,如果process_it为0,则loop中一直在空循环,只有当所有的数据全部接收完毕后,才会一次性打印出所有的数据。在打印完数据后,程序将自动将buf清0, 清0是通过将pos简单置0而实现的,实际的数据其实还在。
###RaspberryPI 端程序
/*
* SPI testing utility (using spidev driver)
*
* Copyright (c) 2007 MontaVista Software, Inc.
* Copyright (c) 2007 Anton Vorontsov <avorontsov@ru.mvista.com>
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License.
*
* Cross-compile with cross-gcc -I/path/to/cross-kernel/include
*/
#include <stdint.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/spi/spidev.h>
#define ARRAY_SIZE(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof((a)[0]))
static void pabort(const char *s)
{
perror(s);
abort();
}
static const char *device = "/dev/spidev0.0";
static uint8_t mode;
static uint8_t bits = 8;
static uint32_t speed = 500000;
static uint16_t delay;
static void transfer(int fd)
{
int ret;
uint8_t tx[] = {
0x48, 0x45, 0x4C, 0x4C, 0x4F,
0x20,
0x57, 0x4F, 0x52, 0x4C, 0x44,
0x0A
};
uint8_t rx[ARRAY_SIZE(tx)] = {0, };
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx,
.len = ARRAY_SIZE(tx),
.delay_usecs = delay,
.speed_hz = speed,
.bits_per_word = bits,
};
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
if (ret < 1)
pabort("can't send spi message");
/*
for (ret = 0; ret < ARRAY_SIZE(tx); ret++) {
if (!(ret % 6))
puts("");
printf("%.2X ", rx[ret]);
}
puts("");
*/
}
static void print_usage(const char *prog)
{
printf("Usage: %s [-DsbdlHOLC3]\n", prog);
puts(" -D --device device to use (default /dev/spidev1.1)\n"
" -s --speed max speed (Hz)\n"
" -d --delay delay (usec)\n"
" -b --bpw bits per word \n"
" -l --loop loopback\n"
" -H --cpha clock phase\n"
" -O --cpol clock polarity\n"
" -L --lsb least significant bit first\n"
" -C --cs-high chip select active high\n"
" -3 --3wire SI/SO signals shared\n");
exit(1);
}
static void parse_opts(int argc, char *argv[])
{
while (1) {
static const struct option lopts[] = {
{ "device", 1, 0, 'D' },
{ "speed", 1, 0, 's' },
{ "delay", 1, 0, 'd' },
{ "bpw", 1, 0, 'b' },
{ "loop", 0, 0, 'l' },
{ "cpha", 0, 0, 'H' },
{ "cpol", 0, 0, 'O' },
{ "lsb", 0, 0, 'L' },
{ "cs-high", 0, 0, 'C' },
{ "3wire", 0, 0, '3' },
{ "no-cs", 0, 0, 'N' },
{ "ready", 0, 0, 'R' },
{ NULL, 0, 0, 0 },
};
int c;
c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "D:s:d:b:lHOLC3NR", lopts, NULL);
if (c == -1)
break;
switch (c) {
case 'D':
device = optarg;
break;
case 's':
speed = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'd':
delay = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'b':
bits = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'l':
mode |= SPI_LOOP;
break;
case 'H':
mode |= SPI_CPHA;
break;
case 'O':
mode |= SPI_CPOL;
break;
case 'L':
mode |= SPI_LSB_FIRST;
break;
case 'C':
mode |= SPI_CS_HIGH;
break;
case '3':
mode |= SPI_3WIRE;
break;
case 'N':
mode |= SPI_NO_CS;
break;
case 'R':
mode |= SPI_READY;
break;
default:
print_usage(argv[0]);
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret = 0;
int fd;
parse_opts(argc, argv);
fd = open(device, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
pabort("can't open device");
/*
* spi mode
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MODE, &mode);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set spi mode");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MODE, &mode);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get spi mode");
/*
* bits per word
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set bits per word");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_BITS_PER_WORD, &bits);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get bits per word");
/*
* max speed hz
*/
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_WR_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't set max speed hz");
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_RD_MAX_SPEED_HZ, &speed);
if (ret == -1)
pabort("can't get max speed hz");
printf("spi mode: %d\n", mode);
printf("bits per word: %d\n", bits);
printf("max speed: %d Hz (%d KHz)\n", speed, speed/1000);
transfer(fd);
close(fd);
return ret;
}
解析: 在main()函数中,设置完spi总线的相关参数后,调用transfer(fd)来传递参数。
transfer()函数的实现如下:
static void transfer(int fd)
{
int ret;
uint8_t tx[] = {
0x48, 0x45, 0x4C, 0x4C, 0x4F,
0x20,
0x57, 0x4F, 0x52, 0x4C, 0x44,
0x0A
};
uint8_t rx[ARRAY_SIZE(tx)] = {0, };
struct spi_ioc_transfer tr = {
.tx_buf = (unsigned long)tx,
.rx_buf = (unsigned long)rx,
.len = ARRAY_SIZE(tx),
.delay_usecs = delay,
.speed_hz = speed,
.bits_per_word = bits,
};
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
if (ret < 1)
pabort("can't send spi message");
/*
for (ret = 0; ret < ARRAY_SIZE(tx); ret++) {
if (!(ret % 6))
puts("");
printf("%.2X ", rx[ret]);
}
puts("");
*/
}
tx即为字符串,‘H'=0x48, ‘E'=0x45, ‘L'=0x4c, ‘L'=0x4c, ‘O'=0x4f, ' ‘=0x20, ‘W'=0x57, ‘O'=0x4f, ‘R'=0x52, ‘L'=0x4c, ‘D'=0x44, ‘\n'=0x0a.
