使用超声波传感器控制LED
Dec 28, 2013
Technology
###Wiring Pictures
The UltraSound sensor is like following picture, it only sold at 8RMB on Taobao:
The Wiring Pictures is listed as following: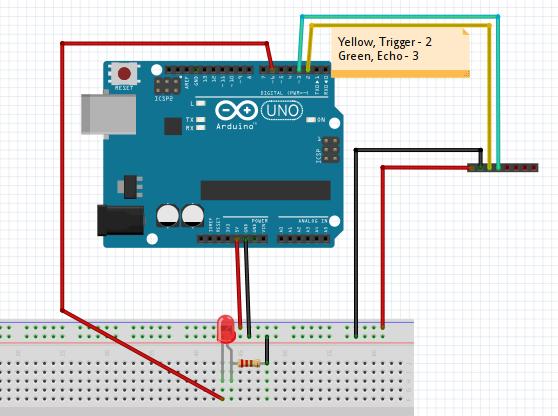 ###Working Principle
Trigger Pin will emit the ultra-sound, then Echo Pin will receive the reflected ultra-sound. Calculate its fleeting time then plus the speed of sound we can get the distance.
###Working Principle
Trigger Pin will emit the ultra-sound, then Echo Pin will receive the reflected ultra-sound. Calculate its fleeting time then plus the speed of sound we can get the distance.
So the working method is:
a. Trig pin emmit a high signal out.
b. Echo pin will wait for receiving the high signal.
c. Calculate the fleeting time.
###The code
const int TrigPin = 2;
const int EchoPin = 3;
const int LedPin = 6;
float cm;
int reverseStatus = 0;
int ledstatus = HIGH;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(TrigPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(EchoPin, INPUT);
pinMode(LedPin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(LedPin, HIGH);
}
void loop()
{
digitalWrite(TrigPin, LOW); //低高低电平发一个短时间脉冲去TrigPin
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(TrigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(TrigPin, LOW);
cm = pulseIn(EchoPin, HIGH) / 58.0; //将回波时间换算成cm
cm = (int(cm * 100.0)) / 100.0; //保留两位小数
if( cm < 10 )
{
reverseStatus = 1;
}
else
{
reverseStatus = 0;
}
if(reverseStatus == 1)
{
if(ledstatus == LOW)
{
digitalWrite(LedPin, HIGH);
ledstatus = HIGH;
}
else if(ledstatus == HIGH)
{
digitalWrite(LedPin, LOW);
ledstatus = LOW;
}
}
Serial.print(cm);
Serial.print("cm");
Serial.println();
delay(1000);
}
###Critical Code Walk-through
digitalWrite(TrigPin, LOW); //低高低电平发一个短时间脉冲去TrigPin
delayMicroseconds(2);
digitalWrite(TrigPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(10);
digitalWrite(TrigPin, LOW);
cm = pulseIn(EchoPin, HIGH) / 58.0; //将回波时间换算成cm
cm = (int(cm * 100.0)) / 100.0; //保留两位小数
First write low, delay 2 microsecond, then write high, continue for 10 microsecond, then switch to low.
pulseIn() will return the time wait the pin switch to High signal. Its output is microseconds. Since the speed of sound is 340m/s, like the following functions:
long microsecondsToCentimeters(long microseconds)
{
// The speed of sound is 340 m/s or 29 microseconds per centimeter.
// The ping travels out and back, so to find the distance of the
// object we take half of the distance travelled.
return microseconds / 29 / 2;
}
the distance we can caculate like: the time is x microseconds, while in 1 microseconds, the sound can walk:
340m/s = 340x100cm/s = 34cm/ms, so the distance will be:
distance == xms x 34cm/ms /2 == xms x 17
Thus the code could alter to :
//cm = pulseIn(EchoPin, HIGH) / 58.0; //将回波时间换算成cm
cm = pulseIn(EchoPin, HIGH) * 17 / 1000;
Both are OK for detecting the distance.
###Effect
When you hold your hands or other object to the ultrasound in less than 10cm, the led status will be changed in 1 seconds.
