Nov 30, 2016
Technology先决条件
启用aliyun CentOS源,安装工具:
$ yum install rpm-build --skip-broken
因为编译可能会占用大量硬盘空间,预先加载某个NFS卷:
# mount -t nfs 192.168.0.221:/xxxx /mnt
下载源码包:
错误!!! rpm-build安装失败。
不建议在xenserver上手动编译,上网搜索,找到collectd正确的源:
# vim /etc/yum.repos.d/collectd-ci.repo
[collectd-ci]
name=collectd CI
baseurl=http://pkg.ci.collectd.org/rpm/collectd-5.5/epel-5-$basearch
enabled=1
gpgkey=http://pkg.ci.collectd.org/pubkey.asc
gpgcheck=0
repo_gpgcheck=0
# yum remove collectd && yum install -y collectd
Trouble-Shooting
如果激活有其他源,则可能会因为优先级顺序,优先安装例如epel里的collectd-i386之类的包,
解决方案是将这些源全盘屏蔽。
[root@xenserver-WolfHunter yum.repos.d]# ls
back Citrix.repo collectd-ci.repo
Nov 30, 2016
TechnologyGenerate blog
Generate the static blog via:
# hugo --theme=hyde-a
Persist Volume
Define a pv:
$ vim blog.yaml
kind: PersistentVolume
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pvblog
labels:
type: local
spec:
capacity:
storage: 5Gi
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
hostPath:
path: "/data/hugoblog"
Create this pv:
$ kubectl create -f blog.yaml
persistentvolume "pvblog" created
Create a pv claim:
$ vim blogclaim.yaml
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: blogclaim
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 3Gi
Create this pv claim:
$ kubectl create -f ./blogclaim.yaml
persistentvolumeclaim "blogclaim" created
Examine the result:
$ kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESSMODES STATUS CLAIM REASON AGE
pvblog 5Gi RWO Bound default/blogclaim 4m
$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESSMODES AGE
blogclaim Bound pvblog 5Gi RWO 2m
Upload your blog website into /data/hugoblog.
Create a pod definition:
$ vim hugo.yaml
kind: Pod
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: hugoblog
labels:
name: hugoblog
spec:
containers:
- name: hugocontainer
image: nginx
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- containerPort: 80
name: "http-server"
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/usr/share/nginx/html"
name: pvblog
volumes:
- name: pvblog
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: blogclaim
Creat this pod via:
$ kubectl create -f hugo.yaml
pod "hugoblog" created
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hugoblog 1/1 Running 0 <invalid>
Expose service:
$ vim nginx.json
{
"kind": "Service",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "frontendservice"
},
"spec": {
"ports": [
{
"protocol": "TCP",
"port": 3000,
"targetPort": "http-server"
}
],
"type": "LoadBalancer",
"selector": {
"name": "hugoblog"
}
}
}
Creat the service via this json file:
$ kubectl create -f nginx.json
Get the service status, and access it via minikube command:
$ kubectl get service
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
frontendservice 10.0.0.217 <pending> 3000/TCP 2m
kubernetes 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 1d
$ minikube service frontendservice --url
http://192.168.99.101:31521
Open your browser and navigate to the corresponding url then you could get the
website running.
port-forward
Use following command, forward the local flows to pod:
$ kubectl port-forward hugoblog 8078:80
Now open your browser visit http://localhost:8078, then you could visit the
blog.
Nov 28, 2016
TechnologyInstallation
On Ubuntu16.04, first download the deb package from
https://github.com/kubernetes/minikube/releases
Install virtualbox:
$ sudo apt-get install -y virtualbox
$ sudo dpkg -i minikube_0.12-2.deb
$ which minikube-linux-amd64
/usr/bin/minikube-linux-amd64
Start Cluster
First install kubectl:
$ curl -Lo kubectl \
https://storage.googleapis.com/kubernetes-release/release/v1.3.0/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl \
&& chmod +x kubectl && sudo mv kubectl /usr/local/bin/
Start kubernetes cluster via:
$ minikube-linux-amd64 start
Starting local Kubernetes cluster...
Downloading Minikube ISO
36.00 MB / 36.00 MB [==============================================] 100.00%
0s
Kubectl is now configured to use the cluster.
Examine the result:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
kube-system kube-addon-manager-minikube 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 1m
Examine the status:
$ minikube-linux-amd64 status
minikubeVM: Running
localkube: Running
View add-on lists:
$ minikube addons list
- heapster: disabled
- ingress: disabled
- registry-creds: disabled
- addon-manager: enabled
- dashboard: enabled
- kube-dns: enabled
Trouble-Shooting:
When getting following error msgs, delete ~/.minikube and run minikube start again solves the problem.
