LeetCodeTips1
Oct 9, 2016
Technology
又到了一年一度的跳Cao准备期间了,来刷刷LeetCode,提升一下编程技巧,准备可能的鄙视或者是 被鄙视。
1. Two Sum
问题:
给定一个整型数组,编写一函数,返回值为两个数组的下标,两个下标所在的数组元素相加的和为
给定的数值。例如:
给定 nums = [2,7,11,15], targe = 9,
因为nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
返回的数组应为[0, 1].
C语言版
用C语言我的解决方案如下:
/* Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
*
* Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
* return [0, 1].
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < numsSize; i++)
{
for(j = i+1; j < numsSize; j++)
{
if(nums[i] + nums[j] == target)
{
// Call malloc() for return value.
int* returnArray = malloc(2*sizeof(int));
returnArray[0] = i;
returnArray[1] = j;
return returnArray;
}
}
}
// Not found, comes here.
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
int nums[4] = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int *result = twoSum(nums, 4, 9);
if(result != NULL)
{
printf("result is %d, %d \n", result[0], result[1]);
}
// Call malloc in function twoSum(), so now will call free()
if(result != NULL)
{
free(result);
}
return 0;
}
心得1: malloc()/free()的调用需要在不同函数体中进行,因而可能存在内存泄漏的风险,使用 valgrind来检测可以看到,有两次请求两次释放动作,并没有内存泄漏:
$ valgrind -v --leak-check=full ./TwoSum
......
==3283== HEAP SUMMARY:
==3283== in use at exit: 0 bytes in 0 blocks
==3283== total heap usage: 2 allocs, 2 frees, 1,032 bytes allocated
==3283==
==3283== All heap blocks were freed -- no leaks are possible
==3283==
==3283== ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
==3283== ERROR SUMMARY: 0 errors from 0 contexts (suppressed: 0 from 0)
心得2: 算法复杂度为O(n^2), 因为有嵌套的for()循环. 官方给出的有通过哈希来做的,在C语言 中内建数据类型并不包括map,因而在后面用python来实现。
心得3: 对函数的返回值需要检测,如free()掉一个NULL的地址。StackOverFlow上关于free(NULL)
的讨论如下:
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/1938735/does-freeptr-where-ptr-is-null-corrupt-memory
看起来也不会有什么严重的后果。
Python版
自己写的Python版本实现如下:
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
returnvalue = []
for num in nums:
for left in nums[nums.index(num)+1:]:
if (num + left == target):
returnvalue.append(nums.index(num))
returnvalue.append(nums.index(left))
return returnvalue
print (Solution().twoSum([5, 4, 11, 17], 9))
心得1: 类(class)的用法.
心得2: 数组的一点点小小的使用。
基本逻辑和C语言实现的差不多,算法复杂度也一样。
引入的bug
设置的test case中,我们的代码在遇到[0,4,3,0]这样的输入时,会报错。原因在于nums.index(0) 总是返回第一个0所在的下标(0),而不是第二个0所在的下标(3),修改后的代码如下:
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
returnvalue = []
index = 0
for num in nums:
index += 1
for left in nums[index:]:
if (num + left == target):
returnvalue.append(nums.index(num))
