Bluetooth Headset on ArchLinux
Dec 19, 2013
Technology
After 4 days struggling, I finally make bluetooth headset working on my ArchLinux. Following is the detailed how-to which shows how to enable bluetooth playing.
###Software Installation
Currently blueman is still the best bluetooth management software, we can install it via:
$ yaourt blueman
1 aur/blueman-bzr 726-2 [installed] (38)
GTK+ bluetooth management utility
Then we have to install bluez related items:
$ pacman -S bluez-utils bluez-libs python2-pybluez
$ yaourt -S bluez4
$ yaourt pulseaudio-bluez4
###Bluetooth Configuration First make sure your bluetooth service is enabled.
$ sudo systemctl start bluetooth
$ sudo systemctl enable bluetooth
Now we need to make change to following files:
[Trusty@XXXyyy ~]$ cat /etc/bluetooth/audio.conf
[General]
Enable=Socket
[A2DP]
SBCSources=1
Now we can manually startup blueman manager via:
$ blueman-manager
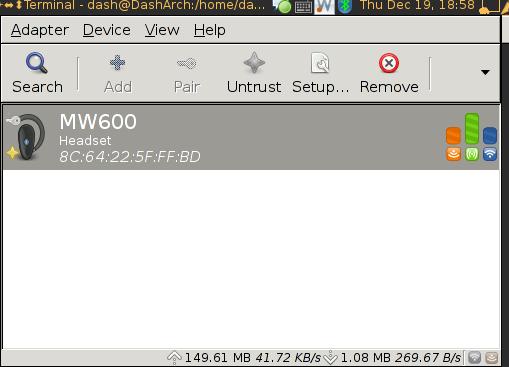
Click “Search” to find the avaiable headset, pair, trust, setup. Right click the found headset, choose “Audio Sink”, if successful, you will see the equipment has been successfully added into the system.
Add blueman automatically to the system startup script. We can add it into the awsome window manager:
autorunApps =
{
--.........
"blueman-manager",
--.........
}
###PulseAudio Configuration First we have to define the alsa device in /etc/asound.conf:
pcm.btheadset {
type plug
slave {
pcm {
type bluetooth
device 8C:64:goewugowugoeu
profile "auto"
}
}
hint {
show on
description "BT Headset"
}
}
ctl.btheadset {
type bluetooth
}
Now via “aplay -l” we can see the following item:
$ aplay -L
null
Discard all samples (playback) or generate zero samples (capture)
pulse
PulseAudio Sound Server
btheadset
BT Headset
In fact currently we can play sounds via mplayer, by specifying its default audio path is OK. But we want to make this audio sink path globally.
The steps for manually enabling the audio sink path via following steps:
Load device of btheadset
$ pactl load-module module-alsa-sink device=btheadset
Load bluetooth discover module
$ pacmd load_module module-bluetooth-discover
List the available cards
$ pactl list cards short
The upper output is still one audio card, but all we care is the audio sink, so we list all of the available audio sinks via:
$ pactl list sinks short
0 alsa_output.pci-0000_00_1b.0.analog-stereo module-alsa-card.c s16le 2ch 44100Hz SUSPENDED
1 alsa_output.btheadset module-alsa-sink.c s16le 2ch 44100Hz SUSPENDED
Set the default audio sink to bluetooth headset:
$ pacmd set-default-sink 1
Congratulations! Now you can listen to music via bluetooth headset!
###Automatically Configuration
Following is the configuration for my machine, you have to adjust the parameters according to yourself:
Comment the following items in /etc/pulse/default.pa, the module-bluetooth-policy should be commented, or the pulse audio will not start:
### Automatically load driver modules for Bluetooth hardware
#.ifexists module-bluetooth-policy.so
#load-module module-bluetooth-policy
#.endif
#
.ifexists module-bluetooth-discover.so
load-module module-bluetooth-discover
.endif
Surely you will start bluetooth daemon by default:
$ sudo systemctl enable bluetooth
Add “blueman-applet” into the awesome startup file(.config/awesome/rc.lua).
The right steps for using bluetooth:
- Startup Your machine with bluetooth background and blueman-applet enabled.
- Power on your bluetooth headset. If your key is accepted permanately, the bluetooth headset will connect automatically.
- Manually add the audio sink via “pactl load-module module-alsa-sink device=btheadset”.
- Set the default route path of the audio sink via “pacmd set-default-sink 1” ( all of the audio sink could be listed via “pactl list sinks short”)
Now you can enjoy the bluetooth, for convenient, I made an alias:
alias enableblue='pactl load-module module-alsa-sink device=btheadset && pacmd set-default-sink 1"
