Jul 3, 2014
TechnologyRecently I’ve set up a ticket system, OTRS, which uses smtp for sending out email. It works well in my virtual machine, and in my own server. But when deploying it onto the lab PC, it cannot send out email via smtp. Following is the solving procedure for this problem.
SMTP Server
When Login into the server, following is how to using smtp for sending out email.
$ telnet localhost 25
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to localhost.
Escape character is '^]'.
220 nxxxxx.xxx.fukcfuck-fugkock.com ESMTP Sendmail 8.14.5+Sun/8.13.3; Thu, 26 Jun 2014 06:43:37 -0500 (CDT)
ehlo localhost
250-nxxxxx.xxx.fukcfuck-fugkock.com Hello localhost [127.0.0.1], pleased to meet you
250-ENHANCEDSTATUSCODES
250-PIPELINING
250-EXPN
250-VERB
250-8BITMIME
250-SIZE
250-DSN
250-ETRN
250-DELIVERBY
250 HELP
mail from: kkkkk@xxxxxx.xx.fugkock.com
250 2.1.0 kkkkk@xxxxxx.xx.fugkock.com... Sender ok
rcpt to:xxx_xxx.mao@fukcfuck-fugkock.com
250 2.1.5 xxx_xxx.mao@fukcfuck-fugkock.com... Recipient ok
data
Subjet:354 Enter mail, end with "." on a line by itself
Hi,
Are you there?
regards,
Admin
.
250 2.0.0 s5QBhbEu014970 Message accepted for delivery
quit
221 2.0.0 xxxxxx.xxx.fukcfuck-fugkock.com closing connection
Connection to localhost closed by foreign host.
Error message
When sending out the /var/log/messages will record the failure message, like:
Jul 1 00:57:10 Linux01 OTRS-CGI-37[2757]: [Info][Kernel::System::CustomerUser::DB::CustomerUserAdd] CustomerUser: '9988@qq.com' created successfully (1)!
Jul 1 00:57:10 Linux01 OTRS-CGI-37[2757]: [Notice][Kernel::System::CustomerUser::DB::SetPassword] CustomerUser: '9988@qq.com' changed password successfully!
Jul 1 00:57:12 Linux01 OTRS-CGI-37[2757]: [Error][Kernel::System::Email::SMTP::Send][Line:139]: Can't send to '9988@qq.com': 5505.7.1 <9988@qq.com>... Relaying denied. IP name lookup failed [104.xxx.xxx.53]#012! Enable Net::SMTP debug for more info!
Jul 1 00:57:12 Linux01 OTRS-CGI-37[2757]: [Info][Kernel::System::Email::Send] Error sending message
It says the IP name lookup failed.
Bug Shooting
Use tcpdump for capturing the package, comparing to the normal package.
It indicates the message “IP name lookup failed [104.xxx.xxx.53]", so I guess this may caused by reverse refer of smtp server.
Use dnslookup for the correct record:
[Trusty@Linux01 ~]$ nslookup 104.xxx.xxx.53
Server: 104.xxx.xxx.xxx
Address: 104.xxx.xxx.xxx#53
** server can't find 53.xxx.xxx.104.in-addr.arpa.: NXDOMAIN
=============================================================
[Trusty@Linux01 ~]$ nslookup 104.xxx.xxx.240
Server: 104.xxx.xxx.xxx
Address: 104.xxx.xxx.xxx#53
Non-authoritative answer:
240.xxx.xxx.104.in-addr.arpa name = xxxxxxxx.xx.fukcfuck-fugkock.com.
So the solution is quite clear: If we give 104.xxx.xxx.140 a name, we could easily reached this machine from smtp server, thus the problem may be solved.
Jul 3, 2014
TechnologyIn fact Joggler initially is released as a digital picture frame, but I turned it into a linux server. Now It’s time to turn this server back.
Change RunLevel
Edit the gdm.conf file:
# cat /etc/init/gdm.conf
# gdm - GNOME Display Manager
#
# The display manager service manages the X servers running on the
# system, providing login and auto-login services
description "GNOME Display Manager"
author "William Jon McCann <mccann@jhu.edu>"
start on ((filesystem
and runlevel [!06]
# Without 03, assume our default level is 03
#and runlevel [!03]
To known your default run level, type:
# runlevel
N 3
Then reboot the joggler, to see if you could get the gdm window.
Disable auto-logon via:
$ cat /etc/init/tty1.conf
respawn
#exec /sbin/mingetty -8 38400 tty1 Trusty -8 38400 tty1
exec /sbin/getty -8 38400 tty1
Install lightdm via:
$ sudo apt-get install lightdm
$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure lightdm
Enable auto-login to lightdm:
$ cat /etc/lightdm/lightdm.conf
[SeatDefaults]
autologin-user=Trusty
autologin-user-timeout=0
greeter-session=lightdm-gtk-greeter
user-session=xubuntu
Enable SlideShow
Find out the resolution via following command:
$ xrandr | grep '*'
800x480 60.0*
Install essential software:
$ sudo apt-get install feh
$ sudo apt-get install unclutter
In fact using feh is not good enough for setting the screenSaver, at last I use xscreensaver, it has a mode of glslideshow, you can specify your own directory.
