RateLimitingOnInstio
May 1, 2018
Technology
Service Example
The yaml file is directly taken from the official example of helloworld, but
I remove the v2 deployment, thus the yaml file is listed as following:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: helloworld
labels:
app: helloworld
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- port: 5000
name: http
selector:
app: helloworld
---
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: helloworld-v1
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: helloworld
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- name: helloworld
image: istio/examples-helloworld-v1
resources:
requests:
cpu: "100m"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent #Always
ports:
- containerPort: 5000
Use istioctl for injecting the sidecar, thus we could later use prometheus for monitoring its traffic flow:
# kubectl create -f <(istioctl kube-inject -f helloworld.yaml)
Examine the deployment/service/pods:
# kubectl get svc helloworld
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
helloworld NodePort 10.96.242.5 <none> 5000:31241/TCP 27m
# kubectl get deployment helloworld-v1
NAME DESIRED CURRENT UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
helloworld-v1 1 1 1 1 27m
# kubectl get pods | grep helloworld
helloworld-v1-7d57446779-dctlv 2/2 Running 0 27m
Make ingress
The helloworld-ingress.yaml is listed as following:
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: helloworld
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: "istio"
spec:
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /hello
backend:
serviceName: helloworld
servicePort: 5000
Create the ingress and verify it:
# kubectl create -f helloworld-ingress.yaml
# kubectl get ingress helloworld
NAME HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
helloworld * 80 1h
# curl http://192.168.99.100:30039/hello
Hello version: v1, instance: helloworld-v1-7d57446779-dctlv
Rate Limiting
Write following rete limiting yaml for defining its traffic:
apiVersion: "config.istio.io/v1alpha2"
kind: memquota
metadata:
name: helloworldservicehandler
namespace: istio-system
spec:
quotas:
- name: helloworldservicerequestcount.quota.istio-system
maxAmount: 5000
validDuration: 1s
# The first matching override is applied.
# A requestcount instance is checked against override dimensions.
overrides:
# The following override applies to 'helloworld' regardless
# of the source.
- dimensions:
destination: helloworld
maxAmount: 2
validDuration: 1s
---
apiVersion: "config.istio.io/v1alpha2"
kind: quota
metadata:
name: helloworldservicerequestcount
namespace: istio-system
spec:
dimensions:
source: source.labels["app"] | source.service | "unknown"
sourceVersion: source.labels["version"] | "unknown"
destination: destination.labels["app"] | destination.service | "unknown"
destinationVersion: destination.labels["version"] | "unknown"
---
apiVersion: "config.istio.io/v1alpha2"
kind: rule
metadata:
name: helloworldservicequota
namespace: istio-system
spec:
actions:
- handler: helloworldservicehandler.memquota
instances:
- helloworldservicerequestcount.quota
---
apiVersion: config.istio.io/v1alpha2
kind: QuotaSpec
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: helloworldservicerequest-count
namespace: istio-system
spec:
rules:
- quotas:
- charge: 1
quota: RequestCount
---
apiVersion: config.istio.io/v1alpha2
kind: QuotaSpecBinding
metadata:
creationTimestamp: null
name: helloworldservicerequest-count
namespace: istio-system
spec:
quotaSpecs:
- name: helloworldservicerequest-count
namespace: istio-system
services:
- name: helloworld
namespace: default
The above items define a 2 qps rate limiting.
Monitoring
Use prometheus for monitoring the traffic, enable prometheus via:
# kubectl create -f ~/Code/istio-0.7.1/install/kubernetes/addons/prometheus.yaml
You could configure the prometheus’s service type to NodePort, thus you could directly access it.