~$ minikube start
Starting local Kubernetes cluster...
E0224 15:08:58.755236 7977 start.go:107] Error starting host: Error getting state for host: machine does not exist.
minikube upgrade
Upgrade minikube in ubuntu by installing the newest deb package.
Upgrade minikube in ArchLinux by yaourt -S minikube, then minikube start
will use the newest version.
Trouble-Shooting In Dashboard
When startup the dashboard, the minikube will complains could not find the endpoint:
$ minikube-linux-amd64 dashboard
Could not find finalized endpoint being pointed to by kubernetes-dashboard: Temporary Error: endpoints "kubernetes-dashboard" not found
Temporary Error: endpoints "kubernetes-dashboard" not found
Temporary Error: endpoints "kubernetes-dashboard" not found
Temporary Error: endpoints "kubernetes-dashboard" not found
Solved:
Get all of the pods in all namespaces:
$ kubectl get pods --all-namespaces
NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
default nginx-3449338310-vna7q 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 2h
kube-system kube-addon-manager-minikube 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3h
Get the description of the pod kube-addon-manager-minikube:
$ kubectl describe --namespace=kube-system po kube-addon-manager-minikube
Name: kube-addon-manager-minikube
Namespace: kube-system
Node: minikube/192.168.99.100
Start Time: Mon, 28 Nov 2016 12:17:40 +0800
Labels: component=kube-addon-manager
version=v5.1
Status: Pending
IP: 192.168.99.100
Controllers: <none>
Containers:
kube-addon-manager:
Container ID:
Image: gcr.io/google-containers/kube-addon-manager:v5.1
Image ID:
Port:
Requests:
cpu: 5m
memory: 50Mi
State: Waiting
Reason: ContainerCreating
Ready: False
Restart Count: 0
Environment Variables: <none>
Conditions:
Type Status
Initialized True
Ready False
PodScheduled True
Volumes:
addons:
Type: HostPath (bare host directory volume)
Path: /etc/kubernetes/
QoS Tier: Burstable
No events.
Then manually download the docker images of
gcr.io/google-containers/kube-addon-manager:v5.1, load it via following command:
$ eval $(minikube-linux-amd64 docker-env)
$ docker load<kubeaddonmanagerv51.tar.bz2
Also the default nginx-3449338310-vna7q is failed, use the same method for manually download
the pause image and load it into the docker system:
$ eval $(minikube-linux-amd64 docker-env)
$ docker load<kubepause30.tar.bz2
Also load the dns:
$ eval $(minikube-linux-amd64 docker-env)
$ docker load<kubedns18.tar.bz2
Wordpress Installation
Refers to :
https://www.linux-toys.com/?p=887
Download yaml file:
$ wget https://gist.githubusercontent.com/rusher81572/ddf2e1487b609f294b21a2463a8be104/raw/1ba33c7a2dfbef9118c6043030b76babb0a80c7b/wordpress-k8s -O wordpress.yaml
$ sudo docker pull rusher81572/phpfpm
$ sudo docker pull rusher81572/mysql
$ sudo docker pull rusher81572/nginx
Create the services from yaml file:
$ kubectl create -f wordpress.yaml
$ minikube-linux-amd64 service nginx --url
http://192.168.99.100:32400
Open the url in your browser:
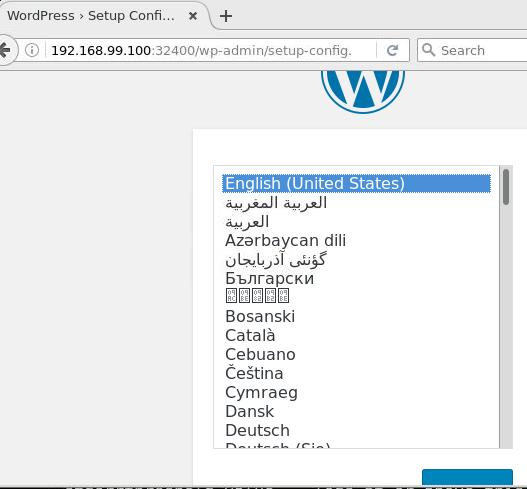
Manually create the database named wordpress:
$ kubectl get pods (To find the Mysql pod name)
$ kubectl exec -it mysql-qe900 bash
$ mysql
$ create database wordpress;
Insert the following items in webpage:
Username: root
Password: sql
Database Name: wordpress
Database Host: mysql
After installation, now refresh the webpage you will see the installed wordpress.