returnvalue.append(nums[index:].index(left)+index)
return returnvalue
print (Solution().twoSum([0,4,3,0], 0))
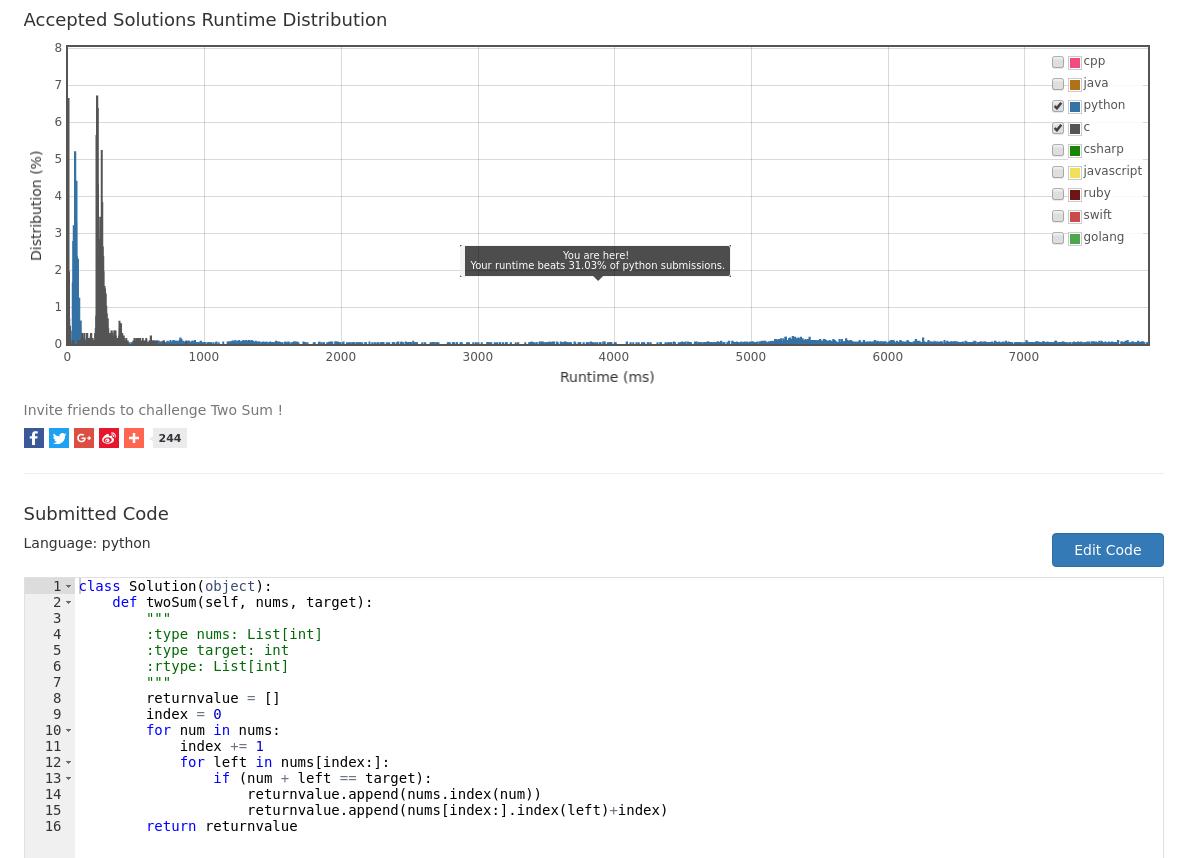
运行后的结果,不是那么理想,只击败了34%左右的提交结果:
Python Hash
经过几番修改以后的代码如下,只循环一次,因而算法复杂度为O(n):
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# Use a dictionary for holding nums
num_dic = {}
for i in range(len(nums)):
if target - nums[i] in num_dic.keys():
return [num_dic[target - nums[i]],i]
else:
# directly put it into the num_dic
num_dic[nums[i]] = i
return []
print (Solution().twoSum([0,4,3,0], 0))
print (Solution().twoSum([3, 4, 2], 6))
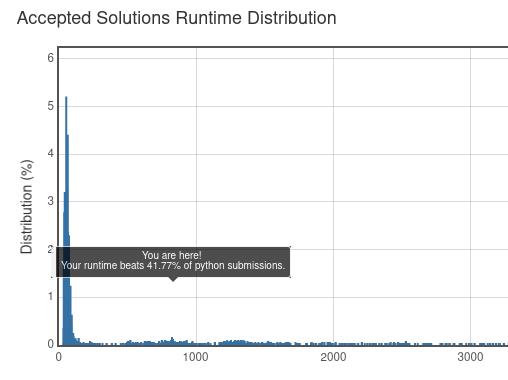
速度稍微提升了一些:
更好的方案,优化:
class Solution(object):
def twoSum(self, nums, target):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:type target: int
:rtype: List[int]
"""
# Use a dictionary for holding nums
num_dic = {}
for i,v in enumerate(nums):
if v in num_dic.keys():
return [num_dic[v],i]
num_dic[target-v] = i
print (Solution().twoSum([0,4,3,0], 0))
print (Solution().twoSum([3, 4, 2], 6))
这个代码大概能跑到击败80%左右的提交答案。
思考1: enumerate()函数调用减少了时间。
思考2: 原代码中有两次减法,而修改后的代码中,只是在写入hash的时候,有一次target-v的减法操作。
思考3: 去掉了一次不必要的return操作。
总结:
Python里对于这个问题的优化大概就到这里了。可以看到,简单的问题也是需要认真思考了,认认真真的来
做leetcode吧。
2. Add Two Numbers
题目说明:
给定两个用链表表示的非负数。数字存储是reverse order, 每个节点存有一个数字。将节点上的数字
相加,以得到一个新的链表
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Oct10晚上的测试框架写成这样:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Definition of the ListNode
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
};
// create_list()
struct ListNode* create_list(int val)
{
printf("\n Creating list with headnode as [%d]\n", val);
struct ListNode *ptr = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
if(NULL == ptr)
{
printf("\n Node creation failed \n");
return NULL;
}
ptr->val = val;
ptr->next = NULL;
return ptr;
}
// print the list
void print_list(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* current = head;
while(current != NULL)
{
printf("%d ->", current->val);
current = current->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
int shiftnumber = 0;
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
printf("\nJust Called this function!\n");
struct ListNode* currentl1 = l1;
struct ListNode* currentl2 = l2;
// Holding the return value
struct ListNode* ptr = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* head = ptr;
ptr->next = NULL;
shiftnumber = 0;
// First calculate the longest Linked List
int lenl1 = 0;
int lenl2 = 0;
while(currentl1 != NULL)
{
lenl1++;
currentl1 = currentl1->next;