Jun 29, 2014
TechnologyFirst get the source code from official website, and untar it via:
$ sudo tar xjvf otrs-3.3.8.tar.bz2 -C /opt/
$ cd /opt
$ sudo mv otrs-3.3.8/ otrs
Check the modules :
$ /opt/otrs/bin/otrs.CheckModules.pl
Install following packages:
$ sudo apt-get install liblwp-useragent-determined-perl libapache2-mod-perl2 libnet-dns-perl libnet-smtp-ssl-perl libnet-smtp-tls-butmaintained-perl libyaml-perl
$ sudo apt-get install libgd-text-perl libjson-xs-perl libpdf-api2-perl libtext-csv-xs-perl libxml-parser-perl
Add corresponding users and group:
$ sudo useradd -d /opt/otrs/ -c 'OTRS user' otrs
$ sudo usermod -G www-data otrs
Create the OTRS Config Files:
$ pwd
/opt/otrs
$ sudo cp Kernel/Config.pm.dist Kernel/Config.pm
$ sudo cp Kernel/Config/GenericAgent.pm.dist Kernel/Config/GenericAgent.pm
Check dependencies via:
$ perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/index.pl
/opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/index.pl syntax OK
$ perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/customer.pl
/opt/otrs/bin/cgi-bin/customer.pl syntax OK
$ perl -cw /opt/otrs/bin/otrs.PostMaster.pl
/opt/otrs/bin/otrs.PostMaster.pl syntax OK
Set permission:
$ sudo bin/otrs.SetPermissions.pl --otrs-user=otrs --web-user=www-data --otrs-group=www-data --web-group=www-data /opt/otrs
Now Set the conf file for apache2:
$ sudo cp /opt/otrs/scripts/apache2-httpd.include.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/otrs
$ sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/otrs.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/otrs
$ sudo a2ensite otrs
$ sudo service apache2 restart
Now go to following URL for installation:
http://joggler.xxx.xxx..com/otrs/installer.pl
After installation, restart mysql and httpd, or you will meet OTRS - Access denied for user otrs@localhost
Add crontab tasks via following commands:
# su otrs
$ cd /opt/otrs/var/cron
$ pwd
/opt/otrs/var/cron
$ for foo in *.dist; do cp $foo `basename $foo .dist`; done
$ /opt/otrs/bin/Cron.sh start
/opt/otrs/var/cron
Cron.sh - start/stop OTRS cronjobs
Copyright (C) 2001-2012 OTRS AG, http://otrs.org/
(using /opt/otrs) done
$ crontab -l
Now everything goes OK, visit joggler.xxx.xxx..com/otrs/customer.pl for visit the customer panel.
Change the password for root@localhost:
# ./otrs.SetPassword.pl root@localhost PLATFORM
Set password for user 'root@localhost'.
Done.
Jun 28, 2014
TechnologyPrerequisite
Install following Packages under CentOS:
$ sudo yum install wget mysql-server mysql php-mysql httpd perl-URI perl-Net-DNS perl-IO-Socket-SSL perl-XML-Parser mod_perl perl-TimeDate perl-Net-DNS procmail perl perl-LDAP perl-Crypt-SSLeay
Now configure the mysqld via:
$ sudo chkconfig --levels 235 mysqld on
$ sudo service mysqld start
$ sudo /usr/bin/mysql_secure_installation
$ sudo chkconfig --levels 235 httpd on
Install otrs
Download the otrs from Official website, I downloaed the rpm package for CentOS, then install it via:
sudo rpm -ivh otrs-3.3.8-01.noarch.rpm
As root do following:
# cd /etc/httpd/conf.d/
# cp zzz_otrs.conf otrs.conf
# service httpd start
We have to disable SELinux and delete all of the iptables rules:
Close the SELinux via:
# cat /etc/sysconfig/selinux
# This file controls the state of SELinux on the system.
# SELINUX= can take one of these three values:
# enforcing - SELinux security policy is enforced.
# permissive - SELinux prints warnings instead of enforcing.
# disabled - SELinux is fully disabled.
# SELINUX=permissive
SELINUX=disabled
If you don’t disable SELINUX, then you may meet following error message:
消息: Kernel/Config.pm isn't writable!
If you want to use the installer, set the Kernel/Config.pm writable for the webserver user!
After disable the SELINUX, Restart the computer.
Flush all of the pre-defined iptables rules:
# iptables -F
# service iptables save
Now open the browser visit:
http://Your_Server/ostr/installer.pl
When Configurating the database, in the second step, the machine should be selected as localhost.
If you want to delete the otrs database, or if the installation step tells you otrs database exists, you can using following command for drop this database:
[root@CentOS conf.d]# mysqladmin -u root -p drop otrs
Enter password:
Dropping the database is potentially a very bad thing to do.
Any data stored in the database will be destroyed.
