Apr 6, 2016
TechnologySteps
Reconfigure the LC_ALL, etc:
$ sudo vim /etc/environment
LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8
LANG=en_US.UTF-8
$ sudo locale-gen "en_US.UTF-8"
$ sudo dpkg-reconfigure locales
$ sudo reboot
Be Sure to use latest repository, like aliyun.com.
$ sudo apt-get update -y
$ sudo bash
# apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://p80.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-keys 58118E89F3A912897C070ADBF76221572C52609D
#
Trouble-Shooting
Docker download too slow, download it to local.
Apr 5, 2016
TechnologyIn Vagrantfile, edit the following definition:
config.vm.provider "virtualbox" do |vb|
# # Display the VirtualBox GUI when booting the machine
# vb.gui = true
#
# # Customize the amount of memory on the VM:
vb.memory = "1024"
file_to_disk = File.realpath( "." ).to_s + "/disk.vdi"
if ARGV[0] == "up" && ! File.exist?(file_to_disk)
puts "Creating 5GB disk #{file_to_disk}."
vb.customize [
'createhd',
'--filename', file_to_disk,
'--format', 'VDI',
'--size', 5000 * 1024 # 5 GB
]
vb.customize [
'storageattach', :id,
'--storagectl', 'SATA',
'--port', 1, '--device', 0,
'--type', 'hdd', '--medium',
file_to_disk
]
end
#config.vm.provision "shell", path: "scripts/add_new_disk.sh"
end
config.vm.provision "shell", path: "scripts/add_new_disk.sh"
The add_new_disk.sh should be written like following:
set -e
set -x
if [ -f /etc/disk_added_date ]
then
echo "disk already added so exiting."
exit 0
fi
sudo fdisk -u /dev/sdb <<EOF
n
p
1
t
8e
w
EOF
pvcreate /dev/sdb1
vgextend VolGroup /dev/sdb1
lvextend -l +100%FREE /dev/VolGroup/lv_root
resize2fs /dev/VolGroup/lv_root
date > /etc/disk_added_date
Notice: this won’t fit for Ubuntu Snappy Core.
Apr 1, 2016
Technology今天更新了一下代码,实现了两行显示,第一行显示CPU Load,第二行显示剩余内存数。
只是部分替代数据显示部分,这个代码还是有BUG的,譬如说最后一位在下一次显示时不会被清零。
import psutil
import serial
import time
# Setup the Serial Port and open it.
ser = serial.Serial()
ser.baudrate = 9600
ser.port = '/dev/ttyUSB0'
ser.open()
## Todo, to check if the port is opened.
# Really talks to the i2c LCD.
# Setup the wiring
ser.write(b'i2c.setup(0, 4, 3, i2c.SLOW)\r\n')
# dofile, load the lcd library
ser.write(b'lcd = dofile("lcd1602.lua")()\r\n')
# Now Refresh the LCD.
ser.write(b'lcd.clear()\r\n')
#ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.light(on))\r\n')
ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(0, 0), "CPU Load: ")\r\n')
ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(1, 0), "Mem Free: ")\r\n')
ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(0, 14), "%")\r\n')
ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(1, 14), "MB")\r\n')
# Fetching the percentage per 1 second
# Todo, change the while true into CTRL+C stopped.
while True:
# Get current percentage
#ser.write(b'lcd.clear()\r\n')
currentPer = str(psutil.cpu_percent()).encode('ascii')
memFree = str(int(psutil.virtual_memory().free/1024/1024)).encode('ascii')
oneLine = b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(0, 9), "' + currentPer + b'")\r\n'
SecondLine = b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(1, 9), "' + memFree + b'")\r\n'
# Format oneLine
#ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(0, 0), "CPU Load: ")\r\n')
#ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(1, 0), "Mem Free: ")\r\n')
#ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(0, 14), "%")\r\n')
#ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(1, 14), "MB")\r\n')
#time.sleep(0.2)
ser.write(oneLine)
time.sleep(0.2)
ser.write(SecondLine)
time.sleep(1)
Mar 31, 2016
Technology最初入手的1602是N个口的, 激活它需要耗掉开发板上N个GPIO口,为此做完Arduino上的实
验就收了起来. 这次采购中看到店家有卖1602 I2C的转接卡,3块钱,顺手就买了回来.打算
用来做一个WIFI显示屏.