}
while(currentl2 != NULL)
{
lenl2++;
currentl2 = currentl2->next;
}
printf("len1 is %d, len2 is %d\n", lenl1, lenl2);
currentl1 = l1;
currentl2 = l2;
// Get the largest length, thus we could do some tricks.
//
//
//
//
//
while((currentl1 != NULL) && (currentl2 != NULL))
{
ptr->val = (currentl1->val + currentl2->val)%10+shiftnumber;
shiftnumber = 0;
if((currentl1->val + currentl2->val)>=10)
{
shiftnumber = (currentl1->val + currentl2->val)/10;
}
//ptr->val = (currentl1->val + currentl2->val)%10;
if(currentl1->next != NULL)
{
ptr->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
ptr->next->next = NULL;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
// shiftnumber exists, so you should assign shiftnumber to the
// newnode
else
{
// Only check shiftnumber
if(shiftnumber != 0)
{
ptr->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
ptr->next->next = NULL;
ptr->next->val = shiftnumber;
}
}
currentl1 = currentl1->next;
currentl2 = currentl2->next;
}
return head;
}
int main(void)
{
struct ListNode test1, test1_2, test1_3;
struct ListNode* p = &test1;
p->val = 2;
p->next = &test1_2;
p->next->val = 4;
p->next->next = &test1_3;
p->next->next->val = 4;
p->next->next->next = NULL;
printf("### List l1!\n");
print_list(p);
struct ListNode test2, test2_2, test2_3;
struct ListNode* q = &test2;
q->val = 5;
q->next = &test2_2;
q->next->val = 6;
q->next->next = &test2_3;
q->next->next->val = 7;
q->next->next->next = NULL;
printf("### List l2!\n");
print_list(q);
printf("\n *** Start testing addTwoNumbers! *** \n");
struct ListNode* r = addTwoNumbers(p, q);
print_list(r);
// Remember to free memory here
//while(r->next != NULL);
//{
// printf("See if you could get the money?\n");
// r = r->next;
//}
printf("\n *** Finished testing addTwoNumbers! *** \n");
return 0;
}
一塌糊涂啊!!!明天继续写。
最后独立写出的答案如下,非常难看。
int shiftnumber = 0;
struct ListNode* addTwoNumbers(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2) {
struct ListNode* currentl1 = l1;
struct ListNode* currentl2 = l2;
// Holding the return value
struct ListNode* ptr = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
struct ListNode* head = ptr;
ptr->next = NULL;
shiftnumber = 0;
// First calculate the longest Linked List
int lenl1 = 0;
int lenl2 = 0;
while(currentl1 != NULL)
{
lenl1++;
currentl1 = currentl1->next;
}
while(currentl2 != NULL)
{
lenl2++;
currentl2 = currentl2->next;
}
currentl1 = l1;
currentl2 = l2;
// Get the largest length, thus we could use this number for controlling the
// return value.
