Jan 26, 2024
Technology准备Img文件:
$ wget https://mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/raspberry-pi-os-images/raspios_lite_arm64/images/raspios_lite_arm64-2023-12-11/2023-12-11-raspios-bookworm-arm64-lite.img.xz
$ unxz 2023-12-11-raspios-bookworm-arm64-lite.img.xz
$ ls
2023-12-11-raspios-bookworm-arm64-lite.img
以准备好的img文件设置loop挂载点, 而后检查挂载点:
$ sudo losetup -fP --show 2023-12-11-raspios-bookworm-arm64-lite.img
/dev/loop17
$ sudo fdisk -l /dev/loop17
Disk /dev/loop17: 2.55 GiB, 2738880512 bytes, 5349376 sectors
Units: sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disklabel type: dos
Disk identifier: 0x4e639091
Device Boot Start End Sectors Size Id Type
/dev/loop17p1 8192 1056767 1048576 512M c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
/dev/loop17p2 1056768 5349375 4292608 2G 83 Linux
将/dev/loop17p2分区挂载到/mnt9后,而后透传给容器:
$ sudo mount /dev/loop17p2 /mnt9/
$ sudo docker run -it -v /mnt9:/raspbian rockylinux:9 bash
在容器中检查/raspbian挂载点所在的位置,分区大小为2G:
[root@34e78094dace /]# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
overlay 1.8T 1.5T 259G 86% /
tmpfs 64M 0 64M 0% /dev
shm 64M 0 64M 0% /dev/shm
/dev/loop17p2 2.0G 1.6G 330M 83% /raspbian
/dev/nvme0n1p2 1.8T 1.5T 259G 86% /etc/hosts
tmpfs 63G 0 63G 0% /proc/asound
tmpfs 63G 0 63G 0% /proc/acpi
tmpfs 63G 0 63G 0% /proc/scsi
tmpfs 63G 0 63G 0% /sys/firmware
Jan 19, 2024
TechnologyHost Preparation
Edit grub configuration:
# vim /etc/default/grub
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash intel_iommu=on iommu=pt"
# update-grub
Edit vfio items:
# vim /etc/modprobe.d/vfio.conf
options vfio-pci ids=10de:2508
Edit initramfs items:
# vim /etc/initramfs-tools/modules
vfio
vfio_iommu_type1
vfio_pci
vfio_virqfd
Bios configuration, disable igpu, and select PEG:
PEG is technically just "PCI Express Graphics" your 16x lane slot to the CPU.