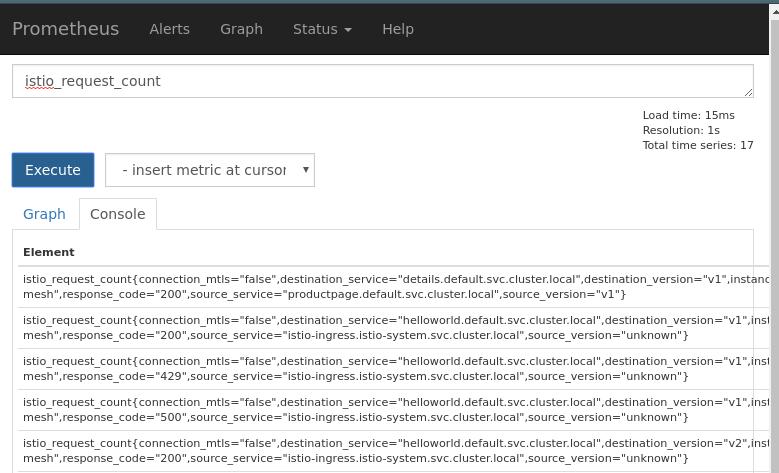
Make the traffic:
# while true; do curl -s -o /dev/null http://192.168.99.100:30039/hello;done
Then view the prometheus via following:
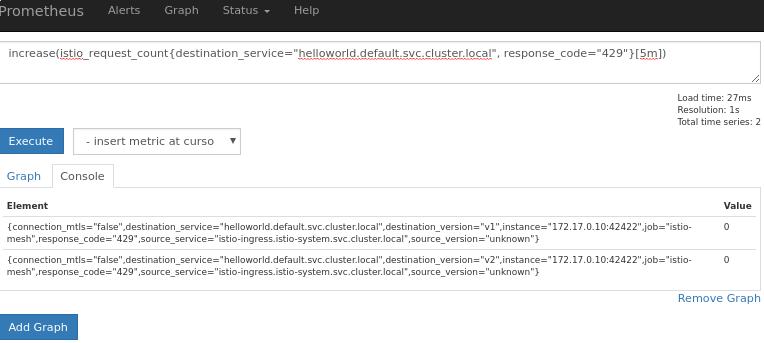
# increase(istio_request_count{destination_service="helloworld.default.svc.cluster.local", response_code="429"}[5m])
Initial:
After aboult 3 minutes:
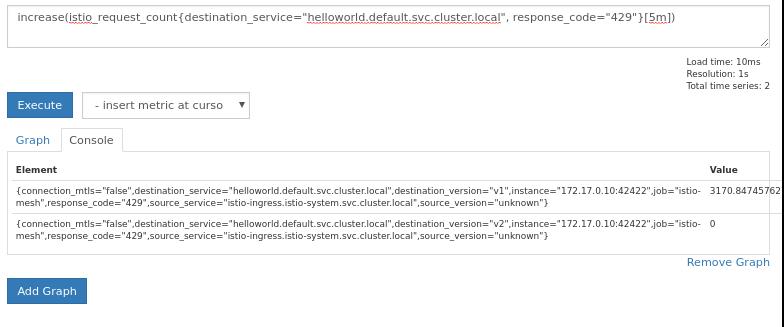
You could change the response code from 429 to 200, this means you get the
succeed rate.
Fetch back the result
Refers to:
https://www.robustperception.io/prometheus-query-results-as-csv/
# wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/RobustPerception/python_examples/master/csv/query_csv.py
For querying the 429/200:
# python query_csv.py http://127.0.0.1:9090 'increase(istio_request_count{destination_service="helloworld.default.svc.cluster.local", response_code="429"}[5m])'
name,timestamp,value,connection_mtls,destination_service,destination_version,instance,job,response_code,source_service,source_version
,1525185609.906,8145.762711864407,false,helloworld.default.svc.cluster.local,v1,172.17.0.10:42422,istio-mesh,429,istio-ingress.istio-system.svc.cluster.local,unknown
# python query_csv.py http://127.0.0.1:9090 'increase(istio_request_count{destination_service="helloworld.default.svc.cluster.local", response_code="200"}[5m])'
name,timestamp,value,connection_mtls,destination_service,destination_version,instance,job,response_code,source_service,source_version
,1525185628.005,886.7796610169491,false,helloworld.default.svc.cluster.local,v1,172.17.0.10:42422,istio-mesh,200,istio-ingress.istio-system.svc.cluster.local,unknown
8145 and 886 are the values for the query, we could use them for 2nd
development.