Echo Server
First download the image and load it into the minikube VM:
$ docker pull gcr.io/google_containers/echoserver:1.4
$ kubectl run hello-minikube --image=gcr.io/google_containers/echoserver:1.4 \
--hostport=8000 --port=8080
$ kubectl get pod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hello-minikube-3383150820-x72om 1/1 Running 0 1m
You could use kubectl describe pod hellxxxx for displaying the detailed
info.
Test echo server:
# curl $(minikube service hello-minikube --url) --data "param1=value1"
CLIENT VALUES:
client_address=172.17.0.1
command=POST
real path=/
query=nil
request_version=1.1
request_uri=http://192.168.99.101:8080/
SERVER VALUES:
server_version=nginx: 1.10.0 - lua: 10001
HEADERS RECEIVED:
accept=*/*
content-length=13
content-type=application/x-www-form-urlencoded
host=192.168.99.101:32520
user-agent=curl/7.51.0
BODY:
param1=value1%
Or use nmap for scan all of the ports:
$ nmap 192.168.99.101
Starting Nmap 7.31 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2016-11-28 22:09 CST
Nmap scan report for 192.168.99.101
Host is up (0.0043s latency).
Not shown: 996 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE
22/tcp open ssh
8000/tcp open http-alt
8443/tcp open https-alt
30000/tcp open ndmps
8000 port is the port listening for, testing this port:
$ curl http://192.168.99.101:8000 --data "param1=value1"
CLIENT VALUES:
client_address=192.168.99.1
command=POST
real path=/
query=nil
request_version=1.1
request_uri=http://192.168.99.101:8080/
SERVER VALUES:
server_version=nginx: 1.10.0 - lua: 10001
HEADERS RECEIVED:
accept=*/*
content-length=13
content-type=application/x-www-form-urlencoded
host=192.168.99.101:8000
user-agent=curl/7.51.0
BODY:
param1=value1%
Deployment Using dashboard
Specify the namespace:
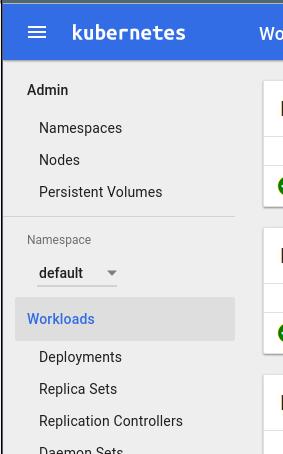
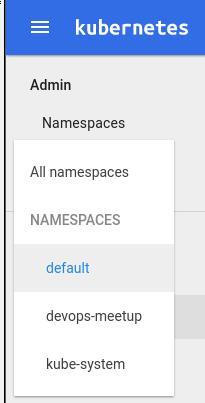
Create app name:
App name: hello-yang
Container Image: gcr.io/google_containers/echoserver:1.4
Number of pods: 5
Service: External
Port: 8080 Target port: 8080 Protocol: TCP
After deployment, examine the result via:
➜ ~ kubectl get namespace
NAME STATUS AGE
default Active 14h
devops-meetup Active 13h
kube-system Active 14h
➜ ~ kubectl get deployment --namespace="devops-meetup"
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
hello-yang 5 5 5 5 24m
Delete the deployment via:
# kubectl delete deployment hello-yang --namespace="devops-meetup"
deployment "hello-yang" deleted
Deployment Using yaml
Download the yaml file:
$ wget
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/master/examples/guestbook/all-in-one/guestbook-all-in-one.yaml
$ vim guestbook-all-in-one.yaml
# type: LoadBalancer
type: LoadBalancer
Create the service via:
$ kubectl create -f guestbook-all-in-one.yaml
Get the service and view the result:
➜ ~ kubectl get services
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
frontend 10.0.0.164 <pending> 80/TCP 15m
kubernetes 10.0.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 15h
redis-master 10.0.0.100 <none> 6379/TCP 15m
redis-slave 10.0.0.14 <none> 6379/TCP 15m
➜ ~ minikube service frontend --url
http://192.168.99.101:30640
Then open the browser and view the result.