Do you really want to drop the 'otrs' database [y/N] y
Database "otrs" dropped
Configuration of otrs
The start page at:
http://Your_Machine/otrs/index.pl
Customer Start page:
http://Your_Machine/otrs/customer.pl
Enable the crons tasks(mandantory):
$ su root
# su -m otrs -c 'cd /opt/otrs/bin/ && ./Cron.sh start'
# crontab -l -u otrs
Add dynamic field via:
系统管理->工单设置->动态字段, at the field of “工单”, click it and then you can add the customized field. This will affect customer’s submitted ticket forms.
Change smtp configuration:
系统管理->系统配置-> 搜索smtp, you will meet Core::Sendmail, define the corresponding field and types, then you can use smtp for sending emails.
Uninstall otrs
Finally the team didn’t use otrs, but its email annoyed me for a long time. Finally I found it’s this machine who runs otrs. so I just login to 53, and run:
# rpm -e otrs
Also remove the crontab jobs and etc.
# su -m otrs
bash: /root/.bashrc: Permission denied
bash-4.1$ ./Cron.sh stop
/opt/otrs/bin
Cron.sh - start/stop OTRS cronjobs
Copyright (C) 2001-2012 OTRS AG, http://otrs.org/
done
[root@Linux01 conf.d]# crontab -l -u otrs
no crontab for otrs
Also remove the configuration file under /etc/httpd/conf.d/otrs.conf, then restart the httpd server.
Jun 24, 2014
TechnologySince I got several Intel powered PC, It’s is essential to know how graphics card works, thus I could get the fastest performance of my PC or Server.
Detect Graphics Card
Use lspci we could get the output of all PCI equipments, get the VGA related information via:
$ lspci | grep VGA
00:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller (rev 09)
To know the detailed information of this equipment:
$ lspci -v -s 00:02.0
00:02.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller (rev 09) (prog-if 00 [VGA controller])
Subsystem: Hewlett-Packard Company Device 161c
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 57
Memory at d4000000 (64-bit, non-prefetchable) [size=4M]
Memory at c0000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=256M]
I/O ports at 4000 [size=64]
Expansion ROM at <unassigned> [disabled]
Capabilities: <access denied>
Kernel driver in use: i915
Kernel modules: i915
Memory at c0000000 (64-bit, prefetchable) [size=256M] shows the Intel Video Card with 256MB of video RAM. Or you can get the detailed via : sudo lspci -v | more.
If you want the graphic ways, simply install following tool:
$ sudo pacman -S hardinfo
$ hardinfo
The picture shows as following:
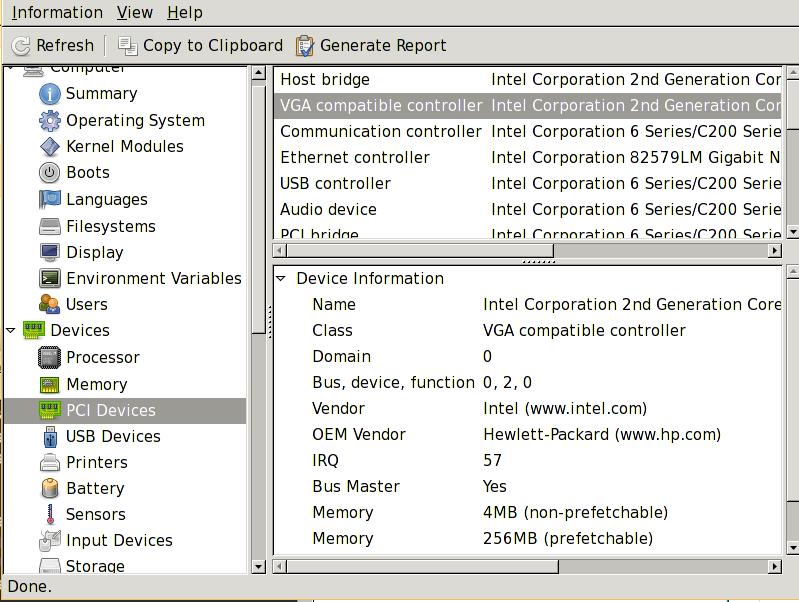
lshw could also shows the result:
$ sudo lshw -class display
*-display
description: VGA compatible controller
product: 2nd Generation Core Processor Family Integrated Graphics Controller
vendor: Intel Corporation
physical id: 2
bus info: pci@0000:00:02.0
version: 09
width: 64 bits
clock: 33MHz
capabilities: msi pm vga_controller bus_master cap_list rom
configuration: driver=i915 latency=0
resources: irq:57 memory:d4000000-d43fffff memory:c0000000-cfffffff ioport:4000(size=64)
Get the config from Intel Doc
Refer to following link:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_Intel_graphics_processing_units, for example, My cpu is Intel(R) Core(TM) i5-2520M , then find the “Core i5-2xxxM”, it shows the graphic card is HD Graphics 3000.
Install driver:
$ sudo pacman -S xf86-video-intel
32-bit 3D Support:
$ sudo pacman -S lib32-intel-dri