Add kvm items:
# vim /etc/modprobe.d/kvm.conf
options kvm ignore_msrs=1
Get the device via devicehunt.com:
GA106 [GeForce RTX 3050 OEM]
Type Information
ID 2508
Vendor Details
NVIDIA Corporation
Type Information
ID 10DE
Use gpu-z under windows to fetch the rom.
Edit the file using bless under linux, find 55AA:
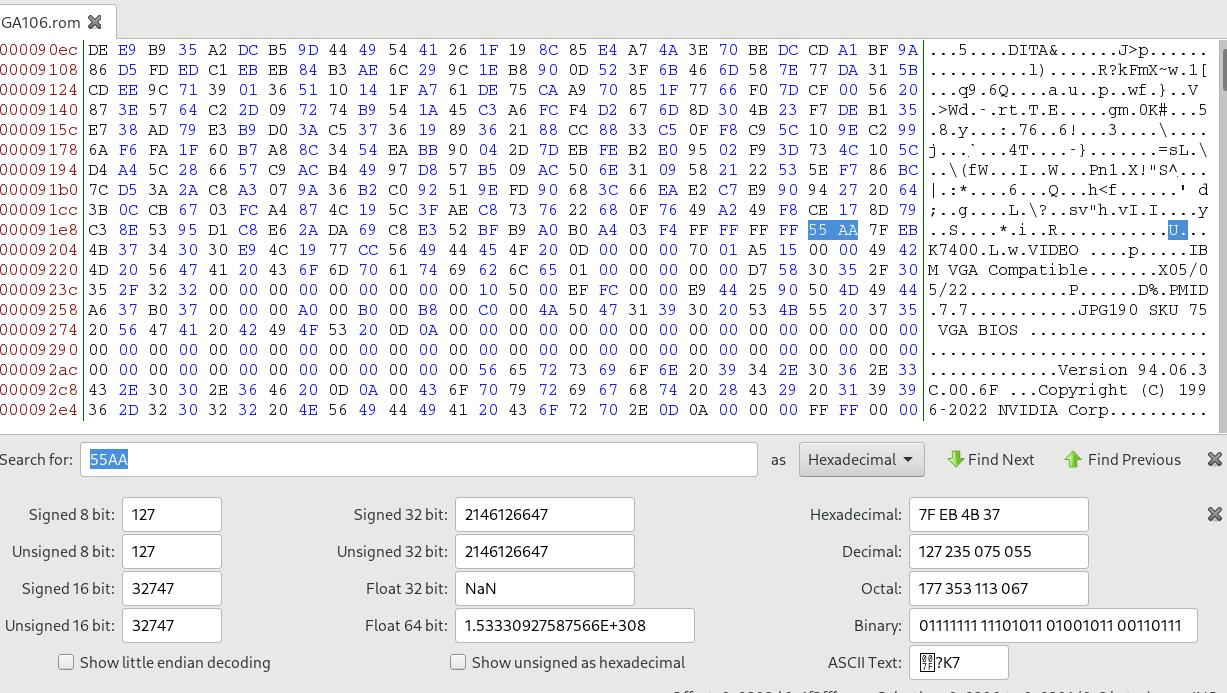
Delete everything before this 55AA :
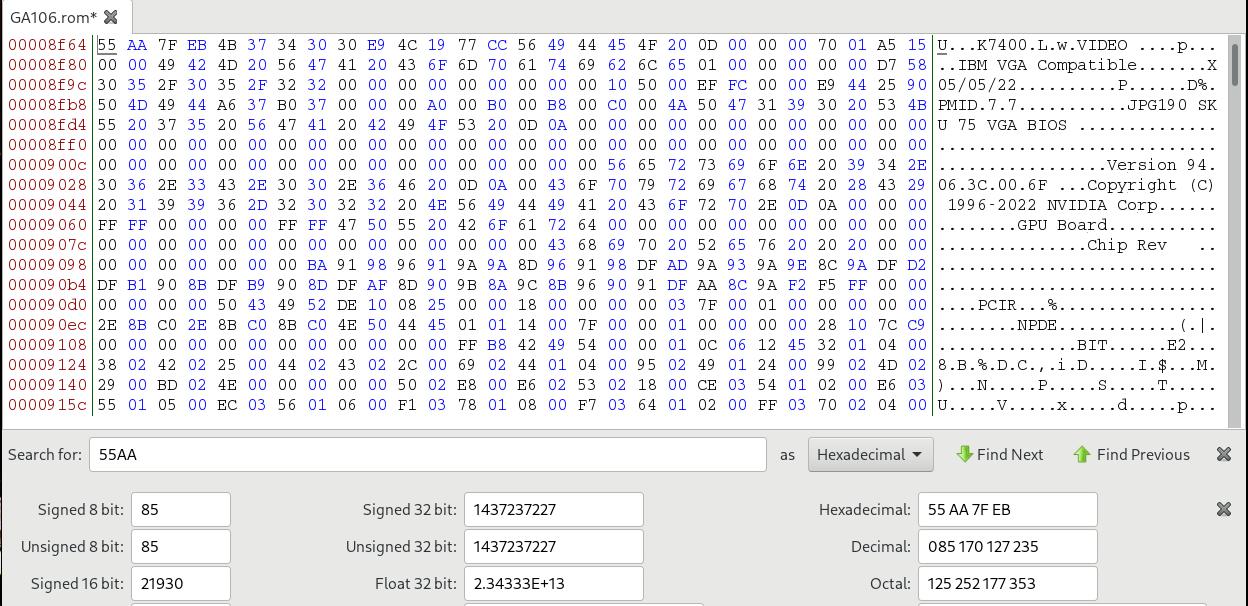
Create the qcow2, specify its backup file:
qemu-img create -f qcow2 -b win10_pure_with_rdp_open.qcow2 -F qcow2 win10_nvidia_3050.qcow2
Create the machine:
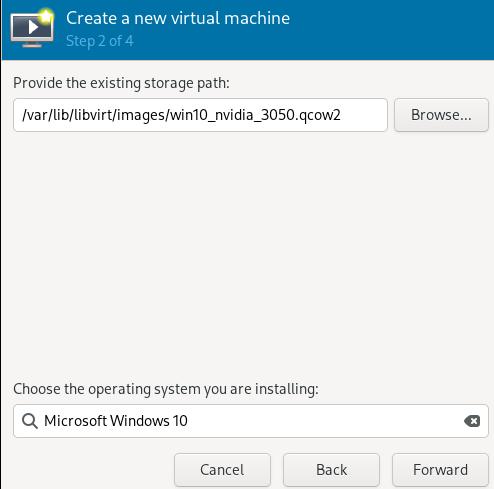
Specify its cpus and memory:
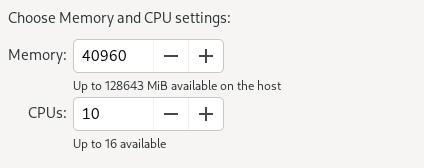
Specify its name:
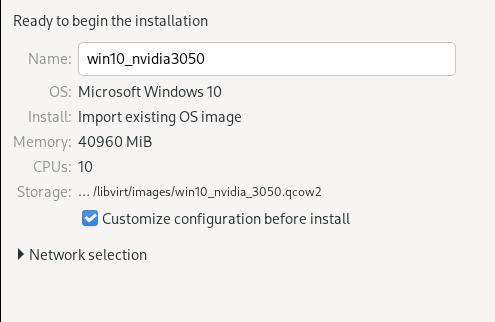
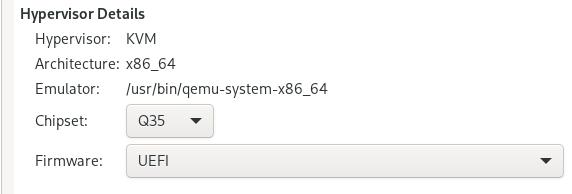
Custom its chipset and firmware:
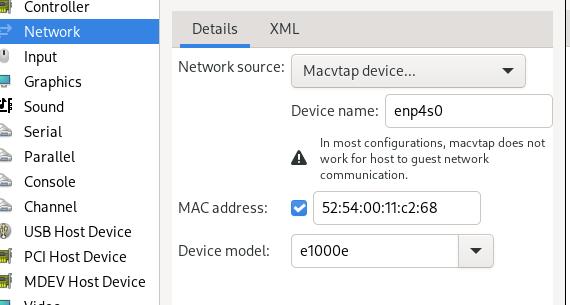
Add a new network(macvtap) for rdp:
Using qxl and spice for verifying its working, then add nvidia 3050.
Adding GPU items
Getting the gpu card related:
$ sudo lspci -nn | grep 03:00
03:00.0 VGA compatible controller [0300]: NVIDIA Corporation Device [10de:2508] (rev a1)
03:00.1 Audio device [0403]: NVIDIA Corporation Device [10de:228e] (rev a1)
Verify its iommu groups:
$ for a in /sys/kernel/iommu_groups/*; do find $a -type l; done | sort --version-sort
......
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/14/devices/0000:03:00.0
/sys/kernel/iommu_groups/14/devices/0000:03:00.1
......
Edit the grub parameters:
GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="quiet splash intel_iommu=on iommu=pt kvm.ignore_msrs=1 vfio-pci.ids=10de:2508,10de:228e"
update grub then reboot. verify kernel driver in use via:
# lspci -kn | grep -A 2 03:00
03:00.0 0300: 10de:2508 (rev a1)
Subsystem: 1028:c97c
Kernel driver in use: vfio-pci