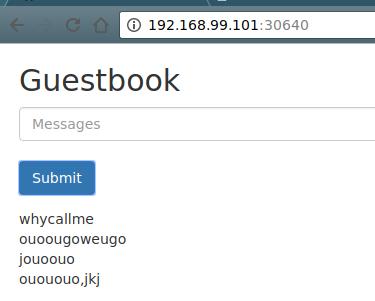
Tips
Login to minikube VM:
$ minikube-linux-amd64 ssh
View minikube dashboard URL:
$ minikube-linux-amd64 dashboard --url
http://192.168.99.100:30000
View minikube service URL:
$ minikube-linux-amd64 service nginx --url
http://192.168.99.100:32400
Delete pod in terminating status in force:
# kubectl delete pod mypod --grace-period=0
Using kubectl proxy:
$ kubectl proxy --port=8001
Starting to serve on localhost:8001
Now visit: http://localhost:8001/ui for accessing the dashboard.
wide output:
$ kubectl get pods -o wide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE
hugoblog 1/1 Running 2 22h 172.17.0.4 minikube
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
hugoblog 1/1 Running 2 22h
Create deployment command:
# kubectl run my-nginx --image=nginx --replicas=2 --port=808 --expose
so if you want to delete all of the pods, simply delete:
# kubectl delete deployments my-nginx
Prevent image pull in json definition files(take zookeeper.json for example):
$ cat zookeeper.json
{
"kind": "Pod",
"apiVersion": "v1",
"metadata": {
"name": "zookeeper",
"labels": {
"name": "zookeeper"
}
},
"spec": {
"containers": [
{
"name": "zookeeper",
"image": "mattf/zookeeper:latest",
"imagePullPolicy": "IfNotPresent",
Nov 26, 2016
Technology先决条件
CentOS 7.2 1511, Vagrant for kvm.
关闭selinux, 关闭firewalld, 使用以下命令安装docker最新版:
$ curl -sSL \
http://acs-public-mirror.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/docker-engine/internet |
\ sh -
IP地址配置:
master 192.168.0.223
node1 192.168.0.224
配置无密码登录,master到master, master到node1.
# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.0.223
# ssh-copy-id root@192.168.0.224
安装kubernetes
修改配置文件如下:
$ cat kubernetes/cluster/centos/config-default.sh
# Master配置
export MASTER=${MASTER:-"root@192.168.0.223"}
export MASTER_IP=${MASTER#*@}
# Minion节点配置
export NODES=${NODES:-"root@192.168.0.223 root@192.168.0.224"}
# Cluster中含有的节点数
export NUM_NODES=${NUM_NODES:-2}
# service cluster配置的IP地址范围
export SERVICE_CLUSTER_IP_RANGE=${SERVICE_CLUSTER_IP_RANGE:-"192.168.22.0/24"}
# flannel的overlay网络IP地址范围, 不能和上面定义的SERVICE_CLUSTER_IP_RANGE地址范围冲突
export FLANNEL_NET=${FLANNEL_NET:-"172.20.0.0/16"}
# Docker参数,这里我们开启daocloud加速模式
export DOCKER_OPTS=${DOCKER_OPTS:-"--cluster-store=etcd://$MASTER_IP:2379, --registry-mirror=http://1a653205.m.daocloud.io"}
开始部署kubernetes集群:
$ KUBERNETES_PROVIDER=centos ./kube-up.sh
安装完毕后,运行以下脚本,重新加载docker的配置后,重启两台机器:
$ sudo systemctl stop docker
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl start docker
重启完毕后,运行以下命令查看节点状态:
# kubectl get nodes
NAME STATUS AGE
192.168.0.223 Ready 10h
192.168.0.224 Ready 10h
加载两个docker镜像:
# docker images
gcr.io/google_containers/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64 v1.4.0
gcr.io/google_containers/pause-amd64 3.0
添加kubectl到系统路径中:
# cp cluster/centos/binaries/kubectl /opt/kubernetes/bin/
# vim ~/.bashrc
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/kubernetes/bin/
启动kubernetes UI
启动dashboard-controller服务和dashboard-service服务:
# cd ./cluster/gce/coreos/kube-manifests/addons/dashboard
# kubectl create -f dashboard-controller.yaml
# kubectl create -f dashboard-service.yaml
在node1上可以查看docker运行状态:
# docker ps
b22047f30d55 gcr.io/google_containers/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.4.0 "/dashboard --port=90"
8979b7b1db14 gcr.io/google_containers/pause-amd64:3.0 "/pause"
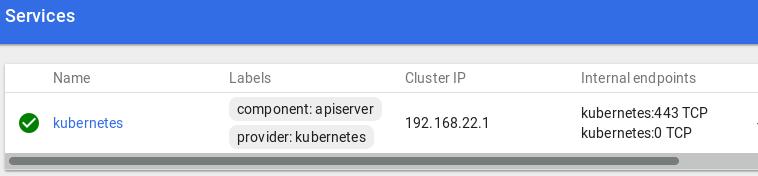
查看http://192.168.0.223:8080/ui,得到dashboard的网页.