int LinkedListLen = lenl1>lenl2?lenl1:lenl2;
while(LinkedListLen > 0)
{
LinkedListLen--;
int ValOfL1, ValOfL2 = 0;
ValOfL1 = (currentl1 == NULL)?0:currentl1->val;
ValOfL2 = (currentl2 == NULL)?0:currentl2->val;
ptr->val = ((ValOfL1 + ValOfL2)%10 + shiftnumber)%10;
if(((ValOfL1 + ValOfL2)%10 + shiftnumber) == 10)
{
shiftnumber = 1;
}
else{
shiftnumber = 0;
if((ValOfL1 + ValOfL2)>=10)
{
shiftnumber = (ValOfL1 + ValOfL2)/10;
}
}
// Allocate memory for new node. Only allocate (LinkedListLen - 1) times
if(LinkedListLen > 0)
{
ptr->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
ptr->next->next = NULL;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
// Switch to next node.
if(currentl1 != NULL)
{
currentl1 = currentl1->next;
}
if(currentl2 != NULL)
{
currentl2 = currentl2->next;
}
}
// If shiftnumber > 0, allocate a new node for holding it
if(shiftnumber != 0)
{
ptr->next = (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
ptr->next->next = NULL;
ptr->next->val = shiftnumber;
}
return head;
}
我的思路:
1,考虑到两个输入的链表长度可能不一样,因而先得到最长的链表长度,用这个最长的长度来做递归。
2, 是否有进位通过一个全局表两shiftnumber来hold. 如果相加到最后依然有进位,则在循环外开辟一块空间来存放这个进位。
3, 两个链表中的任何一个一旦走到了NULL指针,则其值用0来代替。
4, 三目运算符的使用。
5, ptr->val = ((ValOfL1 + ValOfL2)%10 + shiftnumber)%10;,这个是考虑到test case:
[9]
[1, 9]
如果不做的话,则得出结果会是[0,10], 进位和该位数字的和为10的时候需要单独考虑。
反思:
1, 对指针的使用要非常小心。
2, 就是凭直觉写出来的,算法很差, 代码可读性也很差。
Longest substr
The sample code is listed, while to be optimized:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAXN 50000
// q should be longer than p
int comlen(char* p, char* q)
{
int i = 0;
while (*q && (*p++ == *q++))
{
i++;
}
return i;
}
int cstring_cmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{
const char **ia = (const char **)a;
const char **ib = (const char **)b;
return strcmp(*ia, *ib);
}
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(char* s) {
char c[MAXN];
char* a[MAXN];
// Create a new array which hold char *s
// Remove all of the duplicated items in array
// no_duplicated[]
char ch;
int n = 0;
for(n = 0; n < strlen(s); n++)
{
printf("%c ",s[n]);
a[n] = &c[n];
c[n] = s[n];
}
a[n] = 0;
qsort(a, n, sizeof(char*), cstring_cmp);
int maxlen = 0;
int len = 0;
int maxi = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
len = comlen(a[i], a[i + 1]);
printf("len is %d\n", len);
if (len > maxlen)
{
maxlen = len;
maxi = i;
}
}
printf("maxlen:%d\tmax string:\t", maxlen);
char ch_tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < maxlen; i++)
{
ch_tmp = *(a[maxi] + i);
printf("%c", ch_tmp);
}
printf("\n");
return maxlen;
}
int main(void)
{
char s[100] = "abcabcccc";
char t[100] = "bbbbbbbbbbbb";
char k[100] = "pwwkew";
lengthOfLongestSubstring(s);
lengthOfLongestSubstring(t);
lengthOfLongestSubstring(k);
return 0;
}