今天做了一个NodeMCU和1602连接实时显示CPU使用率的方案, 如下图所示,这里简单记录
一下制作过程.
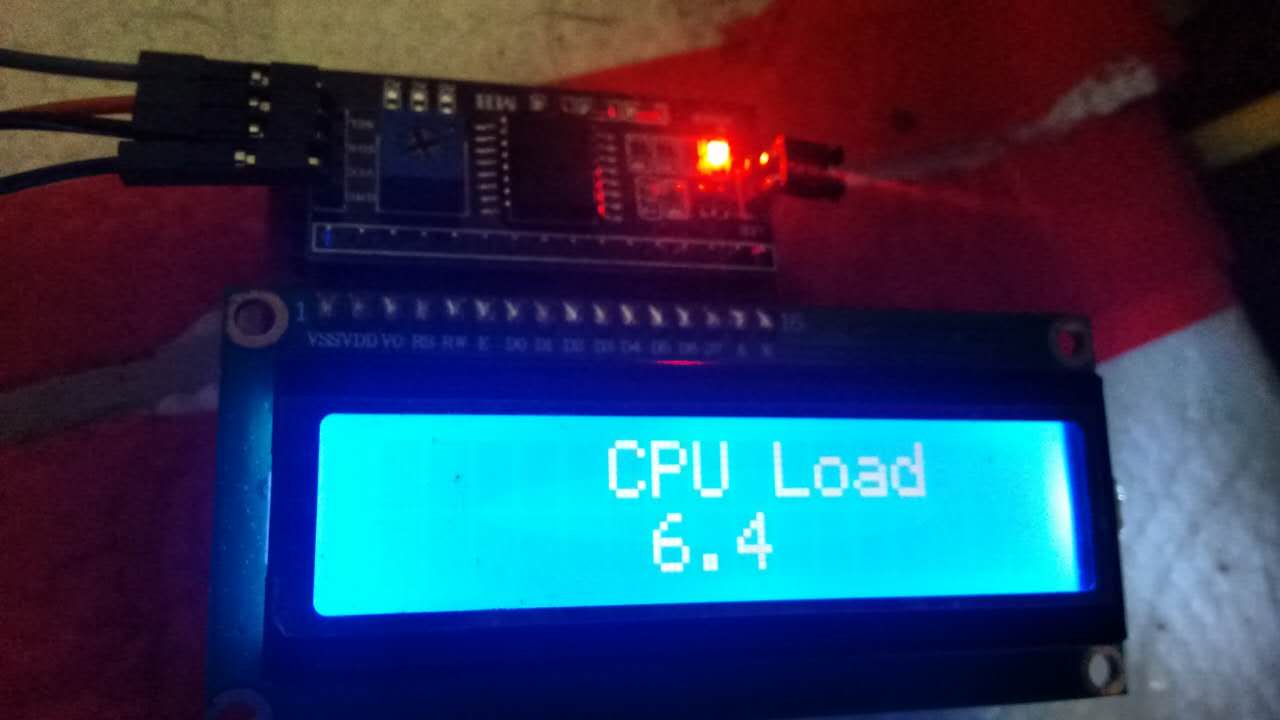
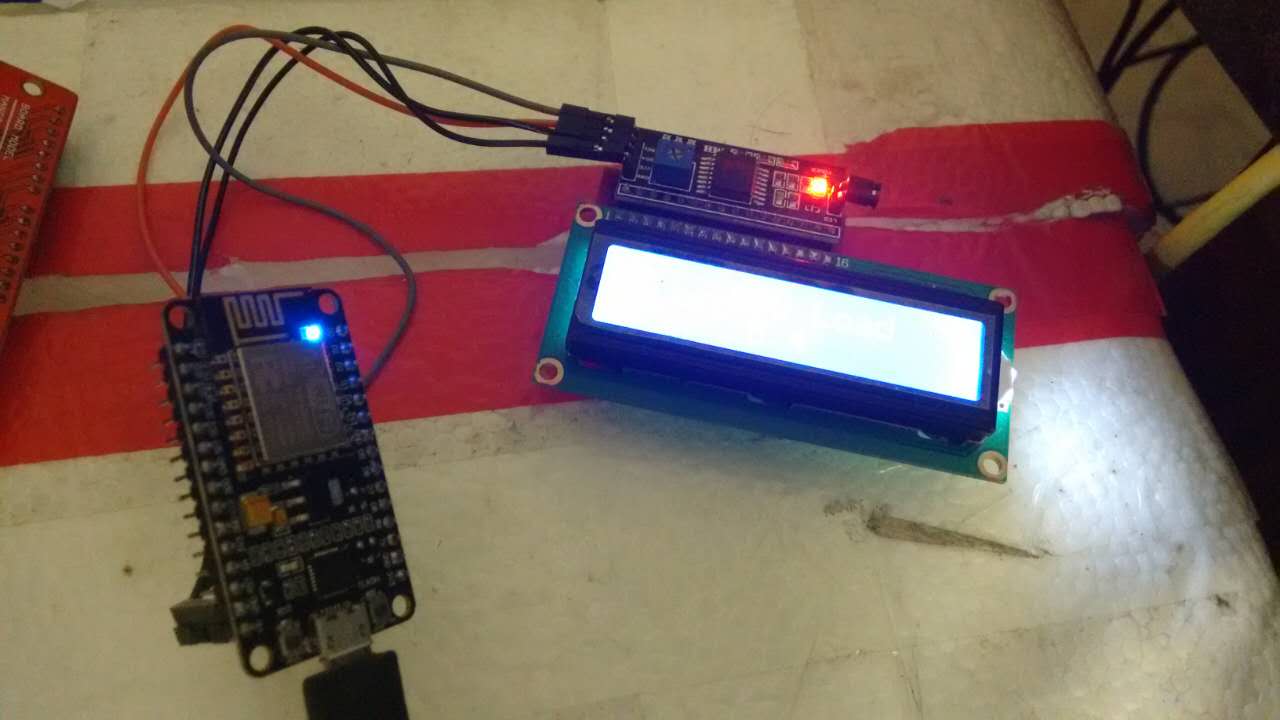
连线图
1602 I2C上有四个口,分别是GND/VCC/SDA/SCL.
GND自然不用多说,连接NodeMCU上的GND即可.
VCC我们使用5V输入,在NodeMCU上则是VIN口. 在下图里我用红色做了标注.
SDA接GPIO0, SDC接GPIO2,在图中我用橙色做了标识.
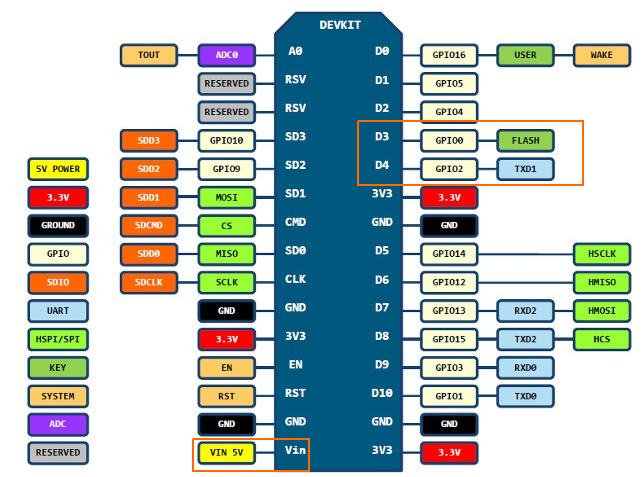
软件准备
我这里参考了
http://domoticx.com/esp8266-wifi-lcd-1602-2004-via-i2c-nodemcu/
上的实例, 所以用ESPlorer来写入1602的库文件. ESPlorer的下载地址在:
http://esp8266.ru/esplorer/#download
如果你使用的是ArchLinux的话,一行命令就够了:
$ yaourt esplorer
如果你运行上述网址上的示例, 故事的结尾你会获得一个Hallo的显示,以及跑马灯式的显
示效果.