service截图:
nginx服务
配置nginx-rc.yaml文件用于启动nginx服务:
$ vim nginx-rc.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ReplicationController
metadata:
name: nginx-controller
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
name: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- containerPort: 80
启动服务:
$ kubectl -s http://192.168.0.223:8080 create -f nginx-rc.yaml
检查创建的pods情况:
# kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
nginx-controller-1bx6j 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 13s
nginx-controller-attgh 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 13s
得到pod的运行情况:
# kubectl describe pod nginx-controller-1bx6j
Name: nginx-controller-1bx6j
Namespace: default
Node: 192.168.0.224/192.168.0.224
Start Time: Sat, 26 Nov 2016 14:08:33 +0000
Labels: name=nginx
Status: Running
IP: 172.20.99.3
Controllers: ReplicationController/nginx-controller
......
此刻可以在对应的节点上看到nginx的运行情况: curl 172.20.99.3在master节点上。
节点内可访问的nginx service
Service的type有ClusterIP和NodePort之分,缺省是ClusterIP,这种类型的Service
只能在集群内部访问。配置文件如下:
$ vim nginx-service-clusterip.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service-clusterip
spec:
ports:
- port: 8001
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
selector:
name: nginx
创建服务:
# kubectl create -f nginx-service-clusterip.yaml
查看创建出的service情况:
# kubectl get service
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes 192.168.22.1 <none> 443/TCP 34m
nginx-service-clusterip 192.168.22.189 <none> 8001/TCP 27s
访问节点内可访问的nginx service, 在master和node1上都可以访问到:
$ curl 192.168.22.189:8001
外部可访问的nginx服务
type为NodePort的为外部可访问的nginx服务,定义文件如下:
$ vim nginx-service-nodeport.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service-nodeport
spec:
ports:
- port: 8000
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
type: NodePort
selector:
name: nginx
运行kubectl create -f nginx-service-nodeport.yaml, 得到服务如下:
# kubectl get service
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes 192.168.22.1 <none> 443/TCP 58m
nginx-service-clusterip 192.168.22.189 <none> 8001/TCP 23m
nginx-service-nodeport 192.168.22.209 <nodes> 8000/TCP 2m
可以看到,新增加了一个nginx-service-nodeport的服务.
查看其端口,30923为其映射的端口号:
# kubectl describe service nginx-service-nodeport
Name: nginx-service-nodeport
Namespace: default
Labels: <none>
Selector: name=nginx
Type: NodePort
IP: 192.168.22.209
Port: <unset> 8000/TCP
NodePort: <unset> 30923/TCP
Endpoints: 172.20.62.2:80,172.20.99.3:80
Session Affinity: None
从外部(192.168.0.220)验证nginx服务:
# curl http://192.168.0.223:30923
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
删除服务
删除我们上面创建的基于nodeport的服务:
# kubectl delete -f ./nginx-service-nodeport.yaml
删除以后,检查service情况:
# kubectl get service
NAME CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
kubernetes 192.168.22.1 <none> 443/TCP 1h
nginx-service-clusterip 192.168.22.189 <none> 8001/TCP 55m
可以看到nginx-service-nodeport服务已经被删除。
指定端口
创建配置文件如下:
$ vim specifynode.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service-nodeport
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
nodePort: 30080
protocol: TCP
type: NodePort
selector:
name: nginx
创建服务:
$ kubectl create -f ./specifynode.yaml
现在访问http://192.168.0.223:30080即可访问到nginx服务.
注: 端口需要绑定在30000-32767.
Nov 24, 2016
TechnologyXenServer配置
XenServer 6.5
下载xscontainer iso并安装之:
# wget http://downloadns.citrix.com.edgesuite.net/10343/XenServer-6.5.0-SP1-xscontainer.iso
# xe-install-supplemental-pack XenServer-6.5.0-SP1-xscontainer.iso
XenServer 7.0
下载并安装:
# wget http://downloadns.citrix.com.edgesuite.net/11621/XenServer-7.0.0-xscontainer.iso
# xe-install-supplemental-pack XenServer-7.0.0-xscontainer.iso
guest虚拟机准备
安装docker:
$ curl -sSL http://acs-public-mirror.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/docker-engine/experimental/internet | sh
$ sudo usermod -aG docker
安装ncat/openssh-server(nmap中包含ncat):
$ sudo apt-get install -y openssh-server nmap
添加guest虚拟机
添加docker monitor:
# xscontainer-prepare-vm -v 05cd5c8f-eb32-86c6-b687-7a296180e3d3 -u dash
添加后的效果如下:






