Using IR-remote for controlling XBMC
Nov 21, 2013
Technology
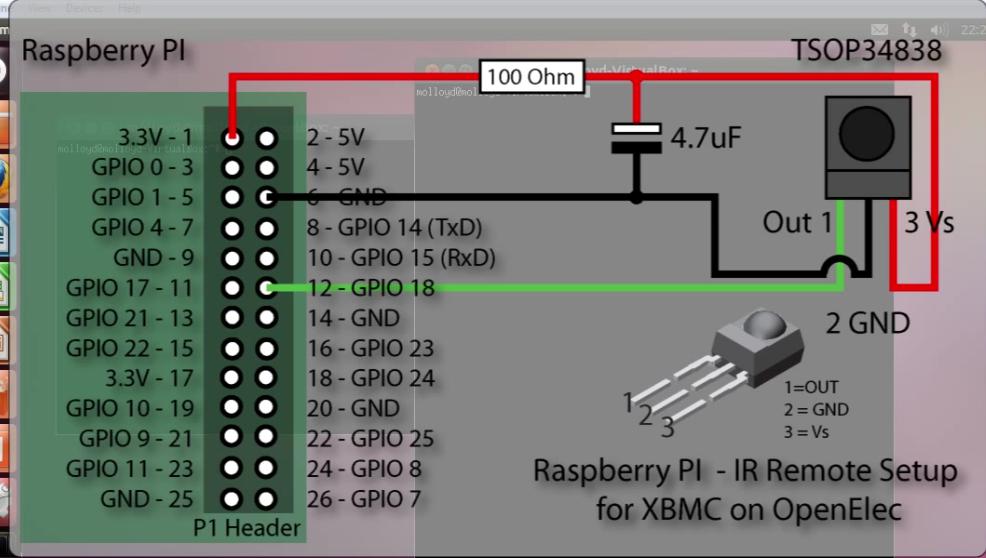
###Wiring The Wiring is listed as following Picture, You got your IR receiver’s pins to corresponding pins on raspberry PI. Positive to Pin1(3.3v), negative to Pin6(GND), the signal pins to Pin12(GPIO 18).
 ###Check the Kernel information
Log on to the raspberry PI, then input dmesg to view the startup information, we can see the lirc has been added to kernel.
###Check the Kernel information
Log on to the raspberry PI, then input dmesg to view the startup information, we can see the lirc has been added to kernel.
$ dmesg
[ 4.976752] systemd-udevd[822]: starting version 208
[ 7.121052] lirc_dev: IR Remote Control driver registered, major 248
[ 7.187858] lirc_rpi: module is from the staging directory, the quality is unknown, you have been warned.
[ 7.234864] lirc_rpi lirc_rpi.0: lirc_dev: driver lirc_rpi registered at minor = 0
[ 7.234894] lirc_rpi: driver registered!
[ 8.191460] lirc_rpi: auto-detected active low receiver on GPIO pin 18
[ 8.981462] input: lircd as /devices/virtual/input/input3
Now Let’s check the GPIO status:
OpenELEC:~ # cat /sys/kernel/debug/gpio
GPIOs 0-53, bcm2708_gpio:
gpio-16 (led0 ) out hi
gpio-17 (lirc_rpi ir/out ) in lo
gpio-18 (lirc_rpi ir/in ) in hi
If it didn’t appear, using:
modprobe lirc_rpi gpio_in_pin=18 gpio_out_pin=1
###Getting your own remote controller’s codes Now let’s kill all of the lircd related process, then use mode2 to detect the infra-red remote input.
OpenELEC:~ # ps -ef | grep lirc
1016 root 0:00 eventlircd --evmap=/etc/eventlircd.d --socket=/var/run/lirc/lircd --release=_UP
1035 root 0:00 /usr/sbin/lircd --driver=default --device=/dev/lirc0 --uinput --output=/var/run/lirc/lircd-lirc0 --pidfile=/var/run/lirc/lircd-lirc0.pid /etc/lirc/lircd.conf.rpi
1070 root 16:02 /usr/lib/xbmc/xbmc.bin --standalone -fs --lircdev /var/run/lirc/lircd
1146 root 0:00 grep lirc
OpenELEC:~ # killall lirc
What is mode2?
Trusty@SomethingMissing:~$ apt-cache search mode2
lirc-x - infra-red remote control support - X utilities
Then Let’s listen the infra_remote’s input.The input is quite strange:
space 4501241
pulse 8917
space 4415
pulse 577
###Catching the code using irrecord The next step is turns these message into some code.
OpenELEC:~/.config # pwd
/storage/.config
OpenELEC:~/.config # ls
aacs samba.conf.sample vpn-config
hosts.conf sysctl.conf.sample
remote.conf udev.rules.d.sample
Use irrecord for recording some signals and transform them into code:
NAME
irrecord - application for recording IR-codes for usage with LIRC
OpenELEC:~/.config # irrecord -d /dev/lirc0 lircd.conf
The method is, first long-press some keys, the result on screen will be several dots, then the program will change to another line, this time when you press some key, it only has one dot. Keep pressing keys until the irrecord tells you successful. Then you should input make some keys meaningful to the following images, when you feel satisfied, press enter to endup the program.

Now your lircd.conf file is generated, let see what’s in it.
$ cat lircd.conf
begin remote
name lircd.conf
flags RAW_CODES|CONST_LENGTH
eps 30
aeps 100
gap 106707
begin raw_codes
name KEY_UP
8953 4401 581 527 595 503
613 506 588 539 581 510
If you want to use the pre-defined files, simply go to the lirc.sourceforge.net/remotes you can find almost all of the remote control information. ###Using the infra-remote for controlling Now call irw, but irw stunned with doing nothing. This command will show you all of the input signal
OpenELEC:~ # irw
6a 0 KEY_RIGHT devinput
6a 0 KEY_RIGHT_UP devinput
69 0 KEY_LEFT devinput
69 0 KEY_LEFT_UP devinput
6c 0 KEY_DOWN devinput
6c 0 KEY_DOWN_UP devinput
Now in your XBMC window, you will see you can navigate and select something using your remote control.