CPU Load Program
先上代码, 用Python写的, 如果你看过上面的示例程序就会明白, 往串口写入1602的lua
脚本,就能获得对应的显示效果,那么以下的Python代码就是每分钟读取CPU的负载值, 将
它封装在一个字符串中发送到NodeMCU连接的串口.
import psutil
import serial
import time
# Setup the Serial Port and open it.
ser = serial.Serial()
ser.baudrate = 9600
ser.port = '/dev/ttyUSB0'
ser.open()
## Todo, to check if the port is opened.
# Really talks to the i2c LCD.
# Setup the wiring
ser.write(b'i2c.setup(0, 4, 3, i2c.SLOW)\r\n')
# dofile, load the lcd library
ser.write(b'lcd = dofile("lcd1602.lua")()\r\n')
# Now Refresh the LCD.
ser.write(b'lcd.clear()\r\n')
# Fetching the percentage per 1 second
# Todo, change the while true into CTRL+C stopped.
while True:
# Get current percentage
ser.write(b'lcd.clear()\r\n')
currentPer = str(psutil.cpu_percent()).encode('ascii')
# Format oneLine
ser.write(b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(0, 5), "CPU Load")\r\n')
oneLine = b'lcd.put(lcd.locate(1, 6), "' + currentPer + b'")\r\n'
# Write oneLine
ser.write(oneLine)
time.sleep(1)
代码运行的前提条件是,在ArchLinux上,安装pyserial库和psutil库,
而后运行sudo python WriteLoadToLCD.py.
$ sudo pacman -S python-psutil
$ sudo pacman -S python-pyserial
可以看到你的系统CPU使用率已经显示在1602 LCD上了,每分钟更新一次.
当然你也可以将显示
值从CPU使用率换成内存占用率,或是CPU温度,或是PM2.5的值等等. 你要做的就是构建自
己的数据CurrentPer和写入的格式oneLine.
通过串口发送数据, 通过NodeMCU驱动1602, 这功能对NodeMCU而言太小儿科了,所以接下
来我会继续做一个WIFI驱动的LCD.
Mar 29, 2016
TechnologyPrerequisition
Refers
tohttps://github.com/crashdump/collectd-xenserver
- Collected 4.9 or later
- Python2.4 Or Later
- sudo pip install XenAPI
- sudo pip install collectd
Configuration
Make a directory under /etc/collectd folder, and copy the
collectd-xenserver.py into this folder:
$ sudo mkdir -p /var/collectd/plugins
$ sudo cp YourDictory/collectd-xenserver.py /var/collectd/plugins/collectd_xenserver.py
Now edit the configuration file of /etc/collectd/collectd.conf:
<LoadPlugin python>
Globals true
</LoadPlugin>
<Plugin python>
ModulePath "/etc/collectd/plugins/"
#LogTraces true
#Interactive true
Import "collectd_xenserver"
<Module "collectd_xenserver">
<Host "192.168.10.187">
User "root"
Password "xxxxx"
</Host>
</Module>
</Plugin>
Now restart the collectd, you will find the data-set has been collectd and
send into the graphite server.
$ sudo service collectd restart