实际传送则是调用:
ret = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(1), &tr);
有关它的解释如下:
SPI_IOC_MESSAGE gives userspace the equivalent of kernel spi_sync().
72 * Pass it an array of related transfers, they'll execute together.
73 * Each transfer may be half duplex (either direction) or full duplex.
74 *
75 * struct spi_ioc_transfer mesg[4];
76 * ...
77 * status = ioctl(fd, SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(4), mesg);
#define SPI_IOC_MESSAGE(N) _IOW(SPI_IOC_MAGIC, 0, char[SPI_MSGSIZE(N)])
调用完transfer()函数后,调用close()来关闭文件描述符。
Dec 28, 2013
Technology###Introduction
The detailed information could be seen as in :
http://www.eefocus.com/zhang700309/blog/13-08/296390_6c438.html
###Wiring:
Notice we use the interrupt 1.
 ###Code
###Code
#include <TimerOne.h>
#define S0 6 // Please notice the Pin's define
#define S1 5
#define S2 4
#define S3 2
#define OUT 3
int g_count = 0; // count the frequecy
int g_array[3]; // store the RGB value
int g_flag = 0; // filter of RGB queue
float g_SF[3]; // save the RGB Scale factor
// Init TSC230 and setting Frequency.
void TSC_Init()
{
pinMode(S0, OUTPUT);
pinMode(S1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(S2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(S3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(OUT, INPUT);
digitalWrite(S0, LOW); // OUTPUT FREQUENCY SCALING 2%
digitalWrite(S1, HIGH);
}
// Select the filter color
void TSC_FilterColor(int Level01, int Level02)
{
if(Level01 != 0)
Level01 = HIGH;
if(Level02 != 0)
Level02 = HIGH;
digitalWrite(S2, Level01);
digitalWrite(S3, Level02);
}
void TSC_Count()
{
g_count ++ ;
}
void TSC_Callback()
{
switch(g_flag)
{
case 0:
Serial.println("->WB Start");
TSC_WB(LOW, LOW); //Filter without Red
break;
case 1:
Serial.print("->Frequency R=");
Serial.println(g_count);
g_array[0] = g_count;
TSC_WB(HIGH, HIGH); //Filter without Green
break;
case 2:
Serial.print("->Frequency G=");
Serial.println(g_count);
g_array[1] = g_count;
TSC_WB(LOW, HIGH); //Filter without Blue
break;
case 3:
Serial.print("->Frequency B=");
Serial.println(g_count);
Serial.println("->WB End");
g_array[2] = g_count;
TSC_WB(HIGH, LOW); //Clear(no filter)
break;
default:
g_count = 0;
break;
}
}
void TSC_WB(int Level0, int Level1) //White Balance
{
g_count = 0;
g_flag ++;
TSC_FilterColor(Level0, Level1);
Timer1.setPeriod(1000000); // set 1s period
}
void setup()
{
TSC_Init();
Serial.begin(9600);
Timer1.initialize(); // defaulte is 1s
Timer1.attachInterrupt(TSC_Callback);
attachInterrupt(1, TSC_Count, RISING);
pinMode(8, OUTPUT);
pinMode(9, OUTPUT);
pinMode(10, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(8,HIGH);
digitalWrite(9,HIGH);
digitalWrite(10,HIGH);
delay(4000);
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
Serial.println(g_array[i]);
g_SF[0] = 255.0/ g_array[0]; //R Scale factor
g_SF[1] = 255.0/ g_array[1] ; //G Scale factor
g_SF[2] = 255.0/ g_array[2] ; //B Scale factor
Serial.println(g_SF[0]);
Serial.println(g_SF[1]);
Serial.println(g_SF[2]);
}
void loop()
{
g_flag = 0;
for(int i=0; i<3; i++)
Serial.println(int(g_array[i] * g_SF[i]));
if(((g_array[0]*g_SF[0])>(g_array[1]*g_SF[1])) && ((g_array[0]*g_SF[0])>(g_array[2]*g_SF[2])))
{
digitalWrite(8,HIGH);
digitalWrite(9,LOW);
digitalWrite(10,LOW);
}
else if(((g_array[1]*g_SF[1])>(g_array[0]*g_SF[0])) && ((g_array[1]*g_SF[1])>(g_array[2]*g_SF[2])))
{
digitalWrite(8,LOW);
digitalWrite(9,HIGH);
digitalWrite(10,LOW);
}
else if(((g_array[2]*g_SF[2])>(g_array[1]*g_SF[1])) && ((g_array[2]*g_SF[2])>(g_array[0]*g_SF[0])))
{
digitalWrite(8,LOW);
digitalWrite(9,LOW);
digitalWrite(10,HIGH);
}
else
{
digitalWrite(8,LOW);
digitalWrite(9,LOW);
digitalWrite(10,LOW);
}
delay(4000);
}
###Effect
First, the program will caculate the RBG base value out.
If you put the sensor on a red object, red LED will be lighten, turn the sensor facing a green object, green LED will be lighten; blue object for blue LED.





 ###Code
###Code