--
03:00.1 0403: 10de:228e (rev a1)
Subsystem: 1028:c97c
Kernel driver in use: vfio-pci
Add the pci devices :
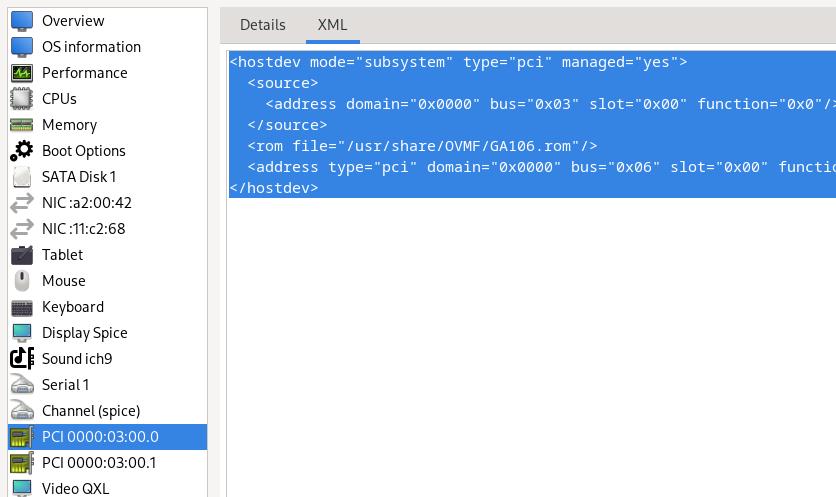
The modified content is listed as :
<hostdev mode="subsystem" type="pci" managed="yes">
<source>
<address domain="0x0000" bus="0x03" slot="0x00" function="0x0"/>
</source>
<rom file="/usr/share/OVMF/GA106.rom"/>
<address type="pci" domain="0x0000" bus="0x06" slot="0x00" function="0x0" multifunction="on"/>
</hostdev>
将显卡从第二槽位到第一槽位,解决了vfio问题。
添加usb设备:

去掉qxl及spice, 只使用实际的物理显卡设备来进行测试. 成功,但是uefi启动的时候无tiano core的画面。
Jan 16, 2024
TechnologyCreate a profile named bridgeprofile:
$ lxc profile create bridgeprofile
$ lxc profile show bridgeprofile
config: {}
description: Bridged networking LXD profile
devices:
eth0:
name: eth0
nictype: bridged
parent: br0
type: nic
name: bridgeprofile
Steps:
$ cat bridge
config: {}
description: Bridged networking LXD profile
devices:
eth0:
name: eth0
nictype: bridged
parent: br0
type: nic
name: bridgeprofile
$ cat bridge | lxc profile edit bridgeprofile
Then create a lxc named distcc:
$ lxc launch -p default -p bridgeprofile ubuntu:22.04 distcc
Edit the netplan confguration in lxc instance(distcc):
root@distcc:~# cat /etc/netplan/50-cloud-init.yaml
network:
version: 2
ethernets:
eth0:
dhcp4: false
addresses: [192.168.1.9/24]
gateway4: 192.168.1.33
root@distcc:~# netplan
Install distcc via:
apt install -y distcc build-essential
Configure the distcc:
STARTDISTCC="true"
ALLOWEDNETS="192.168.1.0/24"
LISTENER="0.0.0.0"
JOBS="12"
Jan 16, 2024
Technologybuild steps for building libvirt on ubuntu18.04:
275 tar xJvf libvirt-8.0.0.tar.xz
276 cd libvirt-8.0.0/
277 ls
278 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
279 apt-cache search xsltproc
280 sudo apt install -y xsltproc
281 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
282 apt-cache search rst2html
283 apt-cache search rst
284 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
285 sudo apt-get install python3-docutils
286 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
287 apt-cache search libtirpc
288 sudo apt install -y libtirpc-dev
289 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
290 apt-cache search gnutls
291 sudo apt install -y libgnutls28-dev
292 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
293 apt-cache search libxml-2.0
294 apt-cache search libxml
295 sudo apt install -y libxml2-dev
296 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
297 apt-cache search pciaccess
298 sudo apt install -y libpciaccess-dev
299 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
300 apt-cache search YAJL
301 sudo apt install -y libyajl-dev
302 meson build -Dsystem=true -Ddriver_qemu=enabled -Ddriver_interface=enabled -Ddriver_libvirtd=enabled -Ddriver_remote=enabled -Ddriver_network=enabled --prefix=/usr
303 history
Jan 15, 2024
TechnologyTips
crontab items:
@reboot /usr/bin/execpipe.sh
execpipe content:
$ cat /usr/bin/execpipe.sh
#!/bin/bash
while true; do eval "$(cat /mypipe)" &> /mypipeoutput.txt;done
#while true; do eval "$(cat /mypipe)";done
Create the pipe via:
$ ls / | grep mypipe
mypipe
mypipeoutput.txt
Kernel Building(VB)
Build the kernel via:
apt install -y git fakeroot build-essential ncurses-dev xz-utils libssl-dev bc flex libelf-dev bison rsync kmod cpio unzip
unzip kernel-config.zip
cp kernel-config/x86_64_defconfig .config
./scripts/config --disable DEBUG_INFO
echo "" | make ARCH=x86_64 olddefconfig
make ARCH=x86_64 -j16 LOCALVERSION=-lts2021-iotg bindeb-pkg
Kernel patch backport:
drivers/gpu/drm/i915/display/intel_fbc.c, line 1029, not equal to tc's implementation
/drivers/gpu/drm/i915# vim i915_driver.c, 存在较大不同